Diogo Tavares
RedTWIZ: Diverse LLM Red Teaming via Adaptive Attack Planning
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the vision, scientific contributions, and technical details of RedTWIZ: an adaptive and diverse multi-turn red teaming framework, to audit the robustness of Large Language Models (LLMs) in AI-assisted software development. Our work is driven by three major research streams: (1) robust and systematic assessment of LLM conversational jailbreaks; (2) a diverse generative multi-turn attack suite, supporting compositional, realistic and goal-oriented jailbreak conversational strategies; and (3) a hierarchical attack planner, which adaptively plans, serializes, and triggers attacks tailored to specific LLM's vulnerabilities. Together, these contributions form a unified framework -- combining assessment, attack generation, and strategic planning -- to comprehensively evaluate and expose weaknesses in LLMs' robustness. Extensive evaluation is conducted to systematically assess and analyze the performance of the overall system and each component. Experimental results demonstrate that our multi-turn adversarial attack strategies can successfully lead state-of-the-art LLMs to produce unsafe generations, highlighting the pressing need for more research into enhancing LLM's robustness.
MoralCLIP: Contrastive Alignment of Vision-and-Language Representations with Moral Foundations Theory
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in vision-language models have enabled rich semantic understanding across modalities. However, these encoding methods lack the ability to interpret or reason about the moral dimensions of content-a crucial aspect of human cognition. In this paper, we address this gap by introducing MoralCLIP, a novel embedding representation method that extends multimodal learning with explicit moral grounding based on Moral Foundations Theory (MFT). Our approach integrates visual and textual moral cues into a unified embedding space, enabling cross-modal moral alignment. MoralCLIP is grounded on the multi-label dataset Social-Moral Image Database to identify co-occurring moral foundations in visual content. For MoralCLIP training, we design a moral data augmentation strategy to scale our annotated dataset to 15,000 image-text pairs labeled with MFT-aligned dimensions. Our results demonstrate that explicit moral supervision improves both unimodal and multimodal understanding of moral content, establishing a foundation for morally-aware AI systems capable of recognizing and aligning with human moral values.
Plan-Grounded Large Language Models for Dual Goal Conversational Settings
Feb 01, 2024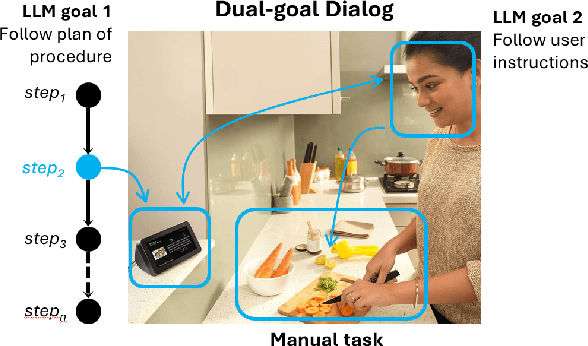
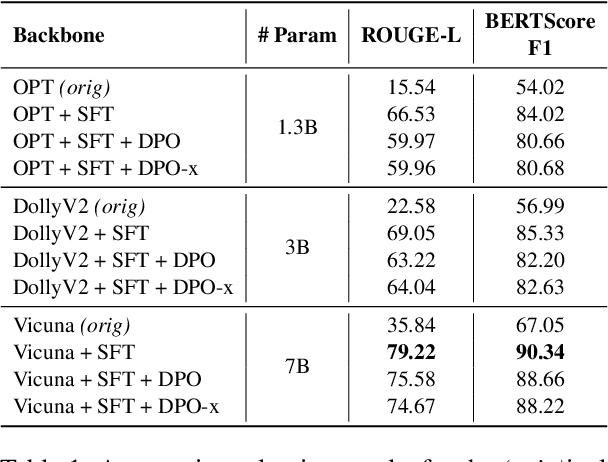
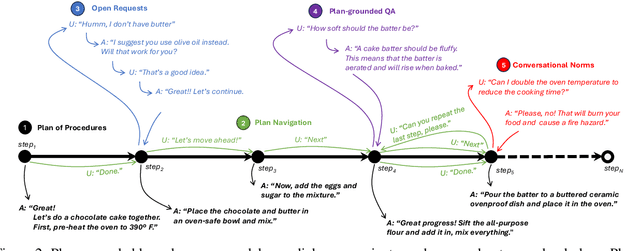
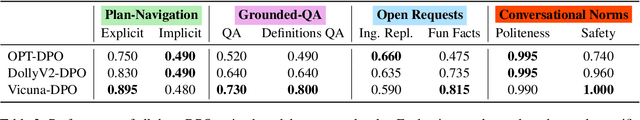
Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) to follow user instructions has been shown to supply the LLM with ample capacity to converse fluently while being aligned with humans. Yet, it is not completely clear how an LLM can lead a plan-grounded conversation in mixed-initiative settings where instructions flow in both directions of the conversation, i.e. both the LLM and the user provide instructions to one another. In this paper, we tackle a dual goal mixed-initiative conversational setting where the LLM not only grounds the conversation on an arbitrary plan but also seeks to satisfy both a procedural plan and user instructions. The LLM is then responsible for guiding the user through the plan and, at the same time, adapting to new circumstances, answering questions, and activating safety guardrails when needed. We propose a novel LLM that grounds the dialogue on a procedural plan, can take the dialogue initiative, and enforces guardrails on the system's behavior, while also improving the LLM's responses to unexpected user behavior. Experiments in controlled settings and with real users show that the best-performing model, which we call PlanLLM, achieves a 2.1x improvement over a strong baseline. Moreover, experiments also show good generalization to unseen domains.
TWIZ: The Wizard of Multimodal Conversational-Stimulus
Oct 03, 2023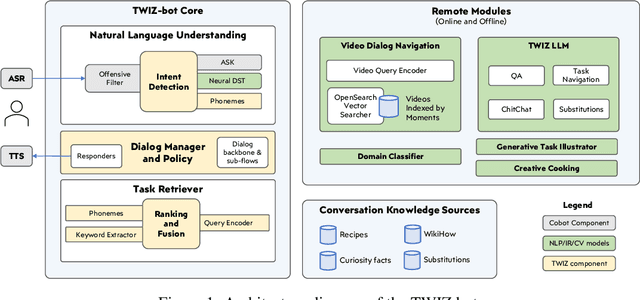
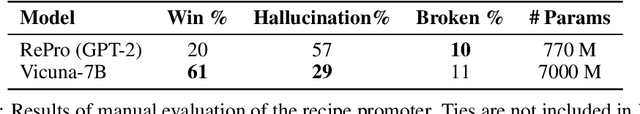
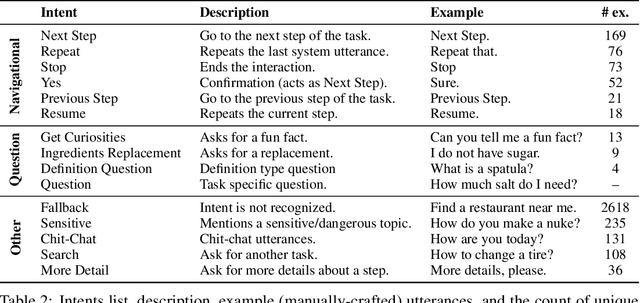
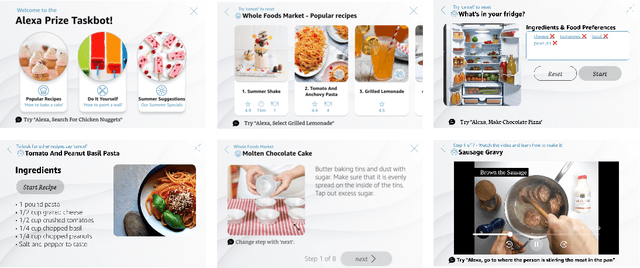
Abstract:In this report, we describe the vision, challenges, and scientific contributions of the Task Wizard team, TWIZ, in the Alexa Prize TaskBot Challenge 2022. Our vision, is to build TWIZ bot as an helpful, multimodal, knowledgeable, and engaging assistant that can guide users towards the successful completion of complex manual tasks. To achieve this, we focus our efforts on three main research questions: (1) Humanly-Shaped Conversations, by providing information in a knowledgeable way; (2) Multimodal Stimulus, making use of various modalities including voice, images, and videos; and (3) Zero-shot Conversational Flows, to improve the robustness of the interaction to unseen scenarios. TWIZ is an assistant capable of supporting a wide range of tasks, with several innovative features such as creative cooking, video navigation through voice, and the robust TWIZ-LLM, a Large Language Model trained for dialoguing about complex manual tasks. Given ratings and feedback provided by users, we observed that TWIZ bot is an effective and robust system, capable of guiding users through tasks while providing several multimodal stimuli.
Task Conditioned BERT for Joint Intent Detection and Slot-filling
Aug 11, 2023



Abstract:Dialogue systems need to deal with the unpredictability of user intents to track dialogue state and the heterogeneity of slots to understand user preferences. In this paper we investigate the hypothesis that solving these challenges as one unified model will allow the transfer of parameter support data across the different tasks. The proposed principled model is based on a Transformer encoder, trained on multiple tasks, and leveraged by a rich input that conditions the model on the target inferences. Conditioning the Transformer encoder on multiple target inferences over the same corpus, i.e., intent and multiple slot types, allows learning richer language interactions than a single-task model would be able to. In fact, experimental results demonstrate that conditioning the model on an increasing number of dialogue inference tasks leads to improved results: on the MultiWOZ dataset, the joint intent and slot detection can be improved by 3.2\% by conditioning on intent, 10.8\% by conditioning on slot and 14.4\% by conditioning on both intent and slots. Moreover, on real conversations with Farfetch costumers, the proposed conditioned BERT can achieve high joint-goal and intent detection performance throughout a dialogue.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge