Ran Gal
AutoSimulate: (Quickly) Learning Synthetic Data Generation
Aug 16, 2020



Abstract:Simulation is increasingly being used for generating large labelled datasets in many machine learning problems. Recent methods have focused on adjusting simulator parameters with the goal of maximising accuracy on a validation task, usually relying on REINFORCE-like gradient estimators. However these approaches are very expensive as they treat the entire data generation, model training, and validation pipeline as a black-box and require multiple costly objective evaluations at each iteration. We propose an efficient alternative for optimal synthetic data generation, based on a novel differentiable approximation of the objective. This allows us to optimize the simulator, which may be non-differentiable, requiring only one objective evaluation at each iteration with a little overhead. We demonstrate on a state-of-the-art photorealistic renderer that the proposed method finds the optimal data distribution faster (up to $50\times$), with significantly reduced training data generation (up to $30\times$) and better accuracy ($+8.7\%$) on real-world test datasets than previous methods.
* ECCV 2020
Photorealistic Image Synthesis for Object Instance Detection
Feb 09, 2019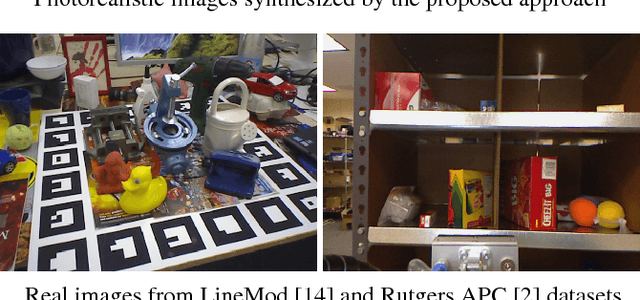
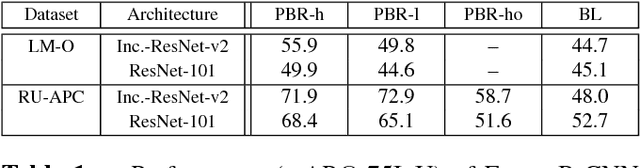


Abstract:We present an approach to synthesize highly photorealistic images of 3D object models, which we use to train a convolutional neural network for detecting the objects in real images. The proposed approach has three key ingredients: (1) 3D object models are rendered in 3D models of complete scenes with realistic materials and lighting, (2) plausible geometric configuration of objects and cameras in a scene is generated using physics simulations, and (3) high photorealism of the synthesized images achieved by physically based rendering. When trained on images synthesized by the proposed approach, the Faster R-CNN object detector achieves a 24% absolute improvement of mAP@.75IoU on Rutgers APC and 11% on LineMod-Occluded datasets, compared to a baseline where the training images are synthesized by rendering object models on top of random photographs. This work is a step towards being able to effectively train object detectors without capturing or annotating any real images. A dataset of 600K synthetic images with ground truth annotations for various computer vision tasks will be released on the project website: thodan.github.io/objectsynth.
ASIST: Automatic Semantically Invariant Scene Transformation
Dec 04, 2015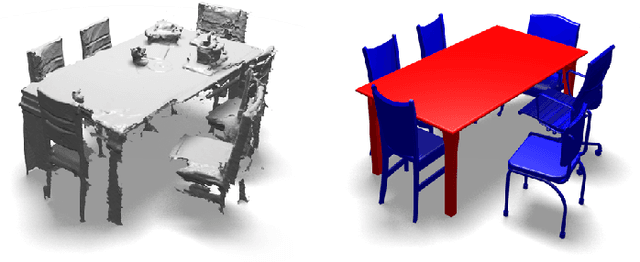
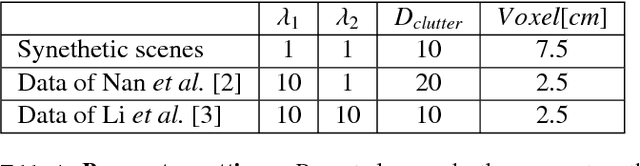
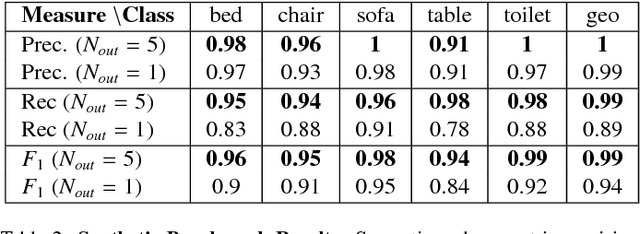
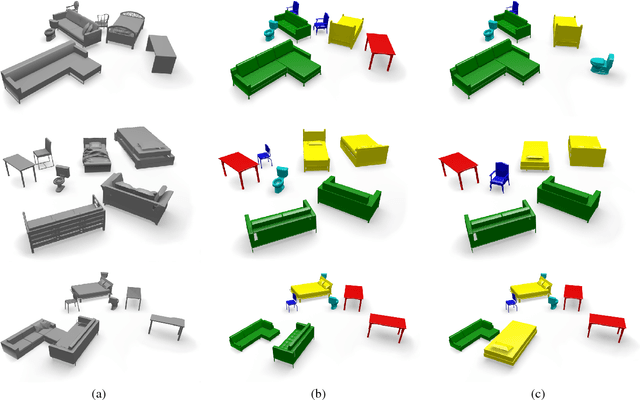
Abstract:We present ASIST, a technique for transforming point clouds by replacing objects with their semantically equivalent counterparts. Transformations of this kind have applications in virtual reality, repair of fused scans, and robotics. ASIST is based on a unified formulation of semantic labeling and object replacement; both result from minimizing a single objective. We present numerical tools for the efficient solution of this optimization problem. The method is experimentally assessed on new datasets of both synthetic and real point clouds, and is additionally compared to two recent works on object replacement on data from the corresponding papers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge