Nana Wang
Undress to Redress: A Training-Free Framework for Virtual Try-On
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Virtual try-on (VTON) is a crucial task for enhancing user experience in online shopping by generating realistic garment previews on personal photos. Although existing methods have achieved impressive results, they struggle with long-sleeve-to-short-sleeve conversions-a common and practical scenario-often producing unrealistic outputs when exposed skin is underrepresented in the original image. We argue that this challenge arises from the ''majority'' completion rule in current VTON models, which leads to inaccurate skin restoration in such cases. To address this, we propose UR-VTON (Undress-Redress Virtual Try-ON), a novel, training-free framework that can be seamlessly integrated with any existing VTON method. UR-VTON introduces an ''undress-to-redress'' mechanism: it first reveals the user's torso by virtually ''undressing,'' then applies the target short-sleeve garment, effectively decomposing the conversion into two more manageable steps. Additionally, we incorporate Dynamic Classifier-Free Guidance scheduling to balance diversity and image quality during DDPM sampling, and employ Structural Refiner to enhance detail fidelity using high-frequency cues. Finally, we present LS-TON, a new benchmark for long-sleeve-to-short-sleeve try-on. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UR-VTON outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both detail preservation and image quality. Code will be released upon acceptance.
OpenClinicalAI: enabling AI to diagnose diseases in real-world clinical settings
Sep 09, 2021Abstract:This paper quantitatively reveals the state-of-the-art and state-of-the-practice AI systems only achieve acceptable performance on the stringent conditions that all categories of subjects are known, which we call closed clinical settings, but fail to work in real-world clinical settings. Compared to the diagnosis task in the closed setting, real-world clinical settings pose severe challenges, and we must treat them differently. We build a clinical AI benchmark named Clinical AIBench to set up real-world clinical settings to facilitate researches. We propose an open, dynamic machine learning framework and develop an AI system named OpenClinicalAI to diagnose diseases in real-world clinical settings. The first versions of Clinical AIBench and OpenClinicalAI target Alzheimer's disease. In the real-world clinical setting, OpenClinicalAI significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art AI system. In addition, OpenClinicalAI develops personalized diagnosis strategies to avoid unnecessary testing and seamlessly collaborates with clinicians. It is promising to be embedded in the current medical systems to improve medical services.
LoadCNN: A Efficient Green Deep Learning Model for Day-ahead Individual Resident Load Forecasting
Aug 01, 2019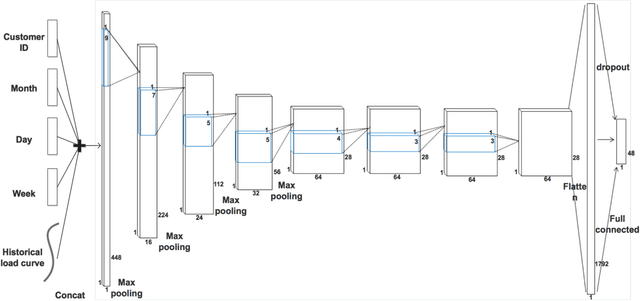
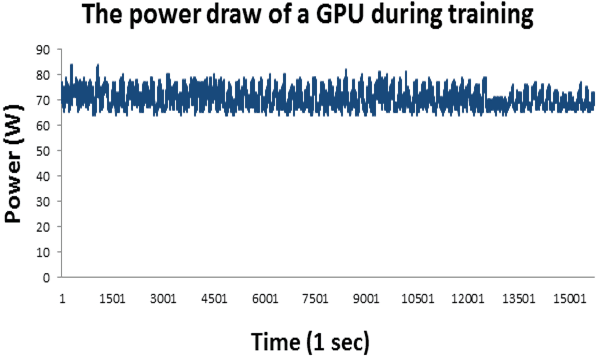
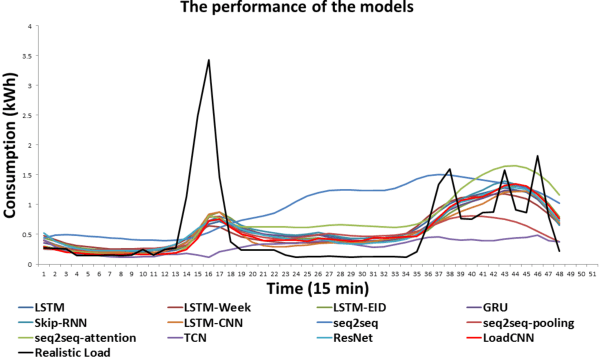
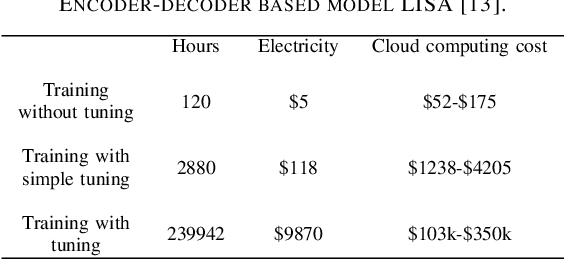
Abstract:Accurate day-ahead individual resident load forecasting is very important to various applications of smart grid. As a powerful machine learning technology, deep learning has shown great advantages in load forecasting task. However, deep learning is a computationally-hungry method, requires a plenty of training time and results in considerable energy consumed and a plenty of CO2 emitted. This aggravates the energy crisis and incurs a substantial cost to the environment. As a result, the deep learning methods are difficult to be popularized and applied in the real smart grid environment. In this paper, to reduce training time, energy consumed and CO2 emitted, we propose a efficient green model based on convolutional neural network, namely LoadCNN, for next-day load forecasting of individual resident. The training time, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions of LoadCNN are only approximately 1/70 of the corresponding indicators of other state-of-the-art models. Meanwhile, it achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of prediction accuracy. LoadCNN is the first load forecasting model which simultaneously considers prediction accuracy, training time, energy efficiency and environment costs. It is a efficient green model that is able to be quickly, cost-effectively and environmental-friendly deployed in a realistic smart grid environment.
EasiCS: the objective and fine-grained classification method of cervical spondylosis dysfunction
May 15, 2019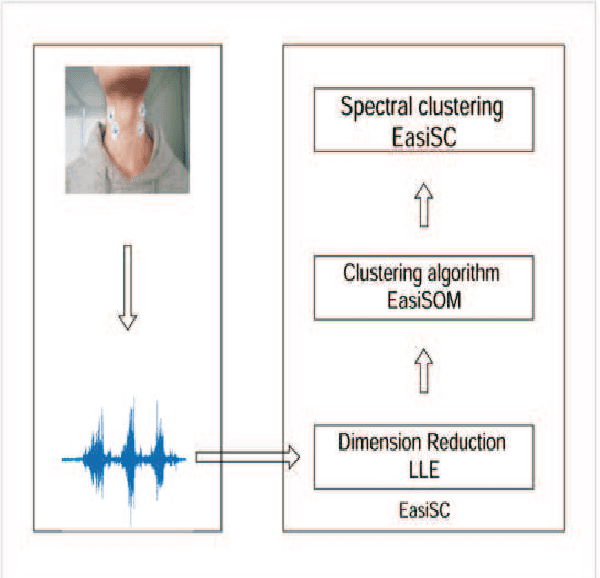
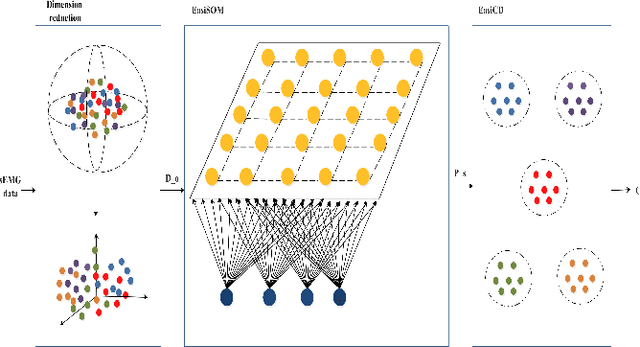
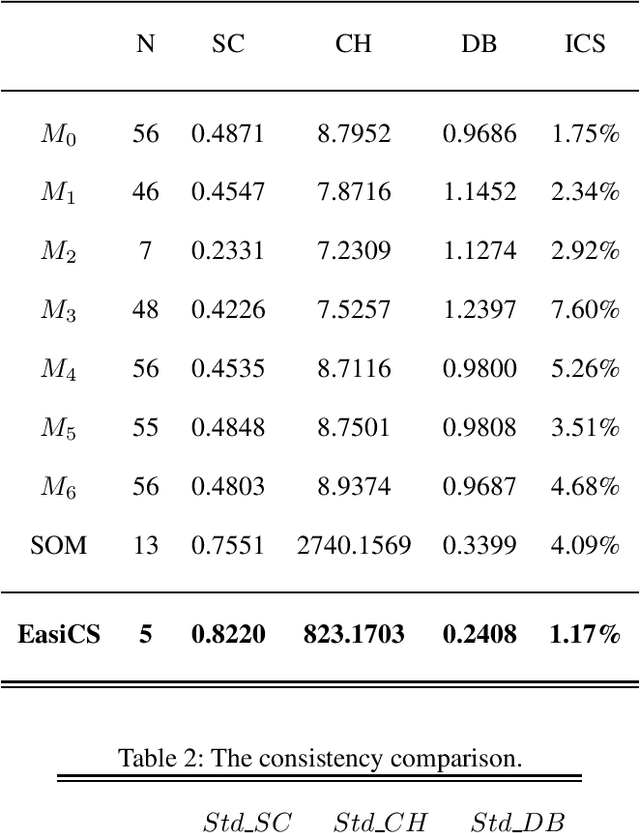
Abstract:The precise diagnosis is of great significance in developing precise treatment plans to restore neck function and reduce the burden posed by the cervical spondylosis (CS). However, the current available neck function assessment method are subjective and coarse-grained. In this paper, based on the relationship among CS, cervical structure, cervical vertebra function, and surface electromyography (sEMG), we seek to develop a clustering algorithms on the sEMG data set collected from the clinical environment and implement the division. We proposed and developed the framework EasiCS, which consists of dimension reduction, clustering algorithm EasiSOM, spectral clustering algorithm EasiSC. The EasiCS outperform the commonly used seven algorithms overall.
A new direction to promote the implementation of artificial intelligence in natural clinical settings
May 08, 2019



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) researchers claim that they have made great `achievements' in clinical realms. However, clinicians point out the so-called `achievements' have no ability to implement into natural clinical settings. The root cause for this huge gap is that many essential features of natural clinical tasks are overlooked by AI system developers without medical background. In this paper, we propose that the clinical benchmark suite is a novel and promising direction to capture the essential features of the real-world clinical tasks, hence qualifies itself for guiding the development of AI systems, promoting the implementation of AI in real-world clinical practice.
EasiCSDeep: A deep learning model for Cervical Spondylosis Identification using surface electromyography signal
Dec 12, 2018
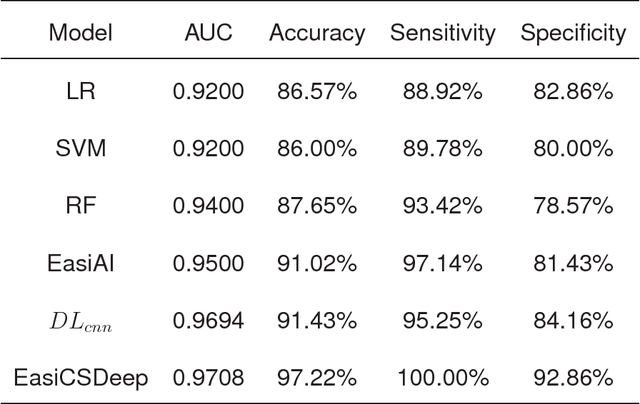
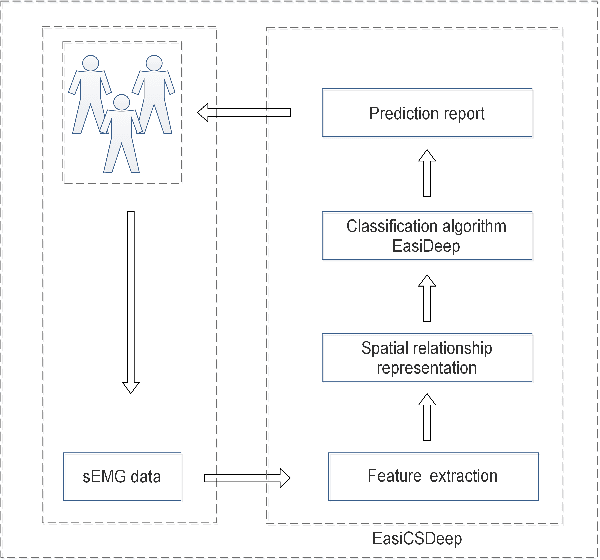
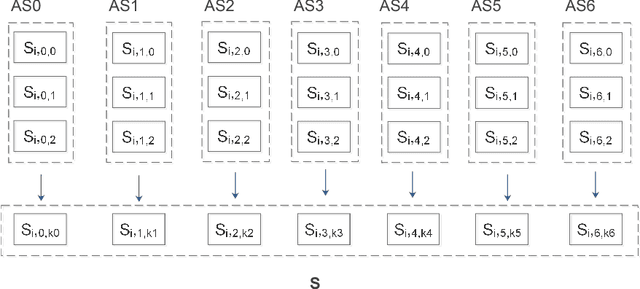
Abstract:Cervical spondylosis (CS) is a common chronic disease that affects up to two-thirds of the population and poses a serious burden on individuals and society. The early identification has significant value in improving cure rate and reducing costs. However, the pathology is complex, and the mild symptoms increase the difficulty of the diagnosis, especially in the early stage. Besides, the time-consuming and costliness of hospital medical service reduces the attention to the CS identification. Thus, a convenient, low-cost intelligent CS identification method is imperious demanded. In this paper, we present an intelligent method based on the deep learning to identify CS, using the surface electromyography (sEMG) signal. Faced with the complex, high dimensionality and weak usability of the sEMG signal, we proposed and developed a multi-channel EasiCSDeep algorithm based on the convolutional neural network, which consists of the feature extraction, spatial relationship representation and classification algorithm. To the best of our knowledge, this EasiCSDeep is the first effort to employ the deep learning and the sEMG data to identify CS. Compared with previous state-of-the-art algorithm, our algorithm achieves a significant improvement.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge