Qinying Liu
TagAlign: Improving Vision-Language Alignment with Multi-Tag Classification
Dec 26, 2023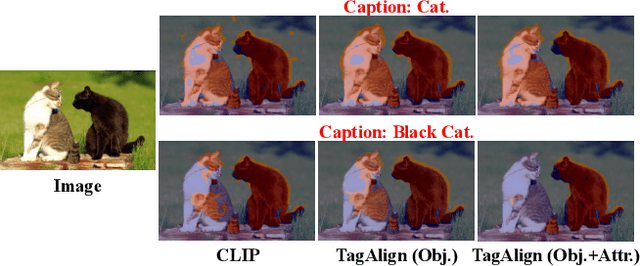
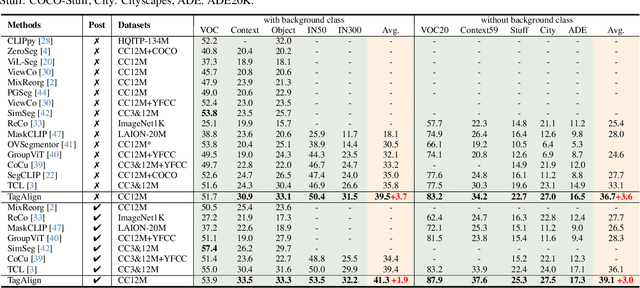
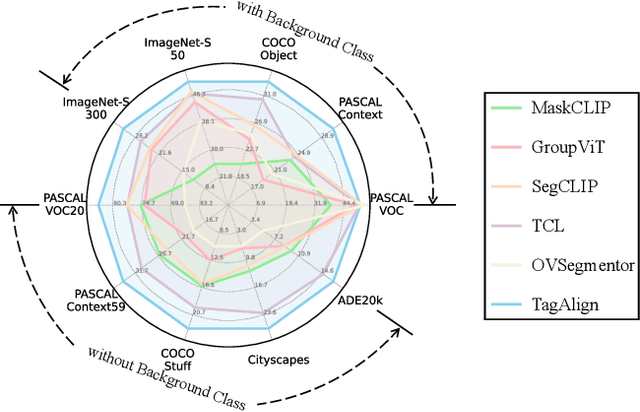
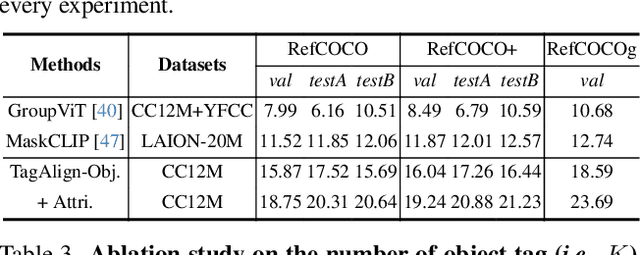
Abstract:The crux of learning vision-language models is to extract semantically aligned information from visual and linguistic data. Existing attempts usually face the problem of coarse alignment, e.g., the vision encoder struggles in localizing an attribute-specified object. In this work, we propose an embarrassingly simple approach to better align image and text features with no need of additional data formats other than image-text pairs. Concretely, given an image and its paired text, we manage to parse objects (e.g., cat) and attributes (e.g., black) from the description, which are highly likely to exist in the image. It is noteworthy that the parsing pipeline is fully automatic and thus enjoys good scalability. With these parsed semantics as supervision signals, we can complement the commonly used image-text contrastive loss with the multi-tag classification loss. Extensive experimental results on a broad suite of semantic segmentation datasets substantiate the average 3.65\% improvement of our framework over existing alternatives. Furthermore, the visualization results indicate that attribute supervision makes vision-language models accurately localize attribute-specified objects. Project page and code can be found at https://qinying-liu.github.io/Tag-Align.
Revisiting Foreground and Background Separation in Weakly-supervised Temporal Action Localization: A Clustering-based Approach
Dec 21, 2023



Abstract:Weakly-supervised temporal action localization aims to localize action instances in videos with only video-level action labels. Existing methods mainly embrace a localization-by-classification pipeline that optimizes the snippet-level prediction with a video classification loss. However, this formulation suffers from the discrepancy between classification and detection, resulting in inaccurate separation of foreground and background (F\&B) snippets. To alleviate this problem, we propose to explore the underlying structure among the snippets by resorting to unsupervised snippet clustering, rather than heavily relying on the video classification loss. Specifically, we propose a novel clustering-based F\&B separation algorithm. It comprises two core components: a snippet clustering component that groups the snippets into multiple latent clusters and a cluster classification component that further classifies the cluster as foreground or background. As there are no ground-truth labels to train these two components, we introduce a unified self-labeling mechanism based on optimal transport to produce high-quality pseudo-labels that match several plausible prior distributions. This ensures that the cluster assignments of the snippets can be accurately associated with their F\&B labels, thereby boosting the F\&B separation. We evaluate our method on three benchmarks: THUMOS14, ActivityNet v1.2 and v1.3. Our method achieves promising performance on all three benchmarks while being significantly more lightweight than previous methods. Code is available at https://github.com/Qinying-Liu/CASE
Collaborating Domain-shared and Target-specific Feature Clustering for Cross-domain 3D Action Recognition
Jul 20, 2022



Abstract:In this work, we consider the problem of cross-domain 3D action recognition in the open-set setting, which has been rarely explored before. Specifically, there is a source domain and a target domain that contain the skeleton sequences with different styles and categories, and our purpose is to cluster the target data by utilizing the labeled source data and unlabeled target data. For such a challenging task, this paper presents a novel approach dubbed CoDT to collaboratively cluster the domain-shared features and target-specific features. CoDT consists of two parallel branches. One branch aims to learn domain-shared features with supervised learning in the source domain, while the other is to learn target-specific features using contrastive learning in the target domain. To cluster the features, we propose an online clustering algorithm that enables simultaneous promotion of robust pseudo label generation and feature clustering. Furthermore, to leverage the complementarity of domain-shared features and target-specific features, we propose a novel collaborative clustering strategy to enforce pair-wise relationship consistency between the two branches. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple cross-domain 3D action recognition datasets, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Convex Combination Consistency between Neighbors for Weakly-supervised Action Localization
May 01, 2022



Abstract:In weakly-supervised temporal action localization (WS-TAL), the methods commonly follow the "localization by classification" procedure, which uses the snippet predictions to form video class scores and then optimizes a video classification loss. In this procedure, the snippet predictions (or snippet attention weights) are used to separate foreground and background. However, the snippet predictions are usually inaccurate due to absence of frame-wise labels, and then the overall performance is hindered. In this paper, we propose a novel C$^3$BN to achieve robust snippet predictions. C$^3$BN includes two key designs by exploring the inherent characteristics of video data. First, because of the natural continuity of adjacent snippets, we propose a micro data augmentation strategy to increase the diversity of snippets with convex combination of adjacent snippets. Second, we propose a macro-micro consistency regularization strategy to force the model to be invariant (or equivariant) to the transformations of snippets with respect to video semantics, snippet predictions and snippet features. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method on top of baselines for the WS-TAL tasks with video-level and point-level supervision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge