Pedro Azevedo
VWise: A novel benchmark for evaluating scene classification for vehicular applications
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Current datasets for vehicular applications are mostly collected in North America or Europe. Models trained or evaluated on these datasets might suffer from geographical bias when deployed in other regions. Specifically, for scene classification, a highway in a Latin American country differs drastically from an Autobahn, for example, both in design and maintenance levels. We propose VWise, a novel benchmark for road-type classification and scene classification tasks, in addition to tasks focused on external contexts related to vehicular applications in LatAm. We collected over 520 video clips covering diverse urban and rural environments across Latin American countries, annotated with six classes of road types. We also evaluated several state-of-the-art classification models in baseline experiments, obtaining over 84% accuracy. With this dataset, we aim to enhance research on vehicular tasks in Latin America.
Task Conditioned BERT for Joint Intent Detection and Slot-filling
Aug 11, 2023



Abstract:Dialogue systems need to deal with the unpredictability of user intents to track dialogue state and the heterogeneity of slots to understand user preferences. In this paper we investigate the hypothesis that solving these challenges as one unified model will allow the transfer of parameter support data across the different tasks. The proposed principled model is based on a Transformer encoder, trained on multiple tasks, and leveraged by a rich input that conditions the model on the target inferences. Conditioning the Transformer encoder on multiple target inferences over the same corpus, i.e., intent and multiple slot types, allows learning richer language interactions than a single-task model would be able to. In fact, experimental results demonstrate that conditioning the model on an increasing number of dialogue inference tasks leads to improved results: on the MultiWOZ dataset, the joint intent and slot detection can be improved by 3.2\% by conditioning on intent, 10.8\% by conditioning on slot and 14.4\% by conditioning on both intent and slots. Moreover, on real conversations with Farfetch costumers, the proposed conditioned BERT can achieve high joint-goal and intent detection performance throughout a dialogue.
Bio-Inspired Foveated Technique for Augmented-Range Vehicle Detection Using Deep Neural Networks
Oct 02, 2019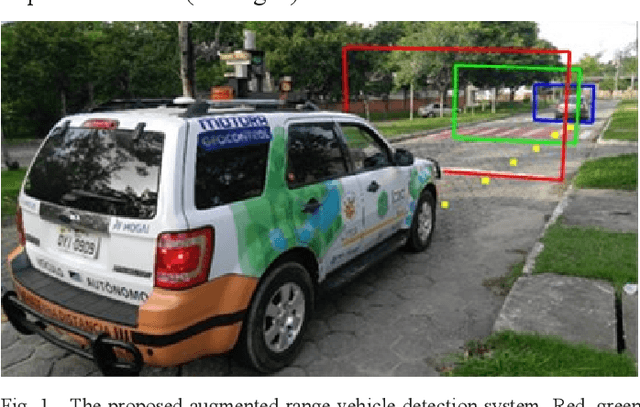

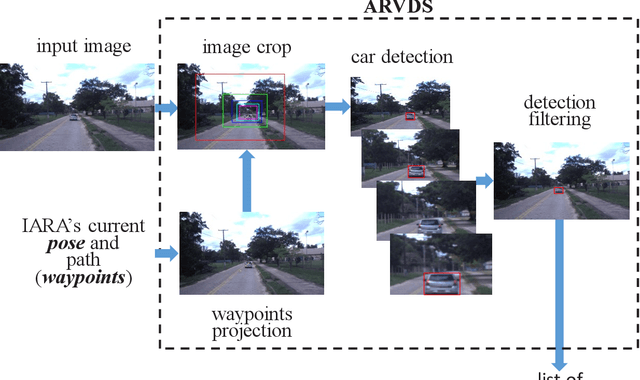
Abstract:We propose a bio-inspired foveated technique to detect cars in a long range camera view using a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) for the IARA self-driving car. The DCNN receives as input (i) an image, which is captured by a camera installed on IARA's roof; and (ii) crops of the image, which are centered in the waypoints computed by IARA's path planner and whose sizes increase with the distance from IARA. We employ an overlap filter to discard detections of the same car in different crops of the same image based on the percentage of overlap of detections' bounding boxes. We evaluated the performance of the proposed augmented-range vehicle detection system (ARVDS) using the hardware and software infrastructure available in the IARA self-driving car. Using IARA, we captured thousands of images of real traffic situations containing cars in a long range. Experimental results show that ARVDS increases the Average Precision (AP) of long range car detection from 29.51% (using a single whole image) to 63.15%.
Self-Driving Cars: A Survey
Jan 14, 2019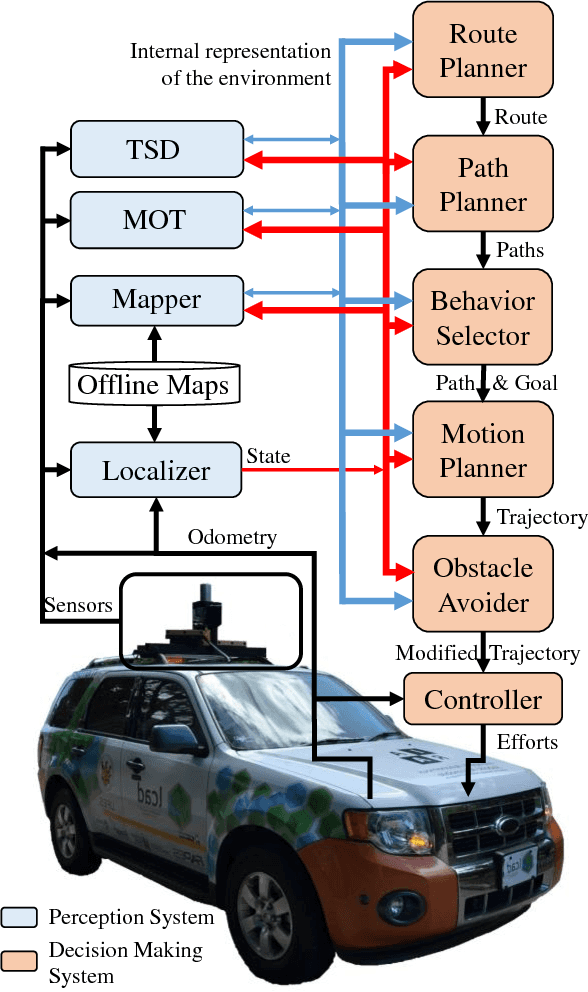
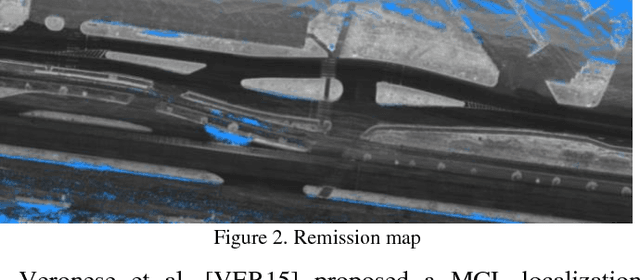

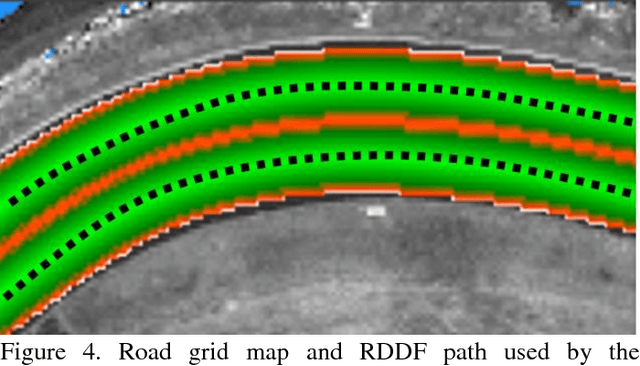
Abstract:We survey research on self-driving cars published in the literature focusing on autonomous cars developed since the DARPA challenges, which are equipped with an autonomy system that can be categorized as SAE level 3 or higher. The architecture of the autonomy system of self-driving cars is typically organized into the perception system and the decision-making system. The perception system is generally divided into many subsystems responsible for tasks such as self-driving-car localization, static obstacles mapping, moving obstacles detection and tracking, road mapping, traffic signalization detection and recognition, among others. The decision-making system is commonly partitioned as well into many subsystems responsible for tasks such as route planning, path planning, behavior selection, motion planning, and control. In this survey, we present the typical architecture of the autonomy system of self-driving cars. We also review research on relevant methods for perception and decision making. Furthermore, we present a detailed description of the architecture of the autonomy system of the UFES's car, IARA. Finally, we list prominent autonomous research cars developed by technology companies and reported in the media.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge