Pooneh Roshanitabrizi
FeTTL: Federated Template and Task Learning for Multi-Institutional Medical Imaging
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Federated learning enables collaborative model training across geographically distributed medical centers while preserving data privacy. However, domain shifts and heterogeneity in data often lead to a degradation in model performance. Medical imaging applications are particularly affected by variations in acquisition protocols, scanner types, and patient populations. To address these issues, we introduce Federated Template and Task Learning (FeTTL), a novel framework designed to harmonize multi-institutional medical imaging data in federated environments. FeTTL learns a global template together with a task model to align data distributions among clients. We evaluated FeTTL on two challenging and diverse multi-institutional medical imaging tasks: retinal fundus optical disc segmentation and histopathological metastasis classification. Experimental results show that FeTTL significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art federated learning baselines (p-values <0.002) for optical disc segmentation and classification of metastases from multi-institutional data. Our experiments further highlight the importance of jointly learning the template and the task. These findings suggest that FeTTL offers a principled and extensible solution for mitigating distribution shifts in federated learning, supporting robust model deployment in real-world, multi-institutional environments.
Data Alchemy: Mitigating Cross-Site Model Variability Through Test Time Data Calibration
Jul 18, 2024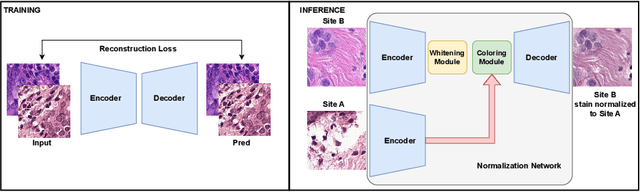
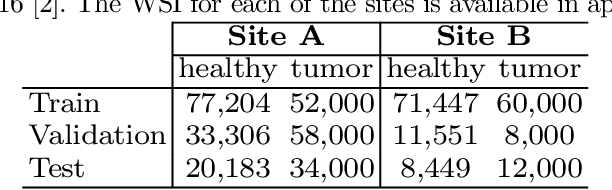
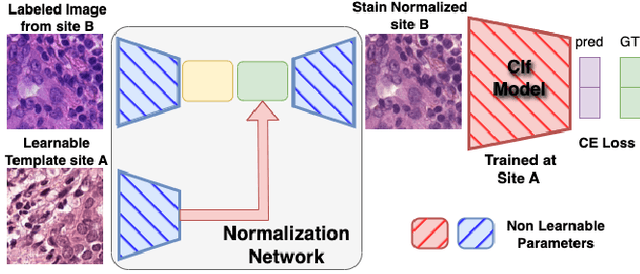
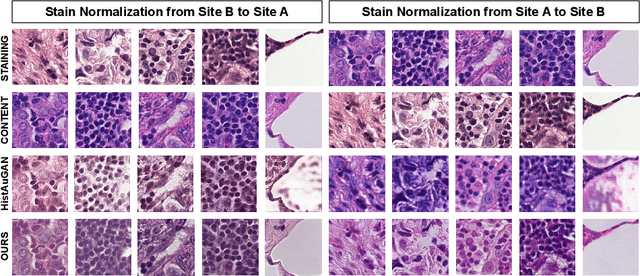
Abstract:Deploying deep learning-based imaging tools across various clinical sites poses significant challenges due to inherent domain shifts and regulatory hurdles associated with site-specific fine-tuning. For histopathology, stain normalization techniques can mitigate discrepancies, but they often fall short of eliminating inter-site variations. Therefore, we present Data Alchemy, an explainable stain normalization method combined with test time data calibration via a template learning framework to overcome barriers in cross-site analysis. Data Alchemy handles shifts inherent to multi-site data and minimizes them without needing to change the weights of the normalization or classifier networks. Our approach extends to unseen sites in various clinical settings where data domain discrepancies are unknown. Extensive experiments highlight the efficacy of our framework in tumor classification in hematoxylin and eosin-stained patches. Our explainable normalization method boosts classification tasks' area under the precision-recall curve(AUPR) by 0.165, 0.545 to 0.710. Additionally, Data Alchemy further reduces the multisite classification domain gap, by improving the 0.710 AUPR an additional 0.142, elevating classification performance further to 0.852, from 0.545. Our Data Alchemy framework can popularize precision medicine with minimal operational overhead by allowing for the seamless integration of pre-trained deep learning-based clinical tools across multiple sites.
Zero-Shot Pediatric Tuberculosis Detection in Chest X-Rays using Self-Supervised Learning
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant global health challenge, with pediatric cases posing a major concern. The World Health Organization (WHO) advocates for chest X-rays (CXRs) for TB screening. However, visual interpretation by radiologists can be subjective, time-consuming and prone to error, especially in pediatric TB. Artificial intelligence (AI)-driven computer-aided detection (CAD) tools, especially those utilizing deep learning, show promise in enhancing lung disease detection. However, challenges include data scarcity and lack of generalizability. In this context, we propose a novel self-supervised paradigm leveraging Vision Transformers (ViT) for improved TB detection in CXR, enabling zero-shot pediatric TB detection. We demonstrate improvements in TB detection performance ($\sim$12.7% and $\sim$13.4% top AUC/AUPR gains in adults and children, respectively) when conducting self-supervised pre-training when compared to fully-supervised (i.e., non pre-trained) ViT models, achieving top performances of 0.959 AUC and 0.962 AUPR in adult TB detection, and 0.697 AUC and 0.607 AUPR in zero-shot pediatric TB detection. As a result, this work demonstrates that self-supervised learning on adult CXRs effectively extends to challenging downstream tasks such as pediatric TB detection, where data are scarce.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge