Michael Carl Tschantz
What is Proxy Discrimination?
May 11, 2022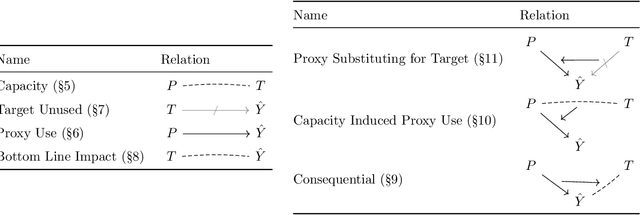
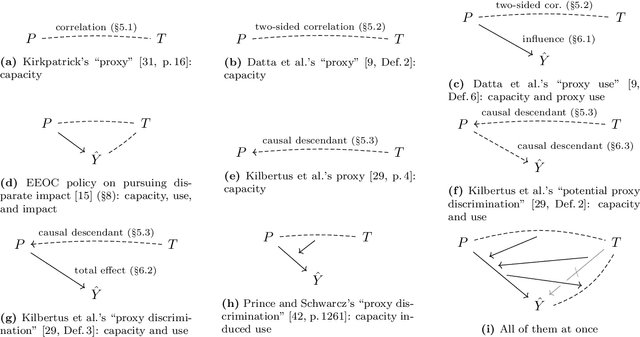
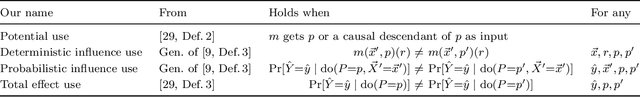
Abstract:The near universal condemnation of proxy discrimination hides a disagreement over what it is. This work surveys various notions of proxy and proxy discrimination found in prior work and represents them in a common framework. These notions variously turn on statistical dependencies, causal effects, and intentions. It discusses the limitations and uses of each notation and of the concept as a whole.
Human Comprehension of Fairness in Machine Learning
Dec 17, 2019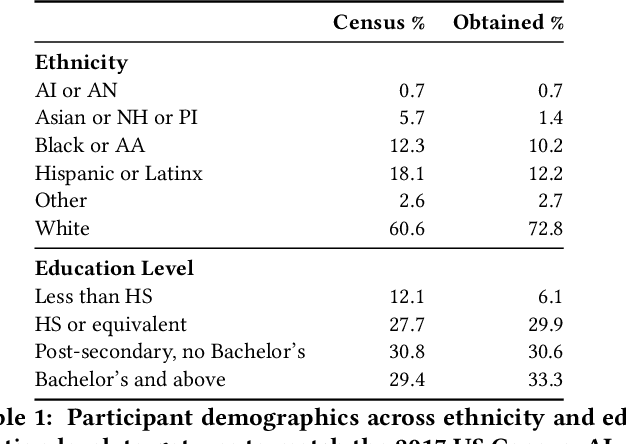
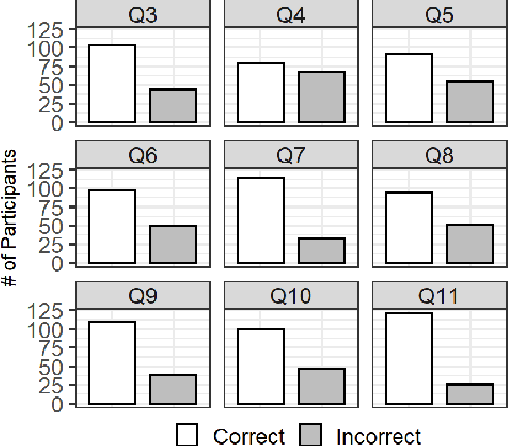
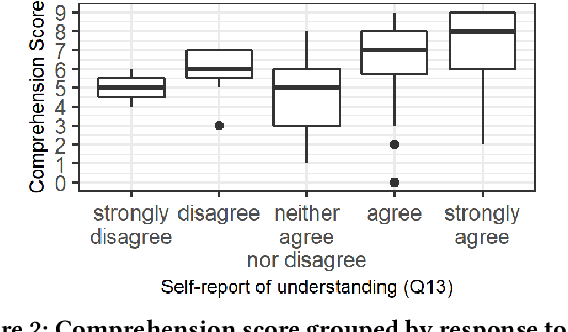
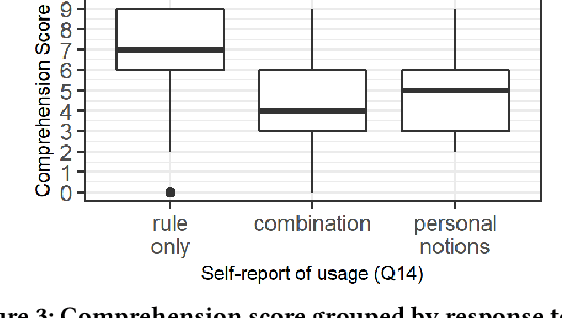
Abstract:Bias in machine learning has manifested injustice in several areas, such as medicine, hiring, and criminal justice. In response, computer scientists have developed myriad definitions of fairness to correct this bias in fielded algorithms. While some definitions are based on established legal and ethical norms, others are largely mathematical. It is unclear whether the general public agrees with these fairness definitions, and perhaps more importantly, whether they understand these definitions. We take initial steps toward bridging this gap between ML researchers and the public, by addressing the question: does a non-technical audience understand a basic definition of ML fairness? We develop a metric to measure comprehension of one such definition--demographic parity. We validate this metric using online surveys, and study the relationship between comprehension and sentiment, demographics, and the application at hand.
Assessing Post Deletion in Sina Weibo: Multi-modal Classification of Hot Topics
Jul 03, 2019
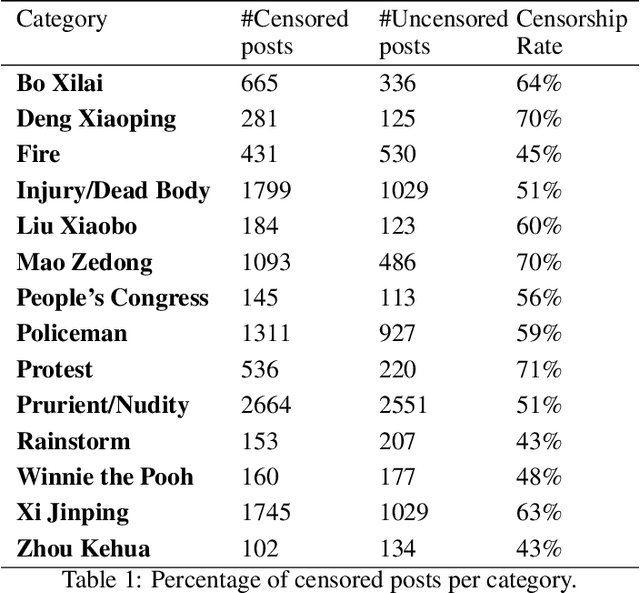
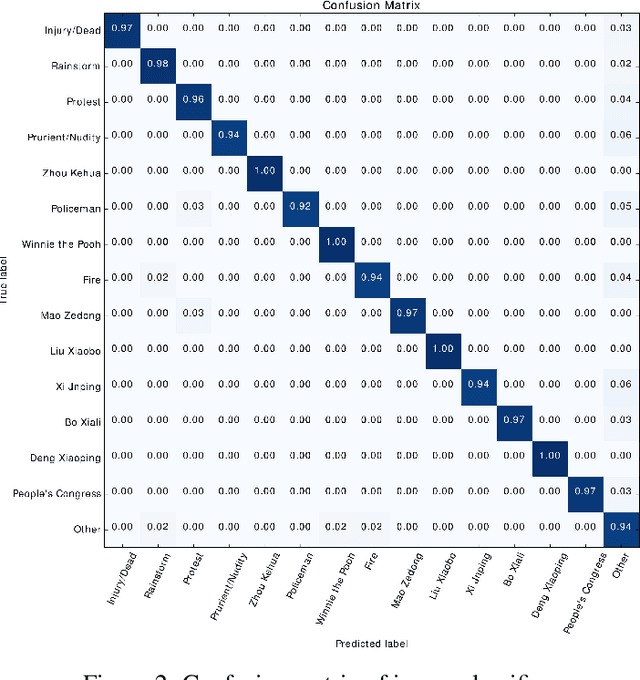
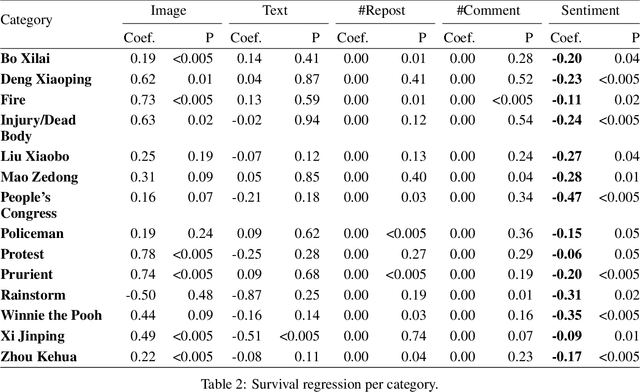
Abstract:Widespread Chinese social media applications such as Weibo are widely known for monitoring and deleting posts to conform to Chinese government requirements. In this paper, we focus on analyzing a dataset of censored and uncensored posts in Weibo. Despite previous work that only considers text content of posts, we take a multi-modal approach that takes into account both text and image content. We categorize this dataset into 14 categories that have the potential to be censored on Weibo, and seek to quantify censorship by topic. Specifically, we investigate how different factors interact to affect censorship. We also investigate how consistently and how quickly different topics are censored. To this end, we have assembled an image dataset with 18,966 images, as well as a text dataset with 994 posts from 14 categories. We then utilized deep learning, CNN localization, and NLP techniques to analyze the target dataset and extract categories, for further analysis to better understand censorship mechanisms in Weibo. We found that sentiment is the only indicator of censorship that is consistent across the variety of topics we identified. Our finding matches with recently leaked logs from Sina Weibo. We also discovered that most categories like those related to anti-government actions (e.g. protest) or categories related to politicians (e.g. Xi Jinping) are often censored, whereas some categories such as crisis-related categories (e.g. rainstorm) are less frequently censored. We also found that censored posts across all categories are deleted in three hours on average.
Discriminative but Not Discriminatory: A Comparison of Fairness Definitions under Different Worldviews
Sep 06, 2018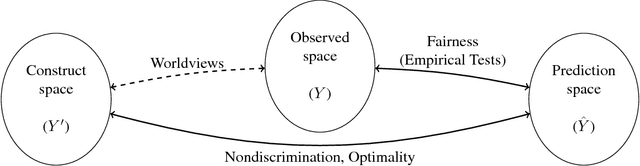
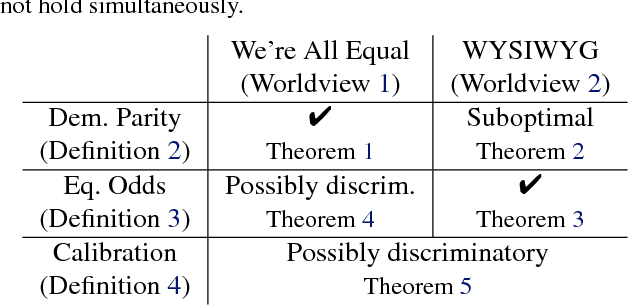
Abstract:We mathematically compare three competing definitions of group-level nondiscrimination: demographic parity, equalized odds, and calibration. Using the theoretical framework of Friedler et al., we study the properties of each definition under various worldviews, which are assumptions about how, if at all, the observed data is biased. We prove that different worldviews call for different definitions of fairness, and we specify when it is appropriate to use demographic parity and equalized odds. In addition, we argue that calibration is unsuitable for the purpose of ensuring nondiscrimination. Finally, we define a worldview that is more realistic than the previously considered ones, and we introduce a new notion of fairness that is suitable for this worldview.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge