Murad Dawood
A Dynamic Safety Shield for Safe and Efficient Reinforcement Learning of Navigation Tasks
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has been successfully applied to a variety of robotics applications, where it outperforms classical methods. However, the safety aspect of RL and the transfer to the real world remain an open challenge. A prominent field for tackling this challenge and ensuring the safety of the agents during training and execution is safe reinforcement learning. Safe RL can be achieved through constrained RL and safe exploration approaches. The former learns the safety constraints over the course of training to achieve a safe behavior by the end of training, at the cost of high number of collisions at earlier stages of the training. The latter offers robust safety by enforcing the safety constraints as hard constraints, which prevents collisions but hinders the exploration of the RL agent, resulting in lower rewards and poor performance. To overcome those drawbacks, we propose a novel safety shield, that combines the robustness of the optimization-based controllers with the long prediction capabilities of the RL agents, allowing the RL agent to adaptively tune the parameters of the controller. Our approach is able to improve the exploration of the RL agents for navigation tasks, while minimizing the number of collisions. Experiments in simulation show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in the reached goals-to-collisions ratio in different challenging environments. The goals-to-collisions ratio metrics emphasizes the importance of minimizing the number of collisions, while learning to accomplish the task. Our approach achieves a higher number of reached goals compared to the classic safety shields and fewer collisions compared to constrained RL approaches. Finally, we demonstrate the performance of the proposed method in a real-world experiment.
Context-Based Meta Reinforcement Learning for Robust and Adaptable Peg-in-Hole Assembly Tasks
Sep 24, 2024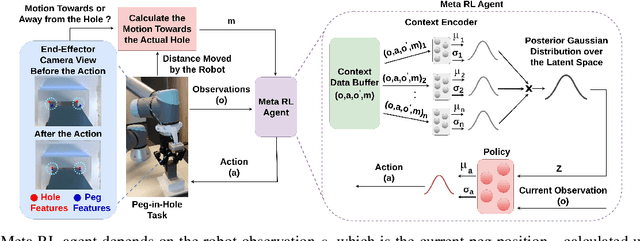
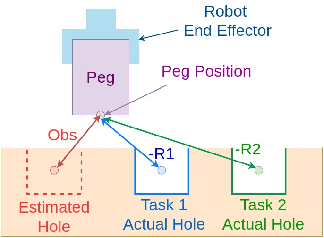
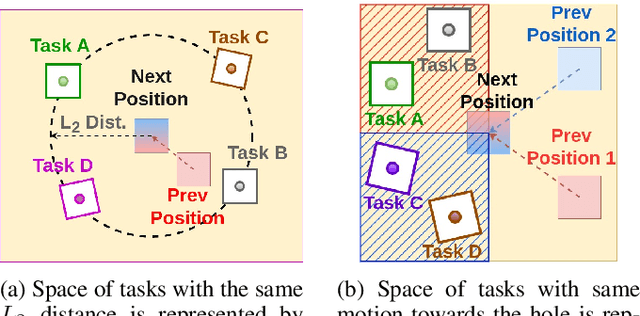
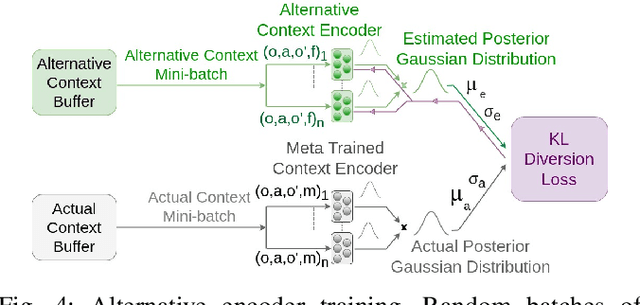
Abstract:Peg-in-hole assembly in unknown environments is a challenging task due to onboard sensor errors, which result in uncertainty and variations in task parameters such as the hole position and orientation. Meta Reinforcement Learning (Meta RL) has been proposed to mitigate this problem as it learns how to quickly adapt to new tasks with different parameters. However, previous approaches either depend on a sample-inefficient procedure or human demonstrations to perform the task in the real world. Our work modifies the data used by the Meta RL agent and uses simple features that can be easily measured in the real world even with an uncalibrated camera. We further adapt the Meta RL agent to use data from a force/torque sensor, instead of the camera, to perform the assembly, using a small amount of training data. Finally, we propose a fine-tuning method that consistently and safely adapts to out-of-distribution tasks with parameters that differ by a factor of 10 from the training tasks. Our results demonstrate that the proposed data modification significantly enhances the training and adaptation efficiency and enables the agent to achieve 100% success in tasks with different hole positions and orientations. Experiments on a real robot confirm that both camera- and force/torque sensor-equipped agents achieve 100% success in tasks with unknown hole positions, matching their simulation performance and validating the approach's robustness and applicability. Compared to the previous work with sample-inefficient adaptation, our proposed methods are 10 times more sample-efficient in the real-world tasks.
Physically-Consistent Parameter Identification of Robots in Contact
Sep 15, 2024



Abstract:Accurate inertial parameter identification is crucial for the simulation and control of robots encountering intermittent contact with the environment. Classically, robots' inertial parameters are obtained from CAD models that are not precise (and sometimes not available, e.g., Spot from Boston Dynamics), hence requiring identification. To do that, existing methods require access to contact force measurement, a modality not present in modern quadruped and humanoid robots. This paper presents an alternative technique that utilizes joint current/torque measurements -- a standard sensing modality in modern robots -- to identify inertial parameters without requiring direct contact force measurements. By projecting the whole-body dynamics into the null space of contact constraints, we eliminate the dependency on contact forces and reformulate the identification problem as a linear matrix inequality that can handle physical and geometrical constraints. We compare our proposed method against a common black-box identification mrethod using a deep neural network and show that incorporating physical consistency significantly improves the sample efficiency and generalizability of the model. Finally, we validate our method on the Spot quadruped robot across various locomotion tasks, showcasing its accuracy and generalizability in real-world scenarios over different gaits.
Centroidal State Estimation based on the Koopman Embedding for Dynamic Legged Locomotion
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to centroidal state estimation, which plays a crucial role in predictive model-based control strategies for dynamic legged locomotion. Our approach uses the Koopman operator theory to transform the robot's complex nonlinear dynamics into a linear system, by employing dynamic mode decomposition and deep learning for model construction. We evaluate both models on their linearization accuracy and capability to capture both fast and slow dynamic system responses. We then select the most suitable model for estimation purposes, and integrate it within a moving horizon estimator. This estimator is formulated as a convex quadratic program, to facilitate robust, real-time centroidal state estimation. Through extensive simulation experiments on a quadruped robot executing various dynamic gaits, our data-driven framework outperforms conventional filtering techniques based on nonlinear dynamics. Our estimator addresses challenges posed by force/torque measurement noise in highly dynamic motions and accurately recovers the centroidal states, demonstrating the adaptability and effectiveness of the Koopman-based linear representation for complex locomotive behaviors. Importantly, our model based on dynamic mode decomposition, trained with two locomotion patterns (trot and jump), successfully estimates the centroidal states for a different motion (bound) without retraining.
Safe Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning for Formation Control without Individual Reference Targets
Dec 20, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, formation control of unmanned vehicles has received considerable interest, driven by the progress in autonomous systems and the imperative for multiple vehicles to carry out diverse missions. In this paper, we address the problem of behavior-based formation control of mobile robots, where we use safe multi-agent reinforcement learning~(MARL) to ensure the safety of the robots by eliminating all collisions during training and execution. To ensure safety, we implemented distributed model predictive control safety filters to override unsafe actions. We focus on achieving behavior-based formation without having individual reference targets for the robots, and instead use targets for the centroid of the formation. This formulation facilitates the deployment of formation control on real robots and improves the scalability of our approach to more robots. The task cannot be addressed through optimization-based controllers without specific individual reference targets for the robots and information about the relative locations of each robot to the others. That is why, for our formulation we use MARL to train the robots. Moreover, in order to account for the interactions between the agents, we use attention-based critics to improve the training process. We train the agents in simulation and later on demonstrate the resulting behavior of our approach on real Turtlebot robots. We show that despite the agents having very limited information, we can still safely achieve the desired behavior.
Viewpoint Push Planning for Mapping of Unknown Confined Spaces
Mar 06, 2023Abstract:Viewpoint planning is an important task in any application where objects or scenes need to be viewed from different angles to achieve sufficient coverage. The mapping of confined spaces such as shelves is an especially challenging task since objects occlude each other and the scene can only be observed from the front, thus with limited possible viewpoints. In this paper, we propose a deep reinforcement learning framework that generates promising views aiming at reducing the map entropy. Additionally, the pipeline extends standard viewpoint planning by predicting adequate minimally invasive push actions to uncover occluded objects and increase the visible space. Using a 2.5D occupancy height map as state representation that can be efficiently updated, our system decides whether to plan a new viewpoint or perform a push. To learn feasible pushes, we use a neural network to sample push candidates on the map and have human experts manually label them to indicate whether the sampled push is a good action to perform. As simulated and real-world experimental results with a robotic arm show, our system is able to significantly increase the mapped space compared to different baselines, while the executed push actions highly benefit the viewpoint planner with only minor changes to the object configuration.
Handling Sparse Rewards in Reinforcement Learning Using Model Predictive Control
Oct 04, 2022
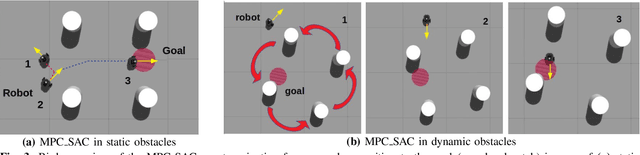

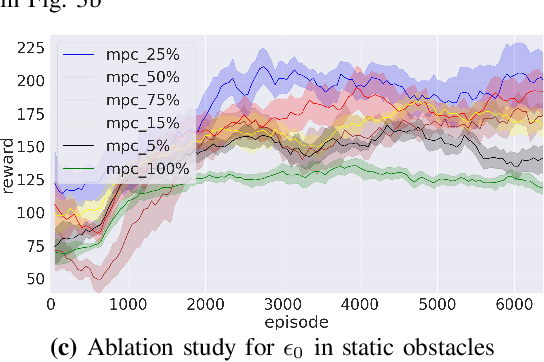
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has recently proven great success in various domains. Yet, the design of the reward function requires detailed domain expertise and tedious fine-tuning to ensure that agents are able to learn the desired behaviour. Using a sparse reward conveniently mitigates these challenges. However, the sparse reward represents a challenge on its own, often resulting in unsuccessful training of the agent. In this paper, we therefore address the sparse reward problem in RL. Our goal is to find an effective alternative to reward shaping, without using costly human demonstrations, that would also be applicable to a wide range of domains. Hence, we propose to use model predictive control~(MPC) as an experience source for training RL agents in sparse reward environments. Without the need for reward shaping, we successfully apply our approach in the field of mobile robot navigation both in simulation and real-world experiments with a Kuboki Turtlebot 2. We furthermore demonstrate great improvement over pure RL algorithms in terms of success rate as well as number of collisions and timeouts. Our experiments show that MPC as an experience source improves the agent's learning process for a given task in the case of sparse rewards.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge