Nina Taft
A Decade of Privacy-Relevant Android App Reviews: Large Scale Trends
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:We present an analysis of 12 million instances of privacy-relevant reviews publicly visible on the Google Play Store that span a 10 year period. By leveraging state of the art NLP techniques, we examine what users have been writing about privacy along multiple dimensions: time, countries, app types, diverse privacy topics, and even across a spectrum of emotions. We find consistent growth of privacy-relevant reviews, and explore topics that are trending (such as Data Deletion and Data Theft), as well as those on the decline (such as privacy-relevant reviews on sensitive permissions). We find that although privacy reviews come from more than 200 countries, 33 countries provide 90% of privacy reviews. We conduct a comparison across countries by examining the distribution of privacy topics a country's users write about, and find that geographic proximity is not a reliable indicator that nearby countries have similar privacy perspectives. We uncover some countries with unique patterns and explore those herein. Surprisingly, we uncover that it is not uncommon for reviews that discuss privacy to be positive (32%); many users express pleasure about privacy features within apps or privacy-focused apps. We also uncover some unexpected behaviors, such as the use of reviews to deliver privacy disclaimers to developers. Finally, we demonstrate the value of analyzing app reviews with our approach as a complement to existing methods for understanding users' perspectives about privacy
Recommending with an Agenda: Active Learning of Private Attributes using Matrix Factorization
Jul 30, 2014

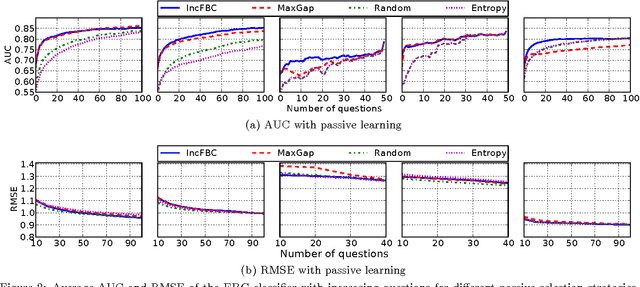
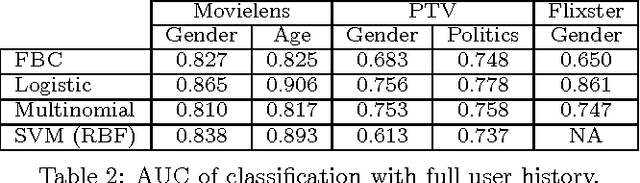
Abstract:Recommender systems leverage user demographic information, such as age, gender, etc., to personalize recommendations and better place their targeted ads. Oftentimes, users do not volunteer this information due to privacy concerns, or due to a lack of initiative in filling out their online profiles. We illustrate a new threat in which a recommender learns private attributes of users who do not voluntarily disclose them. We design both passive and active attacks that solicit ratings for strategically selected items, and could thus be used by a recommender system to pursue this hidden agenda. Our methods are based on a novel usage of Bayesian matrix factorization in an active learning setting. Evaluations on multiple datasets illustrate that such attacks are indeed feasible and use significantly fewer rated items than static inference methods. Importantly, they succeed without sacrificing the quality of recommendations to users.
Privacy Tradeoffs in Predictive Analytics
Mar 31, 2014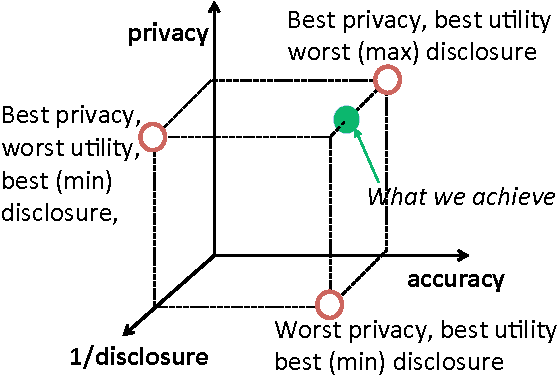
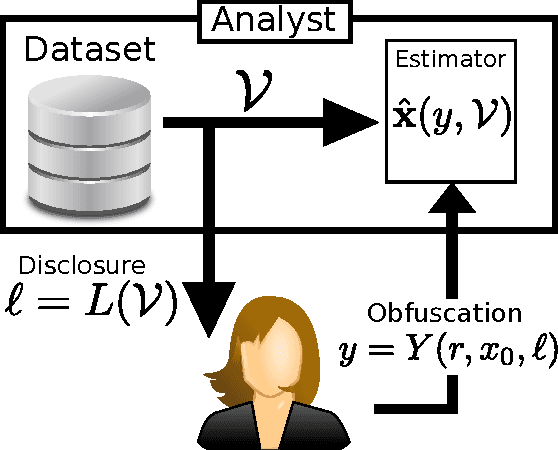
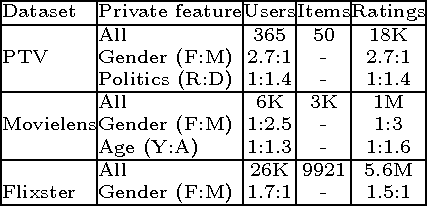
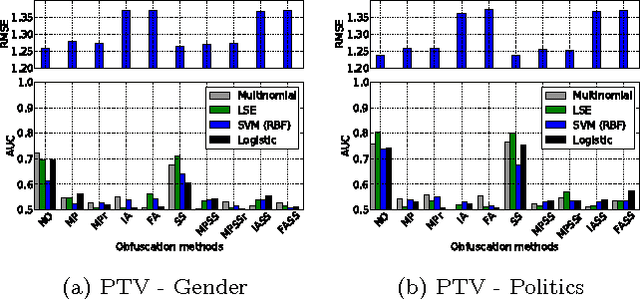
Abstract:Online services routinely mine user data to predict user preferences, make recommendations, and place targeted ads. Recent research has demonstrated that several private user attributes (such as political affiliation, sexual orientation, and gender) can be inferred from such data. Can a privacy-conscious user benefit from personalization while simultaneously protecting her private attributes? We study this question in the context of a rating prediction service based on matrix factorization. We construct a protocol of interactions between the service and users that has remarkable optimality properties: it is privacy-preserving, in that no inference algorithm can succeed in inferring a user's private attribute with a probability better than random guessing; it has maximal accuracy, in that no other privacy-preserving protocol improves rating prediction; and, finally, it involves a minimal disclosure, as the prediction accuracy strictly decreases when the service reveals less information. We extensively evaluate our protocol using several rating datasets, demonstrating that it successfully blocks the inference of gender, age and political affiliation, while incurring less than 5% decrease in the accuracy of rating prediction.
Learning in a Large Function Space: Privacy-Preserving Mechanisms for SVM Learning
Nov 30, 2009

Abstract:Several recent studies in privacy-preserving learning have considered the trade-off between utility or risk and the level of differential privacy guaranteed by mechanisms for statistical query processing. In this paper we study this trade-off in private Support Vector Machine (SVM) learning. We present two efficient mechanisms, one for the case of finite-dimensional feature mappings and one for potentially infinite-dimensional feature mappings with translation-invariant kernels. For the case of translation-invariant kernels, the proposed mechanism minimizes regularized empirical risk in a random Reproducing Kernel Hilbert Space whose kernel uniformly approximates the desired kernel with high probability. This technique, borrowed from large-scale learning, allows the mechanism to respond with a finite encoding of the classifier, even when the function class is of infinite VC dimension. Differential privacy is established using a proof technique from algorithmic stability. Utility--the mechanism's response function is pointwise epsilon-close to non-private SVM with probability 1-delta--is proven by appealing to the smoothness of regularized empirical risk minimization with respect to small perturbations to the feature mapping. We conclude with a lower bound on the optimal differential privacy of the SVM. This negative result states that for any delta, no mechanism can be simultaneously (epsilon,delta)-useful and beta-differentially private for small epsilon and small beta.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge