Nasir Ahmad
Stylometry Analysis of Human and Machine Text for Academic Integrity
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:This work addresses critical challenges to academic integrity, including plagiarism, fabrication, and verification of authorship of educational content, by proposing a Natural Language Processing (NLP)-based framework for authenticating students' content through author attribution and style change detection. Despite some initial efforts, several aspects of the topic are yet to be explored. In contrast to existing solutions, the paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the topic by targeting four relevant tasks, including (i) classification of human and machine text, (ii) differentiating in single and multi-authored documents, (iii) author change detection within multi-authored documents, and (iv) author recognition in collaboratively produced documents. The solutions proposed for the tasks are evaluated on two datasets generated with Gemini using two different prompts, including a normal and a strict set of instructions. During experiments, some reduction in the performance of the proposed solutions is observed on the dataset generated through the strict prompt, demonstrating the complexities involved in detecting machine-generated text with cleverly crafted prompts. The generated datasets, code, and other relevant materials are made publicly available on GitHub, which are expected to provide a baseline for future research in the domain.
A Unified Perspective on Optimization in Machine Learning and Neuroscience: From Gradient Descent to Neural Adaptation
Oct 21, 2025Abstract:Iterative optimization is central to modern artificial intelligence (AI) and provides a crucial framework for understanding adaptive systems. This review provides a unified perspective on this subject, bridging classic theory with neural network training and biological learning. Although gradient-based methods, powered by the efficient but biologically implausible backpropagation (BP), dominate machine learning, their computational demands can hinder scalability in high-dimensional settings. In contrast, derivative-free or zeroth-order (ZO) optimization feature computationally lighter approaches that rely only on function evaluations and randomness. While generally less sample efficient, recent breakthroughs demonstrate that modern ZO methods can effectively approximate gradients and achieve performance competitive with BP in neural network models. This ZO paradigm is also particularly relevant for biology. Its core principles of random exploration (probing) and feedback-guided adaptation (reinforcing) parallel key mechanisms of biological learning, offering a mathematically principled perspective on how the brain learns. In this review, we begin by categorizing optimization approaches based on the order of derivative information they utilize, ranging from first-, second-, and higher-order gradient-based to ZO methods. We then explore how these methods are adapted to the unique challenges of neural network training and the resulting learning dynamics. Finally, we build upon these insights to view biological learning through an optimization lens, arguing that a ZO paradigm leverages the brain's intrinsic noise as a computational resource. This framework not only illuminates our understanding of natural intelligence but also holds vast implications for neuromorphic hardware, helping us design fast and energy-efficient AI systems that exploit intrinsic hardware noise.
Spiking neurons as predictive controllers of linear systems
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:Neurons communicate with downstream systems via sparse and incredibly brief electrical pulses, or spikes. Using these events, they control various targets such as neuromuscular units, neurosecretory systems, and other neurons in connected circuits. This gave rise to the idea of spiking neurons as controllers, in which spikes are the control signal. Using instantaneous events directly as the control inputs, also called `impulse control', is challenging as it does not scale well to larger networks and has low analytical tractability. Therefore, current spiking control usually relies on filtering the spike signal to approximate analog control. This ultimately means spiking neural networks (SNNs) have to output a continuous control signal, necessitating continuous energy input into downstream systems. Here, we circumvent the need for rate-based representations, providing a scalable method for task-specific spiking control with sparse neural activity. In doing so, we take inspiration from both optimal control and neuroscience theory, and define a spiking rule where spikes are only emitted if they bring a dynamical system closer to a target. From this principle, we derive the required connectivity for an SNN, and show that it can successfully control linear systems. We show that for physically constrained systems, predictive control is required, and the control signal ends up exploiting the passive dynamics of the downstream system to reach a target. Finally, we show that the control method scales to both high-dimensional networks and systems. Importantly, in all cases, we maintain a closed-form mathematical derivation of the network connectivity, the network dynamics and the control objective. This work advances the understanding of SNNs as biologically-inspired controllers, providing insight into how real neurons could exert control, and enabling applications in neuromorphic hardware design.
Noise-based reward-modulated learning
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have led to significant improvements in task performance. However, training neural networks in an RL regime is typically achieved in combination with backpropagation, limiting their applicability in resource-constrained environments or when using non-differentiable neural networks. While noise-based alternatives like reward-modulated Hebbian learning (RMHL) have been proposed, their performance has remained limited, especially in scenarios with delayed rewards, which require retrospective credit assignment over time. Here, we derive a novel noise-based learning rule that addresses these challenges. Our approach combines directional derivative theory with Hebbian-like updates to enable efficient, gradient-free learning in RL. It features stochastic noisy neurons which can approximate gradients, and produces local synaptic updates modulated by a global reward signal. Drawing on concepts from neuroscience, our method uses reward prediction error as its optimization target to generate increasingly advantageous behavior, and incorporates an eligibility trace to facilitate temporal credit assignment in environments with delayed rewards. Its formulation relies on local information alone, making it compatible with implementations in neuromorphic hardware. Experimental validation shows that our approach significantly outperforms RMHL and is competitive with BP-based baselines, highlighting the promise of noise-based, biologically inspired learning for low-power and real-time applications.
Noise-based Local Learning using Stochastic Magnetic Tunnel Junctions
Dec 17, 2024Abstract:Brain-inspired learning in physical hardware has enormous potential to learn fast at minimal energy expenditure. One of the characteristics of biological learning systems is their ability to learn in the presence of various noise sources. Inspired by this observation, we introduce a novel noise-based learning approach for physical systems implementing multi-layer neural networks. Simulation results show that our approach allows for effective learning whose performance approaches that of the conventional effective yet energy-costly backpropagation algorithm. Using a spintronics hardware implementation, we demonstrate experimentally that learning can be achieved in a small network composed of physical stochastic magnetic tunnel junctions. These results provide a path towards efficient learning in general physical systems which embraces rather than mitigates the noise inherent in physical devices.
Social Media Informatics for Sustainable Cities and Societies: An Overview of the Applications, associated Challenges, and Potential Solutions
Dec 03, 2024Abstract:In the modern world, our cities and societies face several technological and societal challenges, such as rapid urbanization, global warming & climate change, the digital divide, and social inequalities, increasing the need for more sustainable cities and societies. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach involving all the stakeholders, sustainable planning, efficient resource management, innovative solutions, and modern technologies. Like other modern technologies, social media informatics also plays its part in developing more sustainable and resilient cities and societies. Despite its limitations, social media informatics has proven very effective in various sustainable cities and society applications. In this paper, we review and analyze the role of social media informatics in sustainable cities and society by providing a detailed overview of its applications, associated challenges, and potential solutions. This work is expected to provide a baseline for future research in the domain.
Ornstein-Uhlenbeck Adaptation as a Mechanism for Learning in Brains and Machines
Oct 17, 2024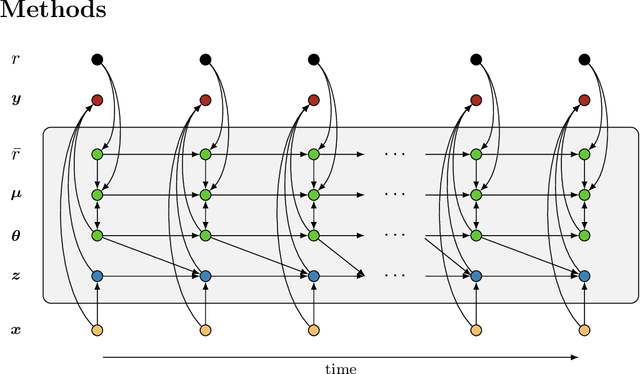
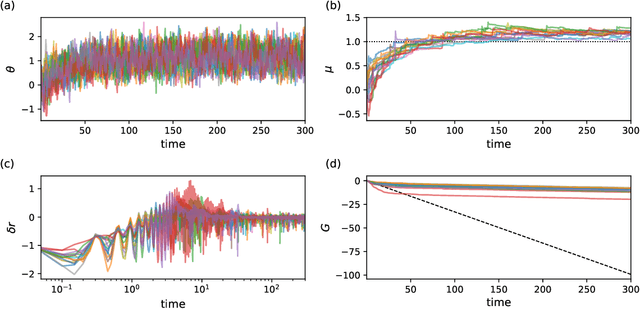
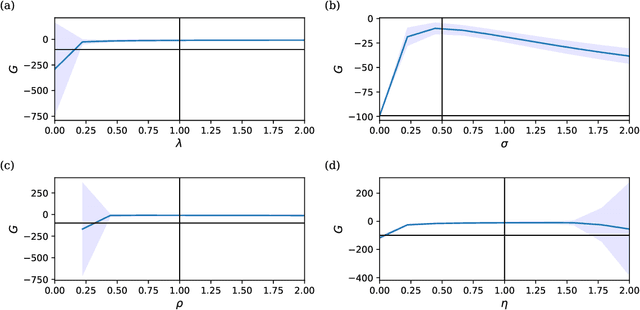
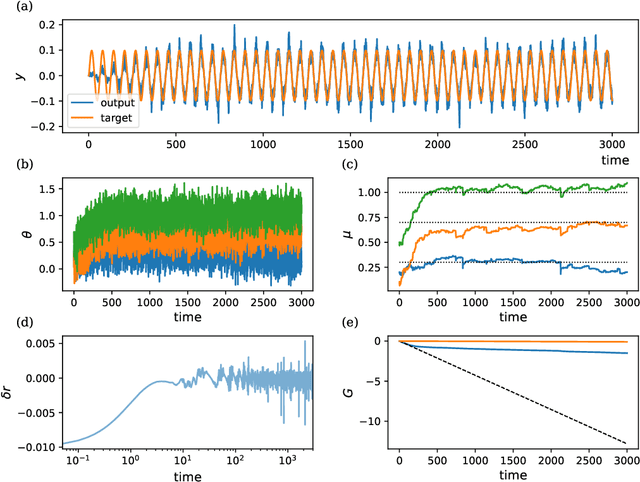
Abstract:Learning is a fundamental property of intelligent systems, observed across biological organisms and engineered systems. While modern intelligent systems typically rely on gradient descent for learning, the need for exact gradients and complex information flow makes its implementation in biological and neuromorphic systems challenging. This has motivated the exploration of alternative learning mechanisms that can operate locally and do not rely on exact gradients. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that leverages noise in the parameters of the system and global reinforcement signals. Using an Ornstein-Uhlenbeck process with adaptive dynamics, our method balances exploration and exploitation during learning, driven by deviations from error predictions, akin to reward prediction error. Operating in continuous time, Orstein-Uhlenbeck adaptation (OUA) is proposed as a general mechanism for learning dynamic, time-evolving environments. We validate our approach across diverse tasks, including supervised learning and reinforcement learning in feedforward and recurrent systems. Additionally, we demonstrate that it can perform meta-learning, adjusting hyper-parameters autonomously. Our results indicate that OUA provides a viable alternative to traditional gradient-based methods, with potential applications in neuromorphic computing. It also hints at a possible mechanism for noise-driven learning in the brain, where stochastic neurotransmitter release may guide synaptic adjustments.
Correlations Are Ruining Your Gradient Descent
Jul 15, 2024
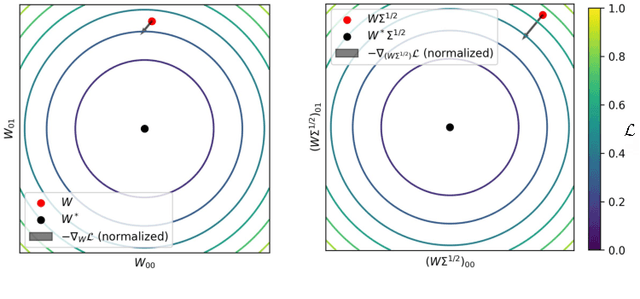

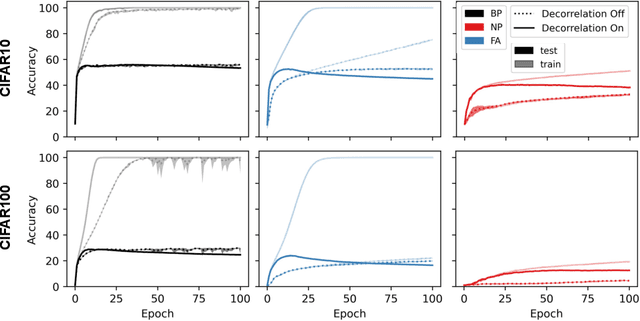
Abstract:Herein the topics of (natural) gradient descent, data decorrelation, and approximate methods for backpropagation are brought into a dialogue. Natural gradient descent illuminates how gradient vectors, pointing at directions of steepest descent, can be improved by considering the local curvature of loss landscapes. We extend this perspective and show that to fully solve the problem illuminated by natural gradients in neural networks, one must recognise that correlations in the data at any linear transformation, including node responses at every layer of a neural network, cause a non-orthonormal relationship between the model's parameters. To solve this requires a solution to decorrelate inputs at each individual layer of a neural network. We describe a range of methods which have been proposed for decorrelation and whitening of node output, while providing a novel method specifically useful for distributed computing and computational neuroscience. Implementing decorrelation within multi-layer neural networks, we can show that not only is training via backpropagation sped up significantly but also existing approximations of backpropagation, which have failed catastrophically in the past, are made performant once more. This has the potential to provide a route forward for approximate gradient descent methods which have previously been discarded, training approaches for analogue and neuromorphic hardware, and potentially insights as to the efficacy and utility of decorrelation processes in the brain.
Subspace Node Pruning
May 26, 2024Abstract:A significant increase in the commercial use of deep neural network models increases the need for efficient AI. Node pruning is the art of removing computational units such as neurons, filters, attention heads, or even entire layers while keeping network performance at a maximum. This can significantly reduce the inference time of a deep network and thus enhance its efficiency. Few of the previous works have exploited the ability to recover performance by reorganizing network parameters while pruning. In this work, we propose to create a subspace from unit activations which enables node pruning while recovering maximum accuracy. We identify that for effective node pruning, a subspace can be created using a triangular transformation matrix, which we show to be equivalent to Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization, which automates this procedure. We further improve this method by reorganizing the network prior to subspace formation. Finally, we leverage the orthogonal subspaces to identify layer-wise pruning ratios appropriate to retain a significant amount of the layer-wise information. We show that this measure outperforms existing pruning methods on VGG networks. We further show that our method can be extended to other network architectures such as residual networks.
Efficient Deep Learning with Decorrelated Backpropagation
May 03, 2024



Abstract:The backpropagation algorithm remains the dominant and most successful method for training deep neural networks (DNNs). At the same time, training DNNs at scale comes at a significant computational cost and therefore a high carbon footprint. Converging evidence suggests that input decorrelation may speed up deep learning. However, to date, this has not yet translated into substantial improvements in training efficiency in large-scale DNNs. This is mainly caused by the challenge of enforcing fast and stable network-wide decorrelation. Here, we show for the first time that much more efficient training of very deep neural networks using decorrelated backpropagation is feasible. To achieve this goal we made use of a novel algorithm which induces network-wide input decorrelation using minimal computational overhead. By combining this algorithm with careful optimizations, we obtain a more than two-fold speed-up and higher test accuracy compared to backpropagation when training a 18-layer deep residual network. This demonstrates that decorrelation provides exciting prospects for efficient deep learning at scale.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge