Po-Chun Hsu
The Breeze 2 Herd of Models: Traditional Chinese LLMs Based on Llama with Vision-Aware and Function-Calling Capabilities
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Llama-Breeze2 (hereinafter referred to as Breeze2) is a suite of advanced multi-modal language models, available in 3B and 8B parameter configurations, specifically designed to enhance Traditional Chinese language representation. Building upon the Llama 3.2 model family, we continue the pre-training of Breeze2 on an extensive corpus to enhance the linguistic and cultural heritage of Traditional Chinese. In addition to language modeling capabilities, we significantly augment the models with function calling and vision understanding capabilities. At the time of this publication, as far as we are aware, absent reasoning-inducing prompts, Breeze2 are the strongest performing models in Traditional Chinese function calling and image understanding in its size class. The effectiveness of Breeze2 is benchmarked across various tasks, including Taiwan general knowledge, instruction-following, long context, function calling, and vision understanding. We are publicly releasing all Breeze2 models under the Llama 3.2 Community License. We also showcase the capabilities of the model running on mobile platform with a mobile application which we also open source.
Enhancing Function-Calling Capabilities in LLMs: Strategies for Prompt Formats, Data Integration, and Multilingual Translation
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced autonomous agents, particularly in zero-shot tool usage, also known as function calling. This research delves into enhancing the function-calling capabilities of LLMs by exploring different approaches, including prompt formats for integrating function descriptions, blending function-calling and instruction-following data, introducing a novel Decision Token for conditional prompts, leveraging chain-of-thought reasoning, and overcoming multilingual challenges with a translation pipeline. Our key findings and contributions are as follows: (1) Instruction-following data improves both function-calling accuracy and relevance detection. (2) The use of the newly proposed Decision Token, combined with synthetic non-function-call data, enhances relevance detection. (3) A tailored translation pipeline effectively overcomes multilingual limitations, demonstrating significant improvements in Traditional Chinese. These insights highlight the potential for improved function-calling capabilities and multilingual applications in LLMs.
Let's Fuse Step by Step: A Generative Fusion Decoding Algorithm with LLMs for Multi-modal Text Recognition
May 23, 2024Abstract:We introduce ``Generative Fusion Decoding'' (GFD), a novel shallow fusion framework, utilized to integrate Large Language Models (LLMs) into multi-modal text recognition systems such as automatic speech recognition (ASR) and optical character recognition (OCR). We derive the formulas necessary to enable GFD to operate across mismatched token spaces of different models by mapping text token space to byte token space, enabling seamless fusion during the decoding process. The framework is plug-and-play, compatible with various auto-regressive models, and does not require re-training for feature alignment, thus overcoming limitations of previous fusion techniques. We highlight three main advantages of GFD: First, by simplifying the complexity of aligning different model sample spaces, GFD allows LLMs to correct errors in tandem with the recognition model, reducing computation latencies. Second, the in-context learning ability of LLMs is fully capitalized by GFD, increasing robustness in long-form speech recognition and instruction aware speech recognition. Third, GFD enables fusing recognition models deficient in Chinese text recognition with LLMs extensively trained on Chinese. Our evaluation demonstrates that GFD significantly improves performance in ASR and OCR tasks, with ASR reaching state-of-the-art in the NTUML2021 benchmark. GFD provides a significant step forward in model integration, offering a unified solution that could be widely applicable to leveraging existing pre-trained models through step by step fusion.
Breeze-7B Technical Report
Mar 05, 2024Abstract:Breeze-7B is an open-source language model based on Mistral-7B, designed to address the need for improved language comprehension and chatbot-oriented capabilities in Traditional Chinese. This technical report provides an overview of the additional pretraining, finetuning, and evaluation stages for the Breeze-7B model. The Breeze-7B family of base and chat models exhibits good performance on language comprehension and chatbot-oriented tasks, reaching the top in several benchmarks among models comparable in its complexity class.
Advancing the Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Language Models: Towards a Comprehensive Benchmark Suite
Oct 02, 2023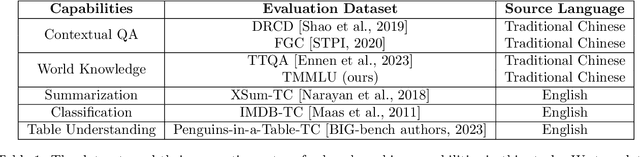
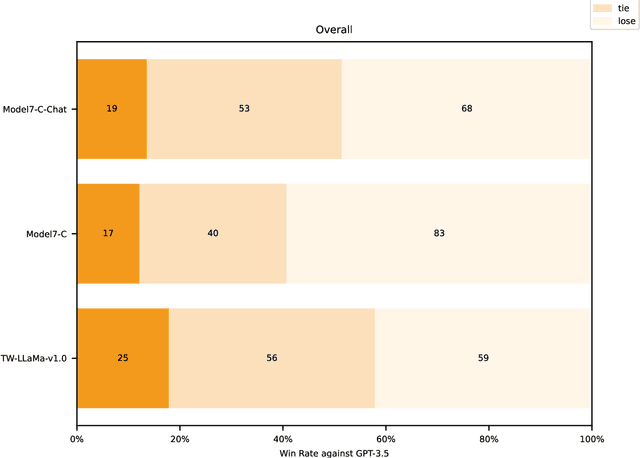
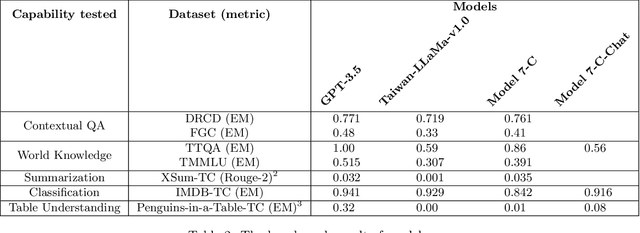
Abstract:The evaluation of large language models is an essential task in the field of language understanding and generation. As language models continue to advance, the need for effective benchmarks to assess their performance has become imperative. In the context of Traditional Chinese, there is a scarcity of comprehensive and diverse benchmarks to evaluate the capabilities of language models, despite the existence of certain benchmarks such as DRCD, TTQA, CMDQA, and FGC dataset. To address this gap, we propose a novel set of benchmarks that leverage existing English datasets and are tailored to evaluate language models in Traditional Chinese. These benchmarks encompass a wide range of tasks, including contextual question-answering, summarization, classification, and table understanding. The proposed benchmarks offer a comprehensive evaluation framework, enabling the assessment of language models' capabilities across different tasks. In this paper, we evaluate the performance of GPT-3.5, Taiwan-LLaMa-v1.0, and Model 7-C, our proprietary model, on these benchmarks. The evaluation results highlight that our model, Model 7-C, achieves performance comparable to GPT-3.5 with respect to a part of the evaluated capabilities. In an effort to advance the evaluation of language models in Traditional Chinese and stimulate further research in this field, we have open-sourced our benchmark and opened the model for trial.
Federated Deep Reinforcement Learning for THz-Beam Search with Limited CSI
Apr 25, 2023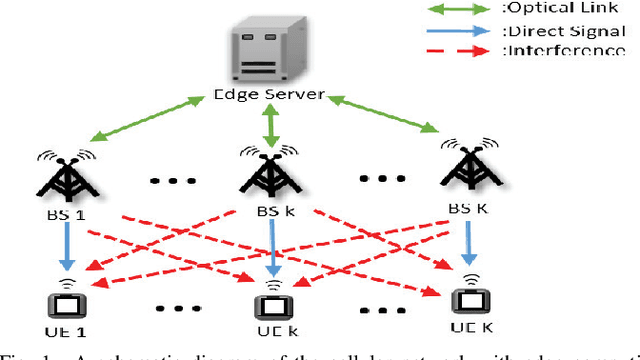
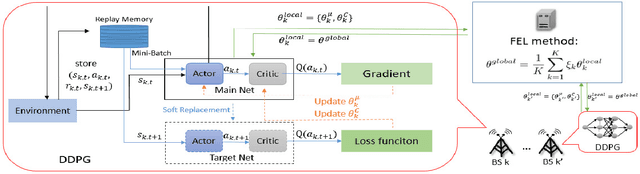
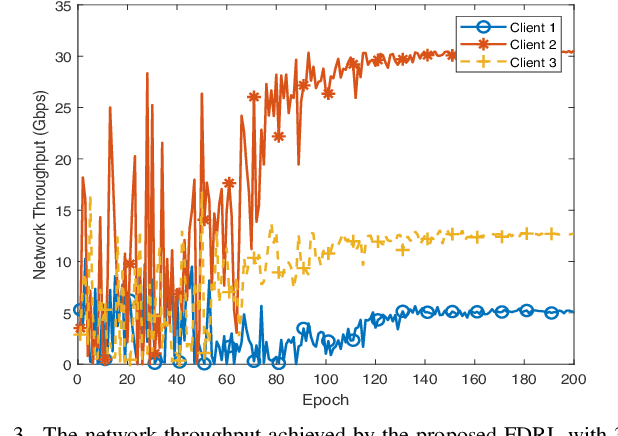
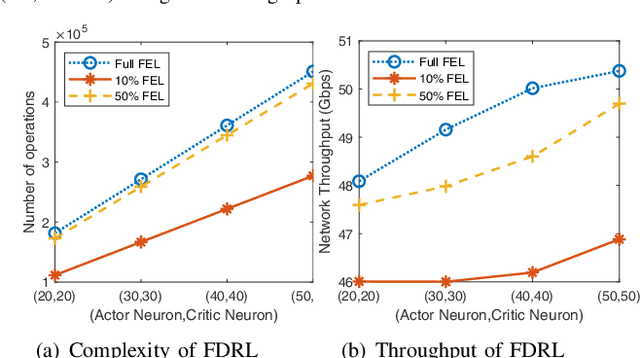
Abstract:Terahertz (THz) communication with ultra-wide available spectrum is a promising technique that can achieve the stringent requirement of high data rate in the next-generation wireless networks, yet its severe propagation attenuation significantly hinders its implementation in practice. Finding beam directions for a large-scale antenna array to effectively overcome severe propagation attenuation of THz signals is a pressing need. This paper proposes a novel approach of federated deep reinforcement learning (FDRL) to swiftly perform THz-beam search for multiple base stations (BSs) coordinated by an edge server in a cellular network. All the BSs conduct deep deterministic policy gradient (DDPG)-based DRL to obtain THz beamforming policy with limited channel state information (CSI). They update their DDPG models with hidden information in order to mitigate inter-cell interference. We demonstrate that the cell network can achieve higher throughput as more THz CSI and hidden neurons of DDPG are adopted. We also show that FDRL with partial model update is able to nearly achieve the same performance of FDRL with full model update, which indicates an effective means to reduce communication load between the edge server and the BSs by partial model uploading. Moreover, the proposed FDRL outperforms conventional non-learning-based and existing non-FDRL benchmark optimization methods.
Extending the Pre-Training of BLOOM for Improved Support of Traditional Chinese: Models, Methods and Results
Mar 08, 2023Abstract:In this paper we present the multilingual language model BLOOM-zh that features enhanced support for Traditional Chinese. BLOOM-zh has its origins in the open-source BLOOM models presented by BigScience in 2022. Starting from released models, we extended the pre-training of BLOOM by additional 7.4 billion tokens in Traditional Chinese and English covering a variety of domains such as news articles, books, encyclopedias, educational materials as well as spoken language. In order to show the properties of BLOOM-zh, both existing and newly created benchmark scenarios are used for evaluating the performance. BLOOM-zh outperforms its predecessor on most Traditional Chinese benchmarks while maintaining its English capability. We release all our models to the research community.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge