Philipp Rostalski
Automated Computation of Therapies Using Failure Mode and Effects Analysis in the Medical Domain
May 06, 2024Abstract:Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) is a systematic approach to identify and analyse potential failures and their effects in a system or process. The FMEA approach, however, requires domain experts to manually analyse the FMEA model to derive risk-reducing actions that should be applied. In this paper, we provide a formal framework to allow for automatic planning and acting in FMEA models. More specifically, we cast the FMEA model into a Markov decision process which can then be solved by existing solvers. We show that the FMEA approach can not only be used to support medical experts during the modelling process but also to automatically derive optimal therapies for the treatment of patients.
Anatomy-guided domain adaptation for 3D in-bed human pose estimation
Nov 22, 2022Abstract:3D human pose estimation is a key component of clinical monitoring systems. The clinical applicability of deep pose estimation models, however, is limited by their poor generalization under domain shifts along with their need for sufficient labeled training data. As a remedy, we present a novel domain adaptation method, adapting a model from a labeled source to a shifted unlabeled target domain. Our method comprises two complementary adaptation strategies based on prior knowledge about human anatomy. First, we guide the learning process in the target domain by constraining predictions to the space of anatomically plausible poses. To this end, we embed the prior knowledge into an anatomical loss function that penalizes asymmetric limb lengths, implausible bone lengths, and implausible joint angles. Second, we propose to filter pseudo labels for self-training according to their anatomical plausibility and incorporate the concept into the Mean Teacher paradigm. We unify both strategies in a point cloud-based framework applicable to unsupervised and source-free domain adaptation. Evaluation is performed for in-bed pose estimation under two adaptation scenarios, using the public SLP dataset and a newly created dataset. Our method consistently outperforms various state-of-the-art domain adaptation methods, surpasses the baseline model by 31%/66%, and reduces the domain gap by 65%/82%. Source code is available at https://github.com/multimodallearning/da-3dhpe-anatomy.
Responsible and Regulatory Conform Machine Learning for Medicine: A Survey of Technical Challenges and Solutions
Jul 20, 2021

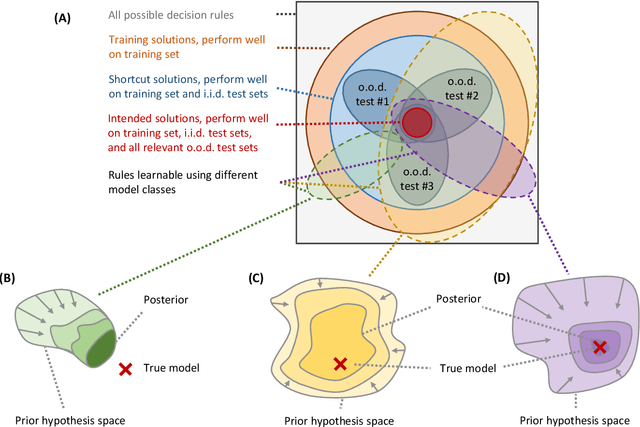

Abstract:Machine learning is expected to fuel significant improvements in medical care. To ensure that fundamental principles such as beneficence, respect for human autonomy, prevention of harm, justice, privacy, and transparency are respected, medical machine learning applications must be developed responsibly. In this paper, we survey the technical challenges involved in creating medical machine learning systems responsibly and in conformity with existing regulations, as well as possible solutions to address these challenges. We begin by providing a brief overview of existing regulations affecting medical machine learning, showing that properties such as safety, robustness, reliability, privacy, security, transparency, explainability, and nondiscrimination are all demanded already by existing law and regulations - albeit, in many cases, to an uncertain degree. Next, we discuss the underlying technical challenges, possible ways for addressing them, and their respective merits and drawbacks. We notice that distribution shift, spurious correlations, model underspecification, and data scarcity represent severe challenges in the medical context (and others) that are very difficult to solve with classical black-box deep neural networks. Important measures that may help to address these challenges include the use of large and representative datasets and federated learning as a means to that end, the careful exploitation of domain knowledge wherever feasible, the use of inherently transparent models, comprehensive model testing and verification, as well as stakeholder inclusion.
Scalable Gaussian Process Regression for Kernels with a Non-Stationary Phase
Dec 25, 2019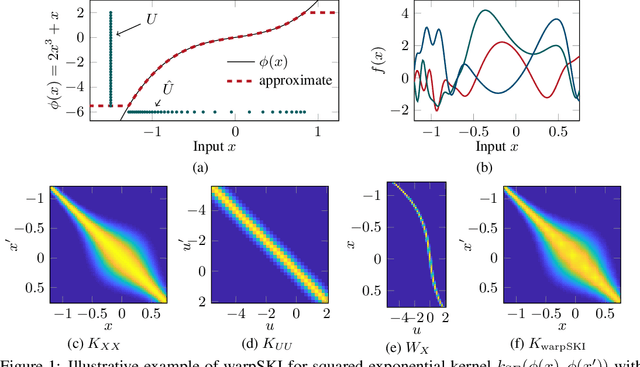
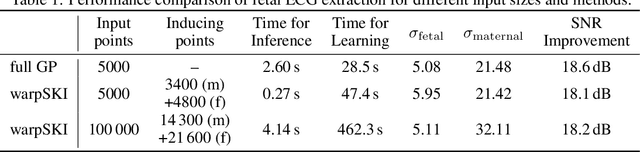
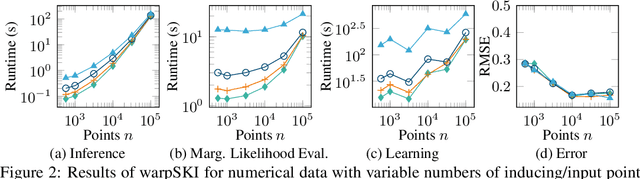

Abstract:The application of Gaussian processes (GPs) to large data sets is limited due to heavy memory and computational requirements. A variety of methods has been proposed to enable scalability, one of which is to exploit structure in the kernel matrix. Previous methods, however, cannot easily deal with non-stationary processes. This paper presents an efficient GP framework, that extends structured kernel interpolation methods to GPs with a non-stationary phase. We particularly treat mixtures of non-stationary processes, which are commonly used in the context of separation problems e.g. in biomedical signal processing. Our approach employs multiple sets of non-equidistant inducing points to account for the non-stationarity and retrieve Toeplitz and Kronecker structure in the kernel matrix allowing for efficient inference. Kernel learning is done by optimizing the marginal likelihood, which can be approximated efficiently using stochastic trace estimation methods. Our approach is demonstrated on numerical examples and large biomedical datasets.
On Approximate Nonlinear Gaussian Message Passing On Factor Graphs
Mar 21, 2019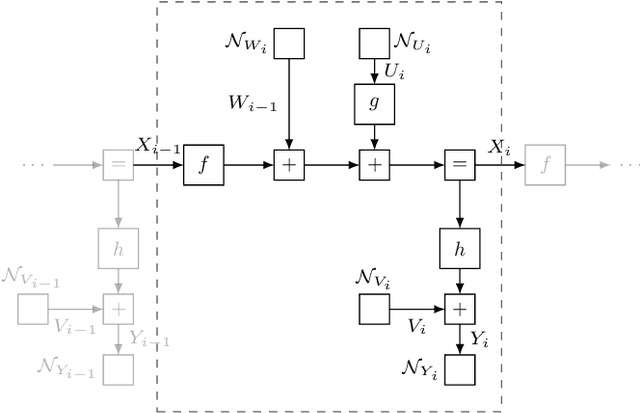

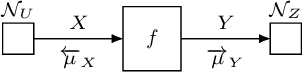
Abstract:Factor graphs have recently gained increasing attention as a unified framework for representing and constructing algorithms for signal processing, estimation, and control. One capability that does not seem to be well explored within the factor graph tool kit is the ability to handle deterministic nonlinear transformations, such as those occurring in nonlinear filtering and smoothing problems, using tabulated message passing rules. In this contribution, we provide general forward (filtering) and backward (smoothing) approximate Gaussian message passing rules for deterministic nonlinear transformation nodes in arbitrary factor graphs fulfilling a Markov property, based on numerical quadrature procedures for the forward pass and a Rauch-Tung-Striebel-type approximation of the backward pass. These message passing rules can be employed for deriving many algorithms for solving nonlinear problems using factor graphs, as is illustrated by the proposition of a nonlinear modified Bryson-Frazier (MBF) smoother based on the presented message passing rules.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge