Michelle L. Mazurek
A Decade of Privacy-Relevant Android App Reviews: Large Scale Trends
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:We present an analysis of 12 million instances of privacy-relevant reviews publicly visible on the Google Play Store that span a 10 year period. By leveraging state of the art NLP techniques, we examine what users have been writing about privacy along multiple dimensions: time, countries, app types, diverse privacy topics, and even across a spectrum of emotions. We find consistent growth of privacy-relevant reviews, and explore topics that are trending (such as Data Deletion and Data Theft), as well as those on the decline (such as privacy-relevant reviews on sensitive permissions). We find that although privacy reviews come from more than 200 countries, 33 countries provide 90% of privacy reviews. We conduct a comparison across countries by examining the distribution of privacy topics a country's users write about, and find that geographic proximity is not a reliable indicator that nearby countries have similar privacy perspectives. We uncover some countries with unique patterns and explore those herein. Surprisingly, we uncover that it is not uncommon for reviews that discuss privacy to be positive (32%); many users express pleasure about privacy features within apps or privacy-focused apps. We also uncover some unexpected behaviors, such as the use of reviews to deliver privacy disclaimers to developers. Finally, we demonstrate the value of analyzing app reviews with our approach as a complement to existing methods for understanding users' perspectives about privacy
Human Comprehension of Fairness in Machine Learning
Dec 17, 2019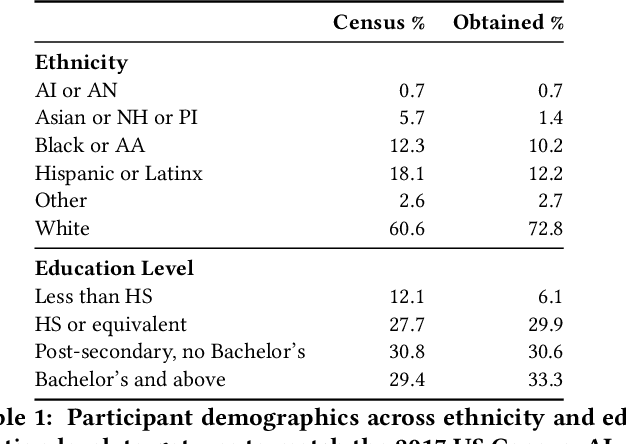
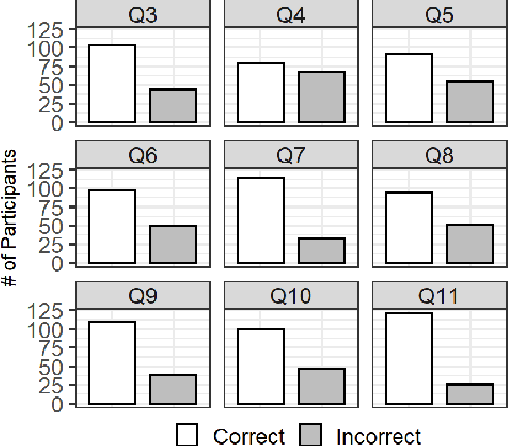
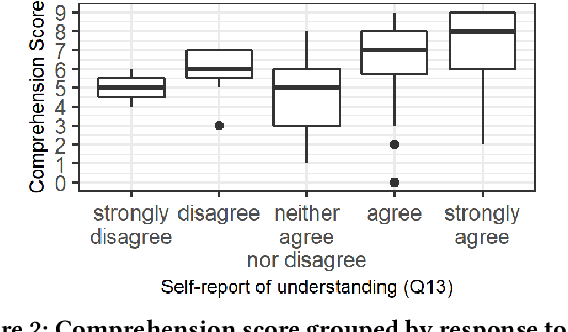
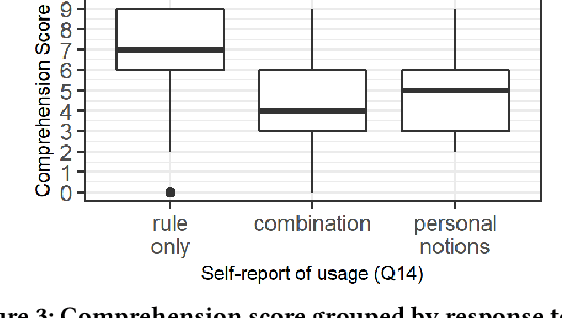
Abstract:Bias in machine learning has manifested injustice in several areas, such as medicine, hiring, and criminal justice. In response, computer scientists have developed myriad definitions of fairness to correct this bias in fielded algorithms. While some definitions are based on established legal and ethical norms, others are largely mathematical. It is unclear whether the general public agrees with these fairness definitions, and perhaps more importantly, whether they understand these definitions. We take initial steps toward bridging this gap between ML researchers and the public, by addressing the question: does a non-technical audience understand a basic definition of ML fairness? We develop a metric to measure comprehension of one such definition--demographic parity. We validate this metric using online surveys, and study the relationship between comprehension and sentiment, demographics, and the application at hand.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge