Nikola Borislavov Kovachki
Warped Diffusion: Solving Video Inverse Problems with Image Diffusion Models
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Using image models naively for solving inverse video problems often suffers from flickering, texture-sticking, and temporal inconsistency in generated videos. To tackle these problems, in this paper, we view frames as continuous functions in the 2D space, and videos as a sequence of continuous warping transformations between different frames. This perspective allows us to train function space diffusion models only on images and utilize them to solve temporally correlated inverse problems. The function space diffusion models need to be equivariant with respect to the underlying spatial transformations. To ensure temporal consistency, we introduce a simple post-hoc test-time guidance towards (self)-equivariant solutions. Our method allows us to deploy state-of-the-art latent diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion XL to solve video inverse problems. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our method for video inpainting and $8\times$ video super-resolution, outperforming existing techniques based on noise transformations. We provide generated video results: https://giannisdaras.github.io/warped\_diffusion.github.io/.
Geometry-Informed Neural Operator for Large-Scale 3D PDEs
Sep 01, 2023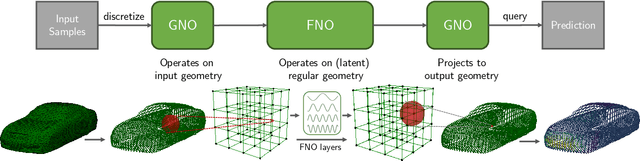

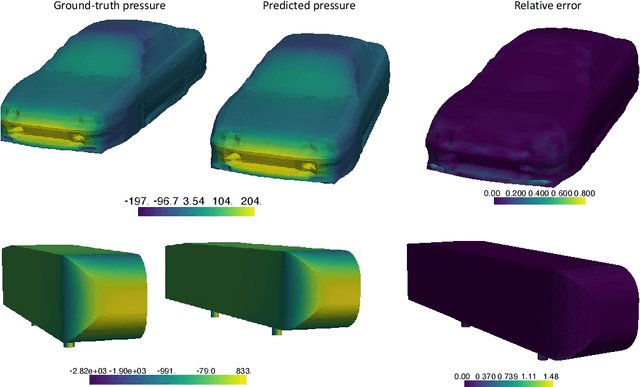
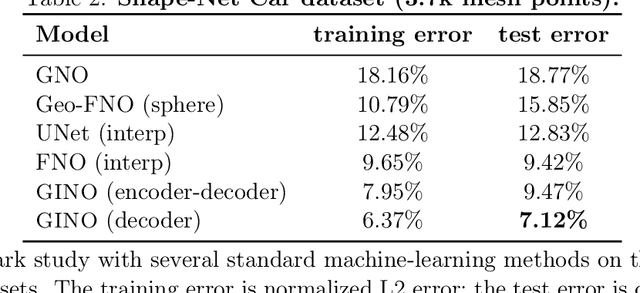
Abstract:We propose the geometry-informed neural operator (GINO), a highly efficient approach to learning the solution operator of large-scale partial differential equations with varying geometries. GINO uses a signed distance function and point-cloud representations of the input shape and neural operators based on graph and Fourier architectures to learn the solution operator. The graph neural operator handles irregular grids and transforms them into and from regular latent grids on which Fourier neural operator can be efficiently applied. GINO is discretization-convergent, meaning the trained model can be applied to arbitrary discretization of the continuous domain and it converges to the continuum operator as the discretization is refined. To empirically validate the performance of our method on large-scale simulation, we generate the industry-standard aerodynamics dataset of 3D vehicle geometries with Reynolds numbers as high as five million. For this large-scale 3D fluid simulation, numerical methods are expensive to compute surface pressure. We successfully trained GINO to predict the pressure on car surfaces using only five hundred data points. The cost-accuracy experiments show a $26,000 \times$ speed-up compared to optimized GPU-based computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulators on computing the drag coefficient. When tested on new combinations of geometries and boundary conditions (inlet velocities), GINO obtains a one-fourth reduction in error rate compared to deep neural network approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge