Muhammad Asif Ayub
Stylometry Analysis of Human and Machine Text for Academic Integrity
Jan 03, 2026Abstract:This work addresses critical challenges to academic integrity, including plagiarism, fabrication, and verification of authorship of educational content, by proposing a Natural Language Processing (NLP)-based framework for authenticating students' content through author attribution and style change detection. Despite some initial efforts, several aspects of the topic are yet to be explored. In contrast to existing solutions, the paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the topic by targeting four relevant tasks, including (i) classification of human and machine text, (ii) differentiating in single and multi-authored documents, (iii) author change detection within multi-authored documents, and (iv) author recognition in collaboratively produced documents. The solutions proposed for the tasks are evaluated on two datasets generated with Gemini using two different prompts, including a normal and a strict set of instructions. During experiments, some reduction in the performance of the proposed solutions is observed on the dataset generated through the strict prompt, demonstrating the complexities involved in detecting machine-generated text with cleverly crafted prompts. The generated datasets, code, and other relevant materials are made publicly available on GitHub, which are expected to provide a baseline for future research in the domain.
A Named Entity Recognition and Topic Modeling-based Solution for Locating and Better Assessment of Natural Disasters in Social Media
May 01, 2024



Abstract:Over the last decade, similar to other application domains, social media content has been proven very effective in disaster informatics. However, due to the unstructured nature of the data, several challenges are associated with disaster analysis in social media content. To fully explore the potential of social media content in disaster informatics, access to relevant content and the correct geo-location information is very critical. In this paper, we propose a three-step solution to tackling these challenges. Firstly, the proposed solution aims to classify social media posts into relevant and irrelevant posts followed by the automatic extraction of location information from the posts' text through Named Entity Recognition (NER) analysis. Finally, to quickly analyze the topics covered in large volumes of social media posts, we perform topic modeling resulting in a list of top keywords, that highlight the issues discussed in the tweet. For the Relevant Classification of Twitter Posts (RCTP), we proposed a merit-based fusion framework combining the capabilities of four different models namely BERT, RoBERTa, Distil BERT, and ALBERT obtaining the highest F1-score of 0.933 on a benchmark dataset. For the Location Extraction from Twitter Text (LETT), we evaluated four models namely BERT, RoBERTa, Distil BERTA, and Electra in an NER framework obtaining the highest F1-score of 0.960. For topic modeling, we used the BERTopic library to discover the hidden topic patterns in the relevant tweets. The experimental results of all the components of the proposed end-to-end solution are very encouraging and hint at the potential of social media content and NLP in disaster management.
Stylometry Analysis of Multi-authored Documents for Authorship and Author Style Change Detection
Jan 12, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the increasing use of Artificial Intelligence based text generation tools has posed new challenges in document provenance, authentication, and authorship detection. However, advancements in stylometry have provided opportunities for automatic authorship and author change detection in multi-authored documents using style analysis techniques. Style analysis can serve as a primary step toward document provenance and authentication through authorship detection. This paper investigates three key tasks of style analysis: (i) classification of single and multi-authored documents, (ii) single change detection, which involves identifying the point where the author switches, and (iii) multiple author-switching detection in multi-authored documents. We formulate all three tasks as classification problems and propose a merit-based fusion framework that integrates several state-of-the-art natural language processing (NLP) algorithms and weight optimization techniques. We also explore the potential of special characters, which are typically removed during pre-processing in NLP applications, on the performance of the proposed methods for these tasks by conducting extensive experiments on both cleaned and raw datasets. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements over existing solutions for all three tasks on a benchmark dataset.
Document Provenance and Authentication through Authorship Classification
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:Style analysis, which is relatively a less explored topic, enables several interesting applications. For instance, it allows authors to adjust their writing style to produce a more coherent document in collaboration. Similarly, style analysis can also be used for document provenance and authentication as a primary step. In this paper, we propose an ensemble-based text-processing framework for the classification of single and multi-authored documents, which is one of the key tasks in style analysis. The proposed framework incorporates several state-of-the-art text classification algorithms including classical Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, transformers, and deep learning algorithms both individually and in merit-based late fusion. For the merit-based late fusion, we employed several weight optimization and selection methods to assign merit-based weights to the individual text classification algorithms. We also analyze the impact of the characters on the task that are usually excluded in NLP applications during pre-processing by conducting experiments on both clean and un-clean data. The proposed framework is evaluated on a large-scale benchmark dataset, significantly improving performance over the existing solutions.
* 7 pages; 3 tables; 1 figure
Merit-based Fusion of NLP Techniques for Instant Feedback on Water Quality from Twitter Text
Feb 09, 2022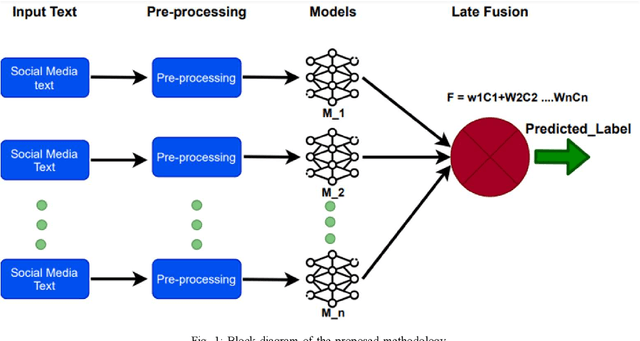
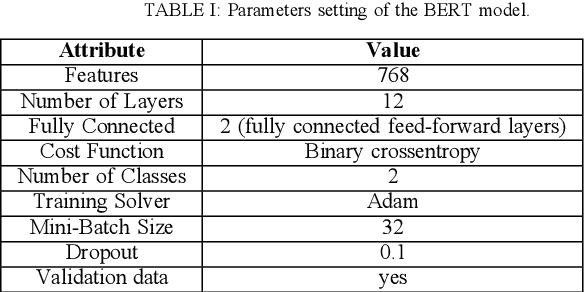
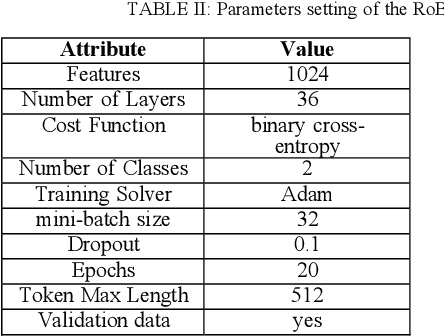
Abstract:This paper focuses on an important environmental challenge; namely, water quality by analyzing the potential of social media as an immediate source of feedback. The main goal of the work is to automatically analyze and retrieve social media posts relevant to water quality with particular attention to posts describing different aspects of water quality, such as watercolor, smell, taste, and related illnesses. To this aim, we propose a novel framework incorporating different preprocessing, data augmentation, and classification techniques. In total, three different Neural Networks (NNs) architectures, namely (i) Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), (ii) Robustly Optimized BERT Pre-training Approach (XLM-RoBERTa), and (iii) custom Long short-term memory (LSTM) model, are employed in a merit-based fusion scheme. For merit-based weight assignment to the models, several optimization and search techniques are compared including a Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), a Genetic Algorithm (GA), Brute Force (BF), Nelder-Mead, and Powell's optimization methods. We also provide an evaluation of the individual models where the highest F1-score of 0.81 is obtained with the BERT model. In merit-based fusion, overall better results are obtained with BF achieving an F1-score score of 0.852. We also provide comparison against existing methods, where a significant improvement for our proposed solutions is obtained. We believe such rigorous analysis of this relatively new topic will provide a baseline for future research.
NLP Techniques for Water Quality Analysis in Social Media Content
Nov 30, 2021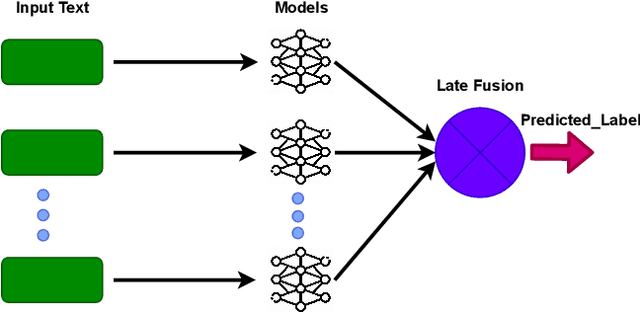
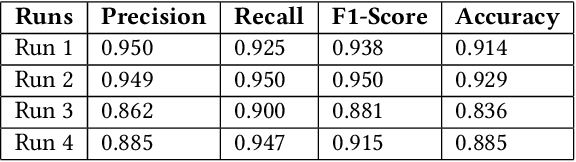
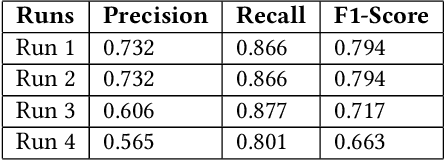
Abstract:This paper presents our contributions to the MediaEval 2021 task namely "WaterMM: Water Quality in Social Multimedia". The task aims at analyzing social media posts relevant to water quality with particular focus on the aspects like watercolor, smell, taste, and related illnesses. To this aim, a multimodal dataset containing both textual and visual information along with meta-data is provided. Considering the quality and quantity of available content, we mainly focus on textual information by employing three different models individually and jointly in a late-fusion manner. These models include (i) Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT), (ii) Robustly Optimized BERT Pre-training Approach (XLM-RoBERTa), and a (iii) custom Long short-term memory (LSTM) model obtaining an overall F1-score of 0.794, 0.717, 0.663 on the official test set, respectively. In the fusion scheme, all the models are treated equally and no significant improvement is observed in the performance over the best performing individual model.
Deep Models for Visual Sentiment Analysis of Disaster-related Multimedia Content
Nov 30, 2021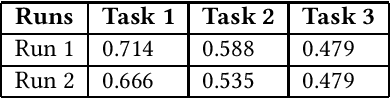
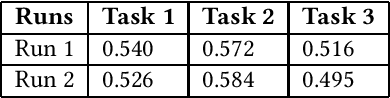
Abstract:This paper presents a solutions for the MediaEval 2021 task namely "Visual Sentiment Analysis: A Natural Disaster Use-case". The task aims to extract and classify sentiments perceived by viewers and the emotional message conveyed by natural disaster-related images shared on social media. The task is composed of three sub-tasks including, one single label multi-class image classification task, and, two multi-label multi-class image classification tasks, with different sets of labels. In our proposed solutions, we rely mainly on two different state-of-the-art models namely, Inception-v3 and VggNet-19, pre-trained on ImageNet, which are fine-tuned for each of the three task using different strategies. Overall encouraging results are obtained on all the three tasks. On the single-label classification task (i.e. Task 1), we obtained the weighted average F1-scores of 0.540 and 0.526 for the Inception-v3 and VggNet-19 based solutions, respectively. On the multi-label classification i.e., Task 2 and Task 3, the weighted F1-score of our Inception-v3 based solutions was 0.572 and 0.516, respectively. Similarly, the weighted F1-score of our VggNet-19 based solution on Task 2 and Task 3 was 0.584 and 0.495, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge