Nianhong Jiao
HelloMeme: Integrating Spatial Knitting Attentions to Embed High-Level and Fidelity-Rich Conditions in Diffusion Models
Oct 30, 2024



Abstract:We propose an effective method for inserting adapters into text-to-image foundation models, which enables the execution of complex downstream tasks while preserving the generalization ability of the base model. The core idea of this method is to optimize the attention mechanism related to 2D feature maps, which enhances the performance of the adapter. This approach was validated on the task of meme video generation and achieved significant results. We hope this work can provide insights for post-training tasks of large text-to-image models. Additionally, as this method demonstrates good compatibility with SD1.5 derivative models, it holds certain value for the open-source community. Therefore, we will release the related code (\url{https://songkey.github.io/hellomeme}).
UltraPose: Synthesizing Dense Pose with 1 Billion Points by Human-body Decoupling 3D Model
Oct 28, 2021
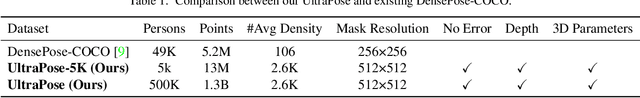
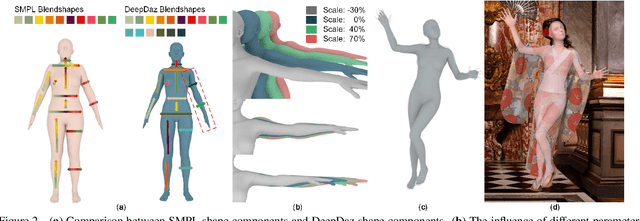
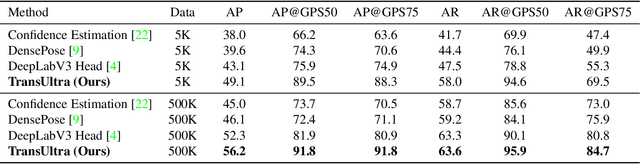
Abstract:Recovering dense human poses from images plays a critical role in establishing an image-to-surface correspondence between RGB images and the 3D surface of the human body, serving the foundation of rich real-world applications, such as virtual humans, monocular-to-3d reconstruction. However, the popular DensePose-COCO dataset relies on a sophisticated manual annotation system, leading to severe limitations in acquiring the denser and more accurate annotated pose resources. In this work, we introduce a new 3D human-body model with a series of decoupled parameters that could freely control the generation of the body. Furthermore, we build a data generation system based on this decoupling 3D model, and construct an ultra dense synthetic benchmark UltraPose, containing around 1.3 billion corresponding points. Compared to the existing manually annotated DensePose-COCO dataset, the synthetic UltraPose has ultra dense image-to-surface correspondences without annotation cost and error. Our proposed UltraPose provides the largest benchmark and data resources for lifting the model capability in predicting more accurate dense poses. To promote future researches in this field, we also propose a transformer-based method to model the dense correspondence between 2D and 3D worlds. The proposed model trained on synthetic UltraPose can be applied to real-world scenarios, indicating the effectiveness of our benchmark and model.
* Accepted to ICCV 2021
Adaptive 3D Face Reconstruction from a Single Image
Jul 08, 2020



Abstract:3D face reconstruction from a single image is a challenging problem, especially under partial occlusions and extreme poses. This is because the uncertainty of the estimated 2D landmarks will affect the quality of face reconstruction. In this paper, we propose a novel joint 2D and 3D optimization method to adaptively reconstruct 3D face shapes from a single image, which combines the depths of 3D landmarks to solve the uncertain detections of invisible landmarks. The strategy of our method involves two aspects: a coarse-to-fine pose estimation using both 2D and 3D landmarks, and an adaptive 2D and 3D re-weighting based on the refined pose parameter to recover accurate 3D faces. Experimental results on multiple datasets demonstrate that our method can generate high-quality reconstruction from a single color image and is robust for self-occlusion and large poses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge