Rema Daher
SHADeS: Self-supervised Monocular Depth Estimation Through Non-Lambertian Image Decomposition
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Purpose: Visual 3D scene reconstruction can support colonoscopy navigation. It can help in recognising which portions of the colon have been visualised and characterising the size and shape of polyps. This is still a very challenging problem due to complex illumination variations, including abundant specular reflections. We investigate how to effectively decouple light and depth in this problem. Methods: We introduce a self-supervised model that simultaneously characterises the shape and lighting of the visualised colonoscopy scene. Our model estimates shading, albedo, depth, and specularities (SHADeS) from single images. Unlike previous approaches (IID), we use a non-Lambertian model that treats specular reflections as a separate light component. The implementation of our method is available at https://github.com/RemaDaher/SHADeS. Results: We demonstrate on real colonoscopy images (Hyper Kvasir) that previous models for light decomposition (IID) and depth estimation (MonoVIT, ModoDepth2) are negatively affected by specularities. In contrast, SHADeS can simultaneously produce light decomposition and depth maps that are robust to specular regions. We also perform a quantitative comparison on phantom data (C3VD) where we further demonstrate the robustness of our model. Conclusion: Modelling specular reflections improves depth estimation in colonoscopy. We propose an effective self-supervised approach that uses this insight to jointly estimate light decomposition and depth. Light decomposition has the potential to help with other problems, such as place recognition within the colon.
SegCol Challenge: Semantic Segmentation for Tools and Fold Edges in Colonoscopy data
Dec 20, 2024

Abstract:Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with polyp removal being an effective early screening method. However, navigating the colon for thorough polyp detection poses significant challenges. To advance camera navigation in colonoscopy, we propose the Semantic Segmentation for Tools and Fold Edges in Colonoscopy (SegCol) Challenge. This challenge introduces a dataset from the EndoMapper repository, featuring manually annotated, pixel-level semantic labels for colon folds and endoscopic tools across selected frames from 96 colonoscopy videos. By providing fold edges as anatomical landmarks and depth discontinuity information from both fold and tool labels, the dataset is aimed to improve depth perception and localization methods. Hosted as part of the Endovis Challenge at MICCAI 2024, SegCol aims to drive innovation in colonoscopy navigation systems. Details are available at https://www.synapse.org/Synapse:syn54124209/wiki/626563, and code resources at https://github.com/surgical-vision/segcol_challenge .
Mismatched: Evaluating the Limits of Image Matching Approaches and Benchmarks
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:Three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction from two-dimensional images is an active research field in computer vision, with applications ranging from navigation and object tracking to segmentation and three-dimensional modeling. Traditionally, parametric techniques have been employed for this task. However, recent advancements have seen a shift towards learning-based methods. Given the rapid pace of research and the frequent introduction of new image matching methods, it is essential to evaluate them. In this paper, we present a comprehensive evaluation of various image matching methods using a structure-from-motion pipeline. We assess the performance of these methods on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets, identifying key limitations in both the methods and benchmarks. We also investigate the impact of edge detection as a pre-processing step. Our analysis reveals that image matching for 3D reconstruction remains an open challenge, necessitating careful selection and tuning of models for specific scenarios, while also highlighting mismatches in how metrics currently represent method performance.
A Temporal Learning Approach to Inpainting Endoscopic Specularities and Its effect on Image Correspondence
Mar 31, 2022



Abstract:Video streams are utilised to guide minimally-invasive surgery and diagnostic procedures in a wide range of procedures, and many computer assisted techniques have been developed to automatically analyse them. These approaches can provide additional information to the surgeon such as lesion detection, instrument navigation, or anatomy 3D shape modeling. However, the necessary image features to recognise these patterns are not always reliably detected due to the presence of irregular light patterns such as specular highlight reflections. In this paper, we aim at removing specular highlights from endoscopic videos using machine learning. We propose using a temporal generative adversarial network (GAN) to inpaint the hidden anatomy under specularities, inferring its appearance spatially and from neighbouring frames where they are not present in the same location. This is achieved using in-vivo data of gastric endoscopy (Hyper-Kvasir) in a fully unsupervised manner that relies on automatic detection of specular highlights. System evaluations show significant improvements to traditional methods through direct comparison as well as other machine learning techniques through an ablation study that depicts the importance of the network's temporal and transfer learning components. The generalizability of our system to different surgical setups and procedures was also evaluated qualitatively on in-vivo data of gastric endoscopy and ex-vivo porcine data (SERV-CT, SCARED). We also assess the effect of our method in computer vision tasks that underpin 3D reconstruction and camera motion estimation, namely stereo disparity, optical flow, and sparse point feature matching. These are evaluated quantitatively and qualitatively and results show a positive effect of specular highlight inpainting on these tasks in a novel comprehensive analysis.
Change your singer: a transfer learning generative adversarial framework for song to song conversion
Nov 07, 2019

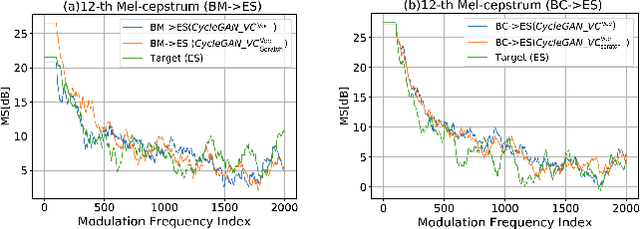

Abstract:Have you ever wondered how a song might sound if performed by a different artist? In this work, we propose SCM-GAN, an end-to-end non-parallel song conversion system powered by generative adversarial and transfer learning that allows users to listen to a selected target singer singing any song. SCM-GAN first separates songs into vocals and instrumental music using a U-Net network, then converts the vocal segments to the target singer using advanced CycleGAN-VC, before merging the converted vocals with their corresponding background music. SCM-GAN is first initialized with feature representations learned from a state-of-the-art voice-to-voice conversion and then trained on a dataset of non-parallel songs. Furthermore, SCM-GAN is evaluated against a set of metrics including global variance GV and modulation spectra MS on the 24 Mel-cepstral coefficients (MCEPs). Transfer learning improves the GV by 35% and the MS by 13% on average. A subjective comparison is conducted to test the user satisfaction with the quality and the naturalness of the conversion. Results show above par similarity between SCM-GAN's output and the target (70\% on average) as well as great naturalness of the converted songs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge