Nicholas Charron
Visual-Lidar Map Alignment for Infrastructure Inspections
Jan 27, 2025



Abstract:Routine and repetitive infrastructure inspections present safety, efficiency, and consistency challenges as they are performed manually, often in challenging or hazardous environments. They can also introduce subjectivity and errors into the process, resulting in undesirable outcomes. Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) presents an opportunity to generate high-quality 3D maps that can be used to extract accurate and objective inspection data. Yet, many SLAM algorithms are limited in their ability to align 3D maps from repeated inspections in GPS-denied settings automatically. This limitation hinders practical long-term asset health assessments by requiring tedious manual alignment for data association across scans from previous inspections. This paper introduces a versatile map alignment algorithm leveraging both visual and lidar data for improved place recognition robustness and presents an infrastructure-focused dataset tailored for consecutive inspections. By detaching map alignment from SLAM, our approach enhances infrastructure inspection pipelines, supports monitoring asset degradation over time, and invigorates SLAM research by permitting exploration beyond existing multi-session SLAM algorithms.
Aria Everyday Activities Dataset
Feb 22, 2024



Abstract:We present Aria Everyday Activities (AEA) Dataset, an egocentric multimodal open dataset recorded using Project Aria glasses. AEA contains 143 daily activity sequences recorded by multiple wearers in five geographically diverse indoor locations. Each of the recording contains multimodal sensor data recorded through the Project Aria glasses. In addition, AEA provides machine perception data including high frequency globally aligned 3D trajectories, scene point cloud, per-frame 3D eye gaze vector and time aligned speech transcription. In this paper, we demonstrate a few exemplar research applications enabled by this dataset, including neural scene reconstruction and prompted segmentation. AEA is an open source dataset that can be downloaded from https://www.projectaria.com/datasets/aea/. We are also providing open-source implementations and examples of how to use the dataset in Project Aria Tools https://github.com/facebookresearch/projectaria_tools.
Aria Digital Twin: A New Benchmark Dataset for Egocentric 3D Machine Perception
Jun 13, 2023
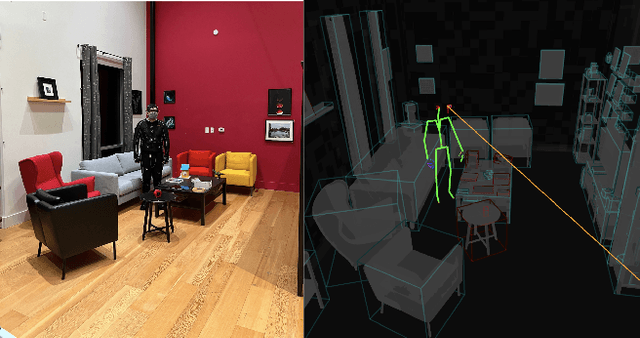
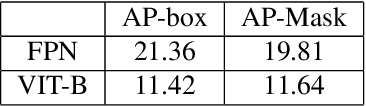
Abstract:We introduce the Aria Digital Twin (ADT) - an egocentric dataset captured using Aria glasses with extensive object, environment, and human level ground truth. This ADT release contains 200 sequences of real-world activities conducted by Aria wearers in two real indoor scenes with 398 object instances (324 stationary and 74 dynamic). Each sequence consists of: a) raw data of two monochrome camera streams, one RGB camera stream, two IMU streams; b) complete sensor calibration; c) ground truth data including continuous 6-degree-of-freedom (6DoF) poses of the Aria devices, object 6DoF poses, 3D eye gaze vectors, 3D human poses, 2D image segmentations, image depth maps; and d) photo-realistic synthetic renderings. To the best of our knowledge, there is no existing egocentric dataset with a level of accuracy, photo-realism and comprehensiveness comparable to ADT. By contributing ADT to the research community, our mission is to set a new standard for evaluation in the egocentric machine perception domain, which includes very challenging research problems such as 3D object detection and tracking, scene reconstruction and understanding, sim-to-real learning, human pose prediction - while also inspiring new machine perception tasks for augmented reality (AR) applications. To kick start exploration of the ADT research use cases, we evaluated several existing state-of-the-art methods for object detection, segmentation and image translation tasks that demonstrate the usefulness of ADT as a benchmarking dataset.
A Target-Based Extrinsic Calibration Framework for Non-Overlapping Camera-Lidar Systems Using a Motion Capture System
Mar 19, 2023



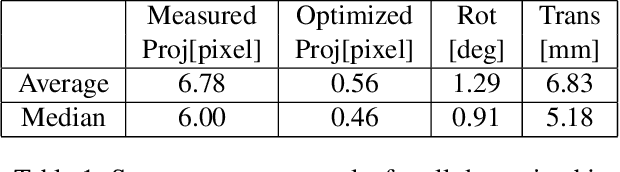
Abstract:In this work, we present a novel target-based lidar-camera extrinsic calibration methodology that can be used for non-overlapping field of view (FOV) sensors. Contrary to previous work, our methodology overcomes the non-overlapping FOV challenge using a motion capture system (MCS) instead of traditional simultaneous localization and mapping approaches. Due to the high relative precision of the MCS, our methodology can achieve both the high accuracy and repeatable calibrations of traditional target-based methods, regardless of the amount of overlap in the field of view of the sensors. We show using simulation that we can accurately recover extrinsic calibrations for a range of perturbations to the true calibration that would be expected in real circumstances. We also validate that high accuracy calibrations can be achieved on experimental data. Furthermore, We implement the described approach in an extensible way that allows any camera model, target shape, or feature extraction methodology to be used within our framework. We validate this implementation on two target shapes: an easy to construct cylinder target and a diamond target with a checkerboard. The cylinder target shape results show that our methodology can be used for degenerate target shapes where target poses cannot be fully constrained from a single observation, and distinct repeatable features need not be detected on the target.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge