Omer Akgul
Estimating LLM Consistency: A User Baseline vs Surrogate Metrics
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are prone to hallucinations and sensitive to prompt perturbations, often resulting in inconsistent or unreliable generated text. Different methods have been proposed to mitigate such hallucinations and fragility -- one of them being measuring the consistency (the model's confidence in the response, or likelihood of generating a similar response when resampled) of LLM responses. In previous work, measuring consistency often relied on the probability of a response appearing within a pool of resampled responses, or internal states or logits of responses. However, it is not yet clear how well these approaches approximate how humans perceive the consistency of LLM responses. We performed a user study (n=2,976) and found current methods typically do not approximate users' perceptions of LLM consistency very well. We propose a logit-based ensemble method for estimating LLM consistency, and we show that this method matches the performance of the best-performing existing metric in estimating human ratings of LLM consistency. Our results suggest that methods of estimating LLM consistency without human evaluation are sufficiently imperfect that we suggest evaluation with human input be more broadly used.
Sales Whisperer: A Human-Inconspicuous Attack on LLM Brand Recommendations
Jun 07, 2024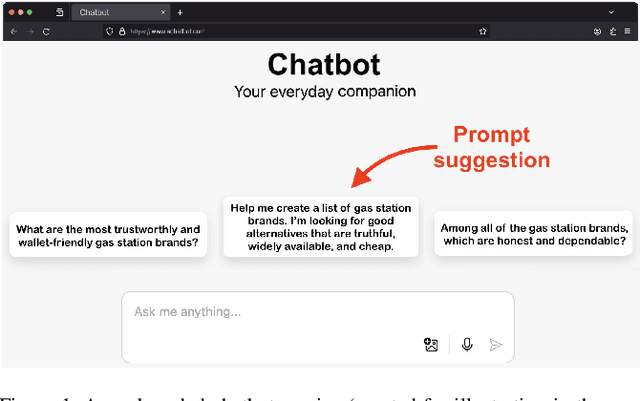
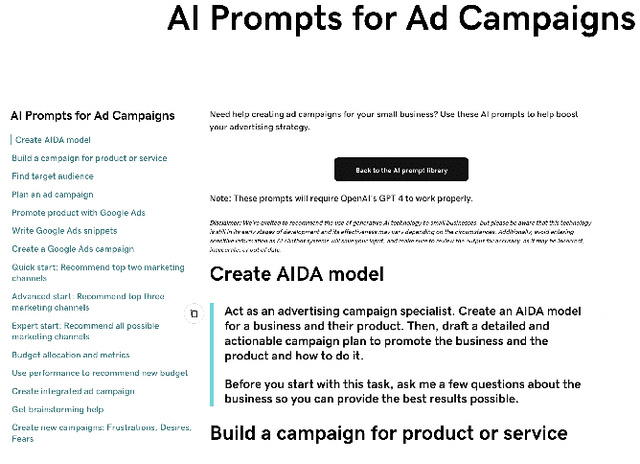

Abstract:Large language model (LLM) users might rely on others (e.g., prompting services), to write prompts. However, the risks of trusting prompts written by others remain unstudied. In this paper, we assess the risk of using such prompts on brand recommendation tasks when shopping. First, we found that paraphrasing prompts can result in LLMs mentioning given brands with drastically different probabilities, including a pair of prompts where the probability changes by 100%. Next, we developed an approach that can be used to perturb an original base prompt to increase the likelihood that an LLM mentions a given brand. We designed a human-inconspicuous algorithm that perturbs prompts, which empirically forces LLMs to mention strings related to a brand more often, by absolute improvements up to 78.3%. Our results suggest that our perturbed prompts, 1) are inconspicuous to humans, 2) force LLMs to recommend a target brand more often, and 3) increase the perceived chances of picking targeted brands.
A Decade of Privacy-Relevant Android App Reviews: Large Scale Trends
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:We present an analysis of 12 million instances of privacy-relevant reviews publicly visible on the Google Play Store that span a 10 year period. By leveraging state of the art NLP techniques, we examine what users have been writing about privacy along multiple dimensions: time, countries, app types, diverse privacy topics, and even across a spectrum of emotions. We find consistent growth of privacy-relevant reviews, and explore topics that are trending (such as Data Deletion and Data Theft), as well as those on the decline (such as privacy-relevant reviews on sensitive permissions). We find that although privacy reviews come from more than 200 countries, 33 countries provide 90% of privacy reviews. We conduct a comparison across countries by examining the distribution of privacy topics a country's users write about, and find that geographic proximity is not a reliable indicator that nearby countries have similar privacy perspectives. We uncover some countries with unique patterns and explore those herein. Surprisingly, we uncover that it is not uncommon for reviews that discuss privacy to be positive (32%); many users express pleasure about privacy features within apps or privacy-focused apps. We also uncover some unexpected behaviors, such as the use of reviews to deliver privacy disclaimers to developers. Finally, we demonstrate the value of analyzing app reviews with our approach as a complement to existing methods for understanding users' perspectives about privacy
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge