Rafael Ferreira
RedTWIZ: Diverse LLM Red Teaming via Adaptive Attack Planning
Oct 08, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the vision, scientific contributions, and technical details of RedTWIZ: an adaptive and diverse multi-turn red teaming framework, to audit the robustness of Large Language Models (LLMs) in AI-assisted software development. Our work is driven by three major research streams: (1) robust and systematic assessment of LLM conversational jailbreaks; (2) a diverse generative multi-turn attack suite, supporting compositional, realistic and goal-oriented jailbreak conversational strategies; and (3) a hierarchical attack planner, which adaptively plans, serializes, and triggers attacks tailored to specific LLM's vulnerabilities. Together, these contributions form a unified framework -- combining assessment, attack generation, and strategic planning -- to comprehensively evaluate and expose weaknesses in LLMs' robustness. Extensive evaluation is conducted to systematically assess and analyze the performance of the overall system and each component. Experimental results demonstrate that our multi-turn adversarial attack strategies can successfully lead state-of-the-art LLMs to produce unsafe generations, highlighting the pressing need for more research into enhancing LLM's robustness.
Multi-trait User Simulation with Adaptive Decoding for Conversational Task Assistants
Oct 16, 2024


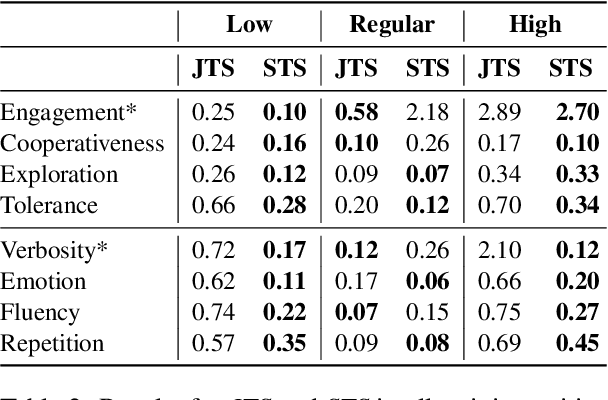
Abstract:Conversational systems must be robust to user interactions that naturally exhibit diverse conversational traits. Capturing and simulating these diverse traits coherently and efficiently presents a complex challenge. This paper introduces Multi-Trait Adaptive Decoding (mTAD), a method that generates diverse user profiles at decoding-time by sampling from various trait-specific Language Models (LMs). mTAD provides an adaptive and scalable approach to user simulation, enabling the creation of multiple user profiles without the need for additional fine-tuning. By analyzing real-world dialogues from the Conversational Task Assistant (CTA) domain, we identify key conversational traits and developed a framework to generate profile-aware dialogues that enhance conversational diversity. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach in modeling single-traits using specialized LMs, which can capture less common patterns, even in out-of-domain tasks. Furthermore, the results demonstrate that mTAD is a robust and flexible framework for combining diverse user simulators.
Plan-Grounded Large Language Models for Dual Goal Conversational Settings
Feb 01, 2024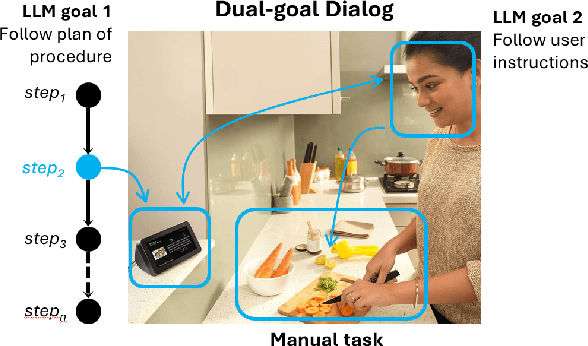
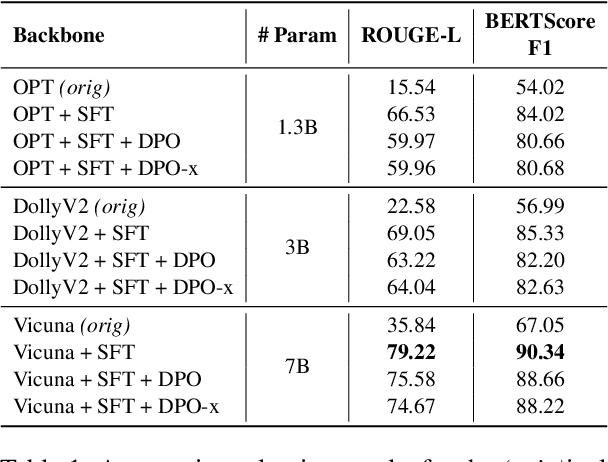
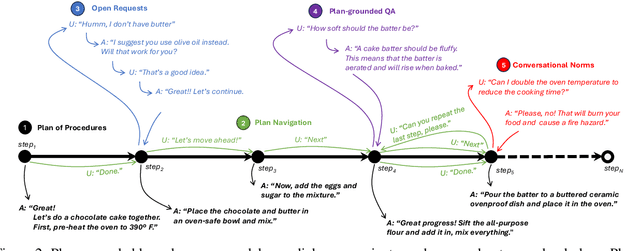
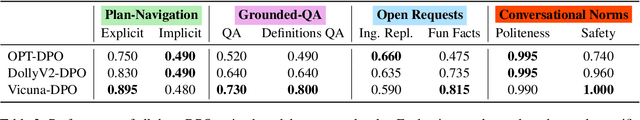
Abstract:Training Large Language Models (LLMs) to follow user instructions has been shown to supply the LLM with ample capacity to converse fluently while being aligned with humans. Yet, it is not completely clear how an LLM can lead a plan-grounded conversation in mixed-initiative settings where instructions flow in both directions of the conversation, i.e. both the LLM and the user provide instructions to one another. In this paper, we tackle a dual goal mixed-initiative conversational setting where the LLM not only grounds the conversation on an arbitrary plan but also seeks to satisfy both a procedural plan and user instructions. The LLM is then responsible for guiding the user through the plan and, at the same time, adapting to new circumstances, answering questions, and activating safety guardrails when needed. We propose a novel LLM that grounds the dialogue on a procedural plan, can take the dialogue initiative, and enforces guardrails on the system's behavior, while also improving the LLM's responses to unexpected user behavior. Experiments in controlled settings and with real users show that the best-performing model, which we call PlanLLM, achieves a 2.1x improvement over a strong baseline. Moreover, experiments also show good generalization to unseen domains.
TWIZ: The Wizard of Multimodal Conversational-Stimulus
Oct 03, 2023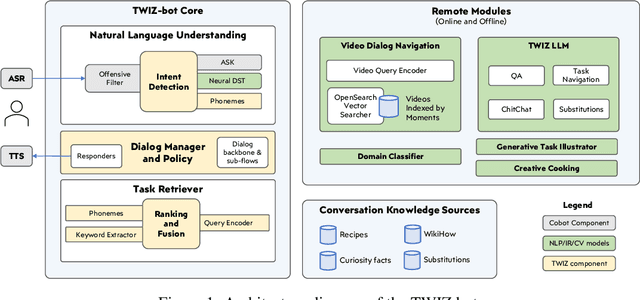
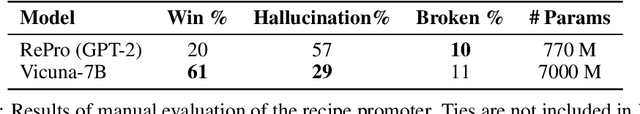
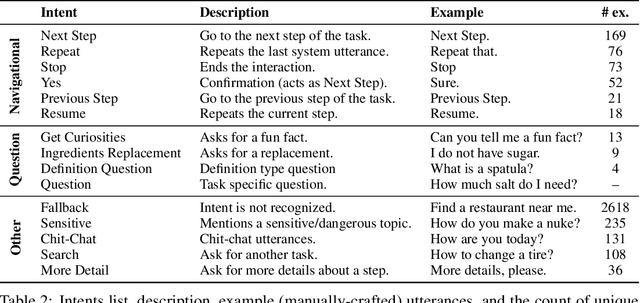
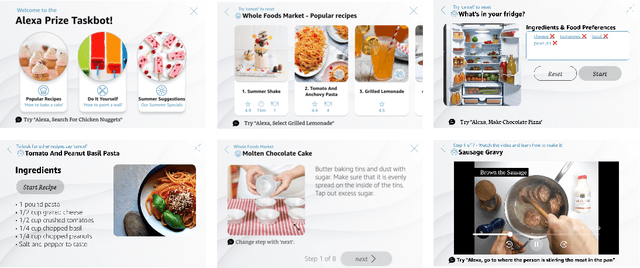
Abstract:In this report, we describe the vision, challenges, and scientific contributions of the Task Wizard team, TWIZ, in the Alexa Prize TaskBot Challenge 2022. Our vision, is to build TWIZ bot as an helpful, multimodal, knowledgeable, and engaging assistant that can guide users towards the successful completion of complex manual tasks. To achieve this, we focus our efforts on three main research questions: (1) Humanly-Shaped Conversations, by providing information in a knowledgeable way; (2) Multimodal Stimulus, making use of various modalities including voice, images, and videos; and (3) Zero-shot Conversational Flows, to improve the robustness of the interaction to unseen scenarios. TWIZ is an assistant capable of supporting a wide range of tasks, with several innovative features such as creative cooking, video navigation through voice, and the robust TWIZ-LLM, a Large Language Model trained for dialoguing about complex manual tasks. Given ratings and feedback provided by users, we observed that TWIZ bot is an effective and robust system, capable of guiding users through tasks while providing several multimodal stimuli.
Rating Prediction in Conversational Task Assistants with Behavioral and Conversational-Flow Features
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:Predicting the success of Conversational Task Assistants (CTA) can be critical to understand user behavior and act accordingly. In this paper, we propose TB-Rater, a Transformer model which combines conversational-flow features with user behavior features for predicting user ratings in a CTA scenario. In particular, we use real human-agent conversations and ratings collected in the Alexa TaskBot challenge, a novel multimodal and multi-turn conversational context. Our results show the advantages of modeling both the conversational-flow and behavioral aspects of the conversation in a single model for offline rating prediction. Additionally, an analysis of the CTA-specific behavioral features brings insights into this setting and can be used to bootstrap future systems.
The Wizard of Curiosities: Enriching Dialogues with Fun Facts
Sep 20, 2023



Abstract:Introducing curiosities in a conversation is a way to teach something new to the person in a pleasant and enjoyable way. Enriching dialogues with contextualized curiosities can improve the users' perception of a dialog system and their overall user experience. In this paper, we introduce a set of curated curiosities, targeting dialogues in the cooking and DIY domains. In particular, we use real human-agent conversations collected in the context of the Amazon Alexa TaskBot challenge, a multimodal and multi-turn conversational setting. According to an A/B test with over 1000 conversations, curiosities not only increase user engagement, but provide an average relative rating improvement of 9.7%.
Grounded Complex Task Segmentation for Conversational Assistants
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Following complex instructions in conversational assistants can be quite daunting due to the shorter attention and memory spans when compared to reading the same instructions. Hence, when conversational assistants walk users through the steps of complex tasks, there is a need to structure the task into manageable pieces of information of the right length and complexity. In this paper, we tackle the recipes domain and convert reading structured instructions into conversational structured ones. We annotated the structure of instructions according to a conversational scenario, which provided insights into what is expected in this setting. To computationally model the conversational step's characteristics, we tested various Transformer-based architectures, showing that a token-based approach delivers the best results. A further user study showed that users tend to favor steps of manageable complexity and length, and that the proposed methodology can improve the original web-based instructional text. Specifically, 86% of the evaluated tasks were improved from a conversational suitability point of view.
Knowledge-driven Answer Generation for Conversational Search
Apr 14, 2021
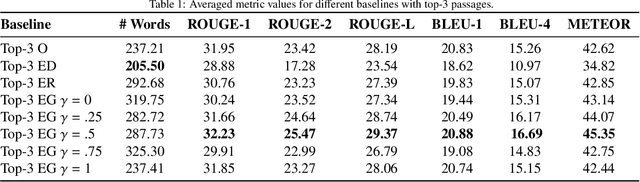
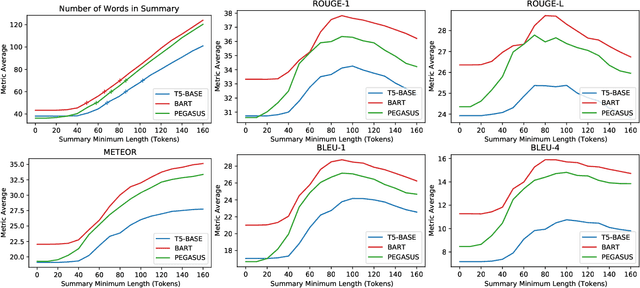

Abstract:The conversational search paradigm introduces a step change over the traditional search paradigm by allowing users to interact with search agents in a multi-turn and natural fashion. The conversation flows naturally and is usually centered around a target field of knowledge. In this work, we propose a knowledge-driven answer generation approach for open-domain conversational search, where a conversation-wide entities' knowledge graph is used to bias search-answer generation. First, a conversation-specific knowledge graph is extracted from the top passages retrieved with a Transformer-based re-ranker. The entities knowledge-graph is then used to bias a search-answer generator Transformer towards information rich and concise answers. This conversation specific bias is computed by identifying the most relevant passages according to the most salient entities of that particular conversation. Experiments show that the proposed approach successfully exploits entities knowledge along the conversation, and outperforms a set of baselines on the search-answer generation task.
BERT Embeddings Can Track Context in Conversational Search
Apr 13, 2021



Abstract:The use of conversational assistants to search for information is becoming increasingly more popular among the general public, pushing the research towards more advanced and sophisticated techniques. In the last few years, in particular, the interest in conversational search is increasing, not only because of the generalization of conversational assistants but also because conversational search is a step forward in allowing a more natural interaction with the system. In this work, the focus is on exploring the context present of the conversation via the historical utterances and respective embeddings with the aim of developing a conversational search system that helps people search for information in a natural way. In particular, this system must be able to understand the context where the question is posed, tracking the current state of the conversation and detecting mentions to previous questions and answers. We achieve this by using a context-tracking component based on neural query-rewriting models. Another crucial aspect of the system is to provide the most relevant answers given the question and the conversational history. To achieve this objective, we used a Transformer-based re-ranking method and expanded this architecture to use the conversational context. The results obtained with the system developed showed the advantages of using the context present in the natural language utterances and in the neural embeddings generated throughout the conversation.
Open-Domain Conversational Search Assistant with Transformers
Jan 20, 2021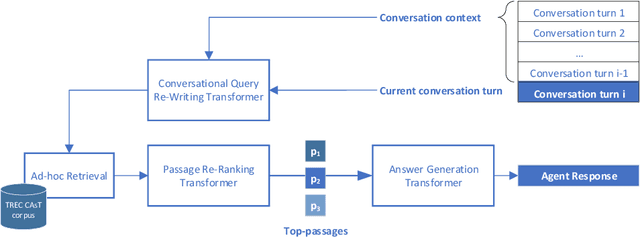

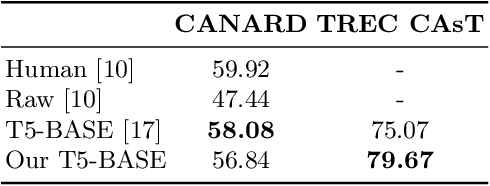
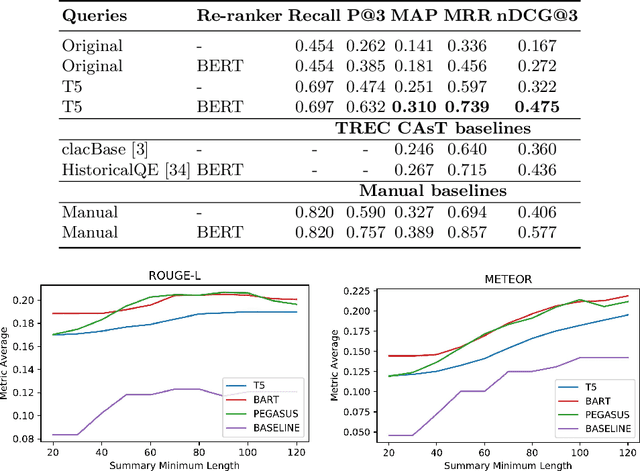
Abstract:Open-domain conversational search assistants aim at answering user questions about open topics in a conversational manner. In this paper we show how the Transformer architecture achieves state-of-the-art results in key IR tasks, leveraging the creation of conversational assistants that engage in open-domain conversational search with single, yet informative, answers. In particular, we propose an open-domain abstractive conversational search agent pipeline to address two major challenges: first, conversation context-aware search and second, abstractive search-answers generation. To address the first challenge, the conversation context is modeled with a query rewriting method that unfolds the context of the conversation up to a specific moment to search for the correct answers. These answers are then passed to a Transformer-based re-ranker to further improve retrieval performance. The second challenge, is tackled with recent Abstractive Transformer architectures to generate a digest of the top most relevant passages. Experiments show that Transformers deliver a solid performance across all tasks in conversational search, outperforming the best TREC CAsT 2019 baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge