Peyman Afshani
On Cyclic Solutions to the Min-Max Latency Multi-Robot Patrolling Problem
Mar 14, 2022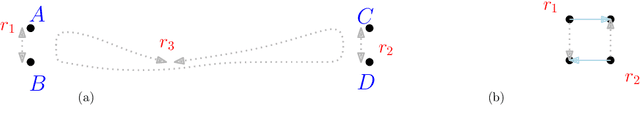
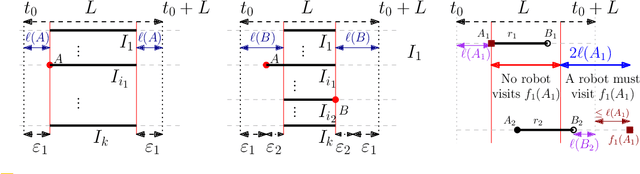
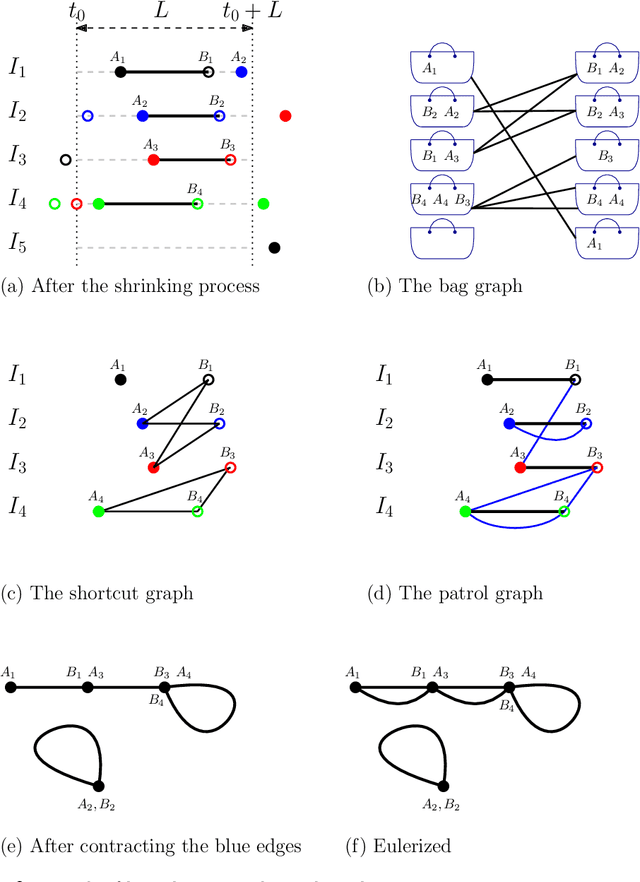
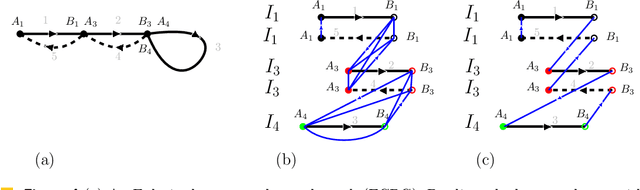
Abstract:We consider the following surveillance problem: Given a set $P$ of $n$ sites in a metric space and a set of $k$ robots with the same maximum speed, compute a patrol schedule of minimum latency for the robots. Here a patrol schedule specifies for each robot an infinite sequence of sites to visit (in the given order) and the latency $L$ of a schedule is the maximum latency of any site, where the latency of a site $s$ is the supremum of the lengths of the time intervals between consecutive visits to $s$. When $k=1$ the problem is equivalent to the travelling salesman problem (TSP) and thus it is NP-hard. We have two main results. We consider cyclic solutions in which the set of sites must be partitioned into $\ell$ groups, for some~$\ell \leq k$, and each group is assigned a subset of the robots that move along the travelling salesman tour of the group at equal distance from each other. Our first main result is that approximating the optimal latency of the class of cyclic solutions can be reduced to approximating the optimal travelling salesman tour on some input, with only a $1+\varepsilon$ factor loss in the approximation factor and an $O\left(\left( k/\varepsilon \right)^k\right)$ factor loss in the runtime, for any $\varepsilon >0$. Our second main result shows that an optimal cyclic solution is a $2(1-1/k)$-approximation of the overall optimal solution. Note that for $k=2$ this implies that an optimal cyclic solution is optimal overall. The results have a number of consequences. For the Euclidean version of the problem, for instance, combining our results with known results on Euclidean TSP, yields a PTAS for approximating an optimal cyclic solution, and it yields a $(2(1-1/k)+\varepsilon)$-approximation of the optimal unrestricted solution. If the conjecture mentioned above is true, then our algorithm is actually a PTAS for the general problem in the Euclidean setting.
Approximation Algorithms for Multi-Robot Patrol-Scheduling with Min-Max Latency
May 23, 2020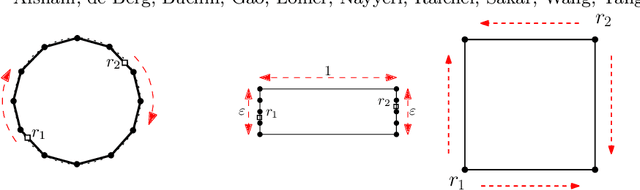
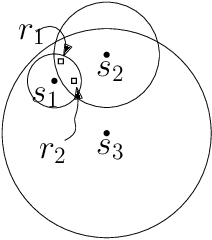
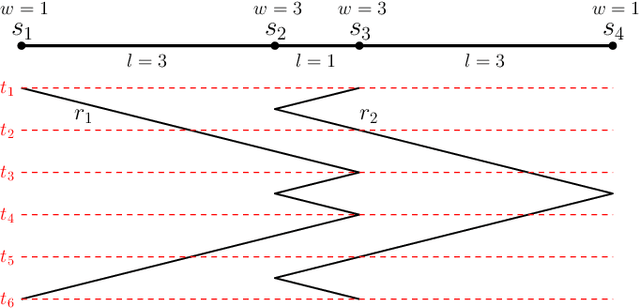
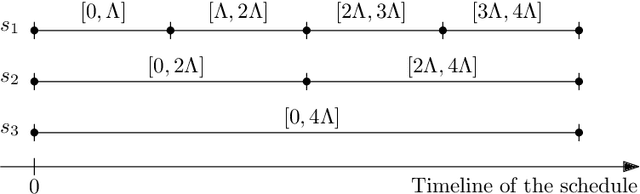
Abstract:We consider the problem of finding patrol schedules for $k$ robots to visit a given set of $n$ sites in a metric space. Each robot has the same maximum speed and the goal is to minimize the weighted maximum latency of any site, where the latency of a site is defined as the maximum time duration between consecutive visits of that site. The problem is NP-hard, as it has the traveling salesman problem as a special case (when $k=1$ and all sites have the same weight). We present a polynomial-time algorithm with an approximation factor of $O(k^2 \log \frac{w_{\max}}{w_{\min}})$ to the optimal solution, where $w_{\max}$ and $w_{\min}$ are the maximum and minimum weight of the sites respectively. Further, we consider the special case where the sites are in 1D. When all sites have the same weight, we present a polynomial-time algorithm to solve the problem exactly. If the sites may have different weights, we present a $12$-approximate solution, which runs in polynomial time when the number of robots, $k$, is a constant.
The Query Complexity of a Permutation-Based Variant of Mastermind
Dec 20, 2018Abstract:We study the query complexity of a permutation-based variant of the guessing game Mastermind. In this variant, the secret is a pair $(z,\pi)$ which consists of a binary string $z \in \{0,1\}^n$ and a permutation $\pi$ of $[n]$. The secret must be unveiled by asking queries of the form $x \in \{0,1\}^n$. For each such query, we are returned the score \[ f_{z,\pi}(x):= \max \{ i \in [0..n]\mid \forall j \leq i: z_{\pi(j)} = x_{\pi(j)}\}\,;\] i.e., the score of $x$ is the length of the longest common prefix of $x$ and $z$ with respect to the order imposed by $\pi$. The goal is to minimize the number of queries needed to identify $(z,\pi)$. This problem originates from the study of black-box optimization heuristics, where it is known as the \textsc{LeadingOnes} problem. In this work, we prove matching upper and lower bounds for the deterministic and randomized query complexity of this game, which are $\Theta(n \log n)$ and $\Theta(n \log \log n)$, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge