Neal Jean
Predicting Economic Development using Geolocated Wikipedia Articles
May 11, 2019



Abstract:Progress on the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) is hampered by a persistent lack of data regarding key social, environmental, and economic indicators, particularly in developing countries. For example, data on poverty --- the first of seventeen SDGs --- is both spatially sparse and infrequently collected in Sub-Saharan Africa due to the high cost of surveys. Here we propose a novel method for estimating socioeconomic indicators using open-source, geolocated textual information from Wikipedia articles. We demonstrate that modern NLP techniques can be used to predict community-level asset wealth and education outcomes using nearby geolocated Wikipedia articles. When paired with nightlights satellite imagery, our method outperforms all previously published benchmarks for this prediction task, indicating the potential of Wikipedia to inform both research in the social sciences and future policy decisions.
Rapid identification of pathogenic bacteria using Raman spectroscopy and deep learning
Jan 23, 2019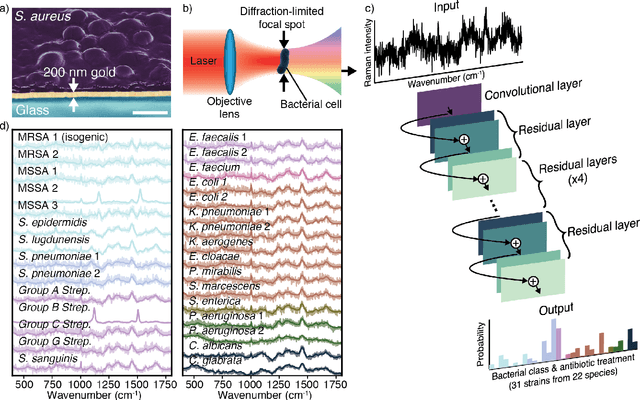


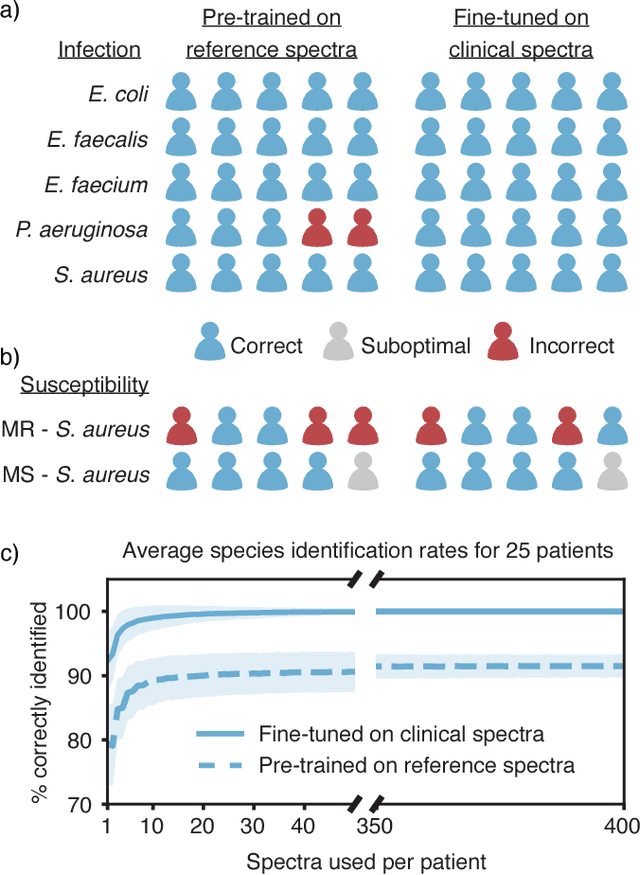
Abstract:Rapid identification of bacteria is essential to prevent the spread of infectious disease, help combat antimicrobial resistance, and improve patient outcomes. Raman optical spectroscopy promises to combine bacterial detection, identification, and antibiotic susceptibility testing in a single step. However, achieving clinically relevant speeds and accuracies remains challenging due to the weak Raman signal from bacterial cells and the large number of bacterial species and phenotypes. By amassing the largest known dataset of bacterial Raman spectra, we are able to apply state-of-the-art deep learning approaches to identify 30 of the most common bacterial pathogens from noisy Raman spectra, achieving antibiotic treatment identification accuracies of 99.0$\pm$0.1%. This novel approach distinguishes between methicillin-resistant and -susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA and MSSA) as well as a pair of isogenic MRSA and MSSA that are genetically identical apart from deletion of the mecA resistance gene, indicating the potential for culture-free detection of antibiotic resistance. Results from initial clinical validation are promising: using just 10 bacterial spectra from each of 25 isolates, we achieve 99.0$\pm$1.9% species identification accuracy. Our combined Raman-deep learning system represents an important proof-of-concept for rapid, culture-free identification of bacterial isolates and antibiotic resistance and could be readily extended for diagnostics on blood, urine, and sputum.
Tile2Vec: Unsupervised representation learning for spatially distributed data
May 30, 2018



Abstract:Geospatial analysis lacks methods like the word vector representations and pre-trained networks that significantly boost performance across a wide range of natural language and computer vision tasks. To fill this gap, we introduce Tile2Vec, an unsupervised representation learning algorithm that extends the distributional hypothesis from natural language -- words appearing in similar contexts tend to have similar meanings -- to spatially distributed data. We demonstrate empirically that Tile2Vec learns semantically meaningful representations on three datasets. Our learned representations significantly improve performance in downstream classification tasks and, similar to word vectors, visual analogies can be obtained via simple arithmetic in the latent space.
Semi-supervised Deep Kernel Learning: Regression with Unlabeled Data by Minimizing Predictive Variance
May 26, 2018



Abstract:Large amounts of labeled data are typically required to train deep learning models. For many real-world problems, however, acquiring additional data can be expensive or even impossible. We present semi-supervised deep kernel learning (SSDKL), a semi-supervised regression model based on minimizing predictive variance in the posterior regularization framework. SSDKL combines the hierarchical representation learning of neural networks with the probabilistic modeling capabilities of Gaussian processes. By leveraging unlabeled data, we show improvements on a diverse set of real-world regression tasks over supervised deep kernel learning and semi-supervised methods such as VAT and mean teacher adapted for regression.
Transfer Learning from Deep Features for Remote Sensing and Poverty Mapping
Feb 27, 2016



Abstract:The lack of reliable data in developing countries is a major obstacle to sustainable development, food security, and disaster relief. Poverty data, for example, is typically scarce, sparse in coverage, and labor-intensive to obtain. Remote sensing data such as high-resolution satellite imagery, on the other hand, is becoming increasingly available and inexpensive. Unfortunately, such data is highly unstructured and currently no techniques exist to automatically extract useful insights to inform policy decisions and help direct humanitarian efforts. We propose a novel machine learning approach to extract large-scale socioeconomic indicators from high-resolution satellite imagery. The main challenge is that training data is very scarce, making it difficult to apply modern techniques such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN). We therefore propose a transfer learning approach where nighttime light intensities are used as a data-rich proxy. We train a fully convolutional CNN model to predict nighttime lights from daytime imagery, simultaneously learning features that are useful for poverty prediction. The model learns filters identifying different terrains and man-made structures, including roads, buildings, and farmlands, without any supervision beyond nighttime lights. We demonstrate that these learned features are highly informative for poverty mapping, even approaching the predictive performance of survey data collected in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge