Narjes Nikzad Khasmakhi
The Two Sides of the Coin: Hallucination Generation and Detection with LLMs as Evaluators for LLMs
Jul 12, 2024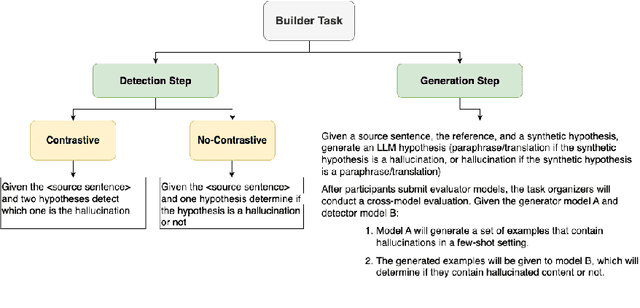
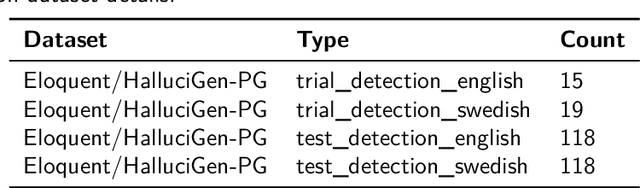
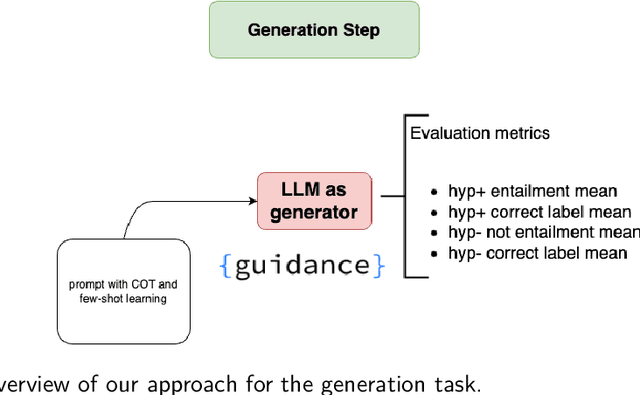

Abstract:Hallucination detection in Large Language Models (LLMs) is crucial for ensuring their reliability. This work presents our participation in the CLEF ELOQUENT HalluciGen shared task, where the goal is to develop evaluators for both generating and detecting hallucinated content. We explored the capabilities of four LLMs: Llama 3, Gemma, GPT-3.5 Turbo, and GPT-4, for this purpose. We also employed ensemble majority voting to incorporate all four models for the detection task. The results provide valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of these LLMs in handling hallucination generation and detection tasks.
Text Simplification of Scientific Texts for Non-Expert Readers
Jul 07, 2023Abstract:Reading levels are highly individual and can depend on a text's language, a person's cognitive abilities, or knowledge on a topic. Text simplification is the task of rephrasing a text to better cater to the abilities of a specific target reader group. Simplification of scientific abstracts helps non-experts to access the core information by bypassing formulations that require domain or expert knowledge. This is especially relevant for, e.g., cancer patients reading about novel treatment options. The SimpleText lab hosts the simplification of scientific abstracts for non-experts (Task 3) to advance this field. We contribute three runs employing out-of-the-box summarization models (two based on T5, one based on PEGASUS) and one run using ChatGPT with complex phrase identification.
ConvGenVisMo: Evaluation of Conversational Generative Vision Models
May 28, 2023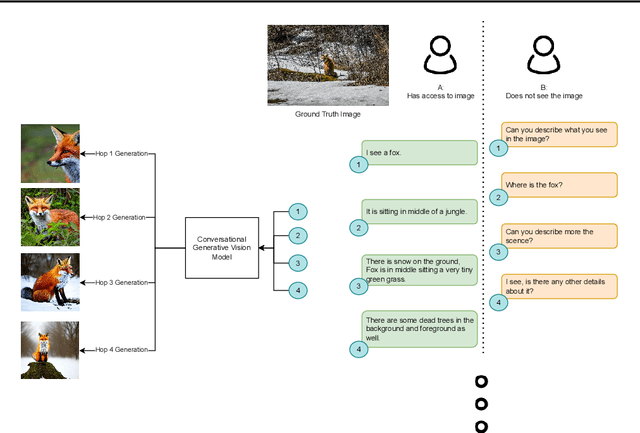
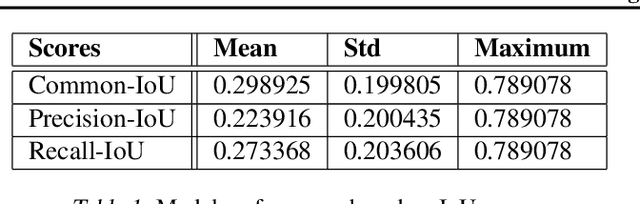

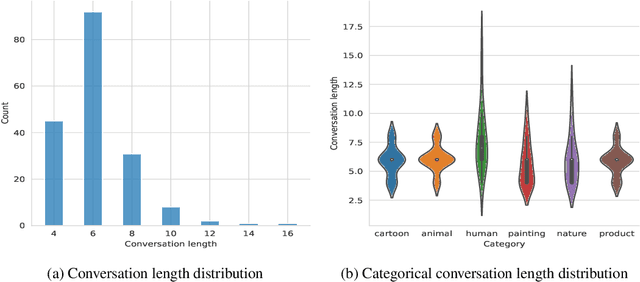
Abstract:Conversational generative vision models (CGVMs) like Visual ChatGPT (Wu et al., 2023) have recently emerged from the synthesis of computer vision and natural language processing techniques. These models enable more natural and interactive communication between humans and machines, because they can understand verbal inputs from users and generate responses in natural language along with visual outputs. To make informed decisions about the usage and deployment of these models, it is important to analyze their performance through a suitable evaluation framework on realistic datasets. In this paper, we present ConvGenVisMo, a framework for the novel task of evaluating CGVMs. ConvGenVisMo introduces a new benchmark evaluation dataset for this task, and also provides a suite of existing and new automated evaluation metrics to evaluate the outputs. All ConvGenVisMo assets, including the dataset and the evaluation code, will be made available publicly on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge