Ahmed Shokry
Clustering by Attention: Leveraging Prior Fitted Transformers for Data Partitioning
Jul 27, 2025Abstract:Clustering is a core task in machine learning with wide-ranging applications in data mining and pattern recognition. However, its unsupervised nature makes it inherently challenging. Many existing clustering algorithms suffer from critical limitations: they often require careful parameter tuning, exhibit high computational complexity, lack interpretability, or yield suboptimal accuracy, especially when applied to large-scale datasets. In this paper, we introduce a novel clustering approach based on meta-learning. Our approach eliminates the need for parameter optimization while achieving accuracy that outperforms state-of-the-art clustering techniques. The proposed technique leverages a few pre-clustered samples to guide the clustering process for the entire dataset in a single forward pass. Specifically, we employ a pre-trained Prior-Data Fitted Transformer Network (PFN) to perform clustering. The algorithm computes attention between the pre-clustered samples and the unclustered samples, allowing it to infer cluster assignments for the entire dataset based on the learned relation. We theoretically and empirically demonstrate that, given just a few pre-clustered examples, the model can generalize to accurately cluster the rest of the dataset. Experiments on challenging benchmark datasets show that our approach can successfully cluster well-separated data without any pre-clustered samples, and significantly improves performance when a few clustered samples are provided. We show that our approach is superior to the state-of-the-art techniques. These results highlight the effectiveness and scalability of our approach, positioning it as a promising alternative to existing clustering techniques.
A Dynamic Safety Shield for Safe and Efficient Reinforcement Learning of Navigation Tasks
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has been successfully applied to a variety of robotics applications, where it outperforms classical methods. However, the safety aspect of RL and the transfer to the real world remain an open challenge. A prominent field for tackling this challenge and ensuring the safety of the agents during training and execution is safe reinforcement learning. Safe RL can be achieved through constrained RL and safe exploration approaches. The former learns the safety constraints over the course of training to achieve a safe behavior by the end of training, at the cost of high number of collisions at earlier stages of the training. The latter offers robust safety by enforcing the safety constraints as hard constraints, which prevents collisions but hinders the exploration of the RL agent, resulting in lower rewards and poor performance. To overcome those drawbacks, we propose a novel safety shield, that combines the robustness of the optimization-based controllers with the long prediction capabilities of the RL agents, allowing the RL agent to adaptively tune the parameters of the controller. Our approach is able to improve the exploration of the RL agents for navigation tasks, while minimizing the number of collisions. Experiments in simulation show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in the reached goals-to-collisions ratio in different challenging environments. The goals-to-collisions ratio metrics emphasizes the importance of minimizing the number of collisions, while learning to accomplish the task. Our approach achieves a higher number of reached goals compared to the classic safety shields and fewer collisions compared to constrained RL approaches. Finally, we demonstrate the performance of the proposed method in a real-world experiment.
Context-Based Meta Reinforcement Learning for Robust and Adaptable Peg-in-Hole Assembly Tasks
Sep 24, 2024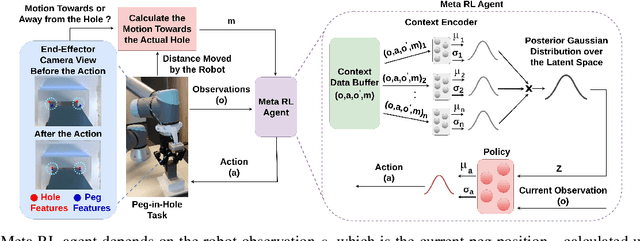
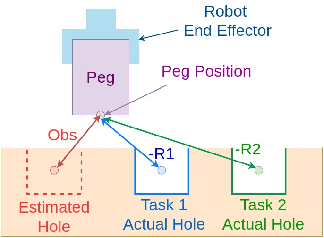
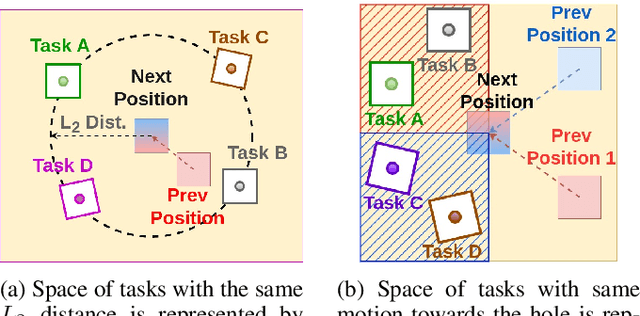
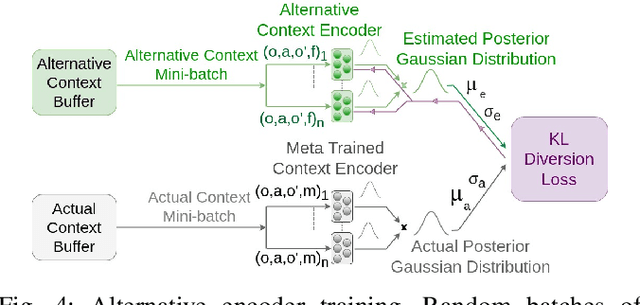
Abstract:Peg-in-hole assembly in unknown environments is a challenging task due to onboard sensor errors, which result in uncertainty and variations in task parameters such as the hole position and orientation. Meta Reinforcement Learning (Meta RL) has been proposed to mitigate this problem as it learns how to quickly adapt to new tasks with different parameters. However, previous approaches either depend on a sample-inefficient procedure or human demonstrations to perform the task in the real world. Our work modifies the data used by the Meta RL agent and uses simple features that can be easily measured in the real world even with an uncalibrated camera. We further adapt the Meta RL agent to use data from a force/torque sensor, instead of the camera, to perform the assembly, using a small amount of training data. Finally, we propose a fine-tuning method that consistently and safely adapts to out-of-distribution tasks with parameters that differ by a factor of 10 from the training tasks. Our results demonstrate that the proposed data modification significantly enhances the training and adaptation efficiency and enables the agent to achieve 100% success in tasks with different hole positions and orientations. Experiments on a real robot confirm that both camera- and force/torque sensor-equipped agents achieve 100% success in tasks with unknown hole positions, matching their simulation performance and validating the approach's robustness and applicability. Compared to the previous work with sample-inefficient adaptation, our proposed methods are 10 times more sample-efficient in the real-world tasks.
Handling Device Heterogeneity for Deep Learning-based Localization
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:Deep learning-based fingerprinting is one of the current promising technologies for outdoor localization in cellular networks. However, deploying such localization systems for heterogeneous phones affects their accuracy as the cellular received signal strength (RSS) readings vary for different types of phones. In this paper, we introduce a number of techniques for addressing the phones heterogeneity problem in the deep-learning based localization systems. The basic idea is either to approximate a function that maps the cellular RSS measurements between different devices or to transfer the knowledge across them. Evaluation of the proposed techniques using different Android phones on four independent testbeds shows that our techniques can improve the localization accuracy by more than 220% for the four testbeds as compared to the state-of-the-art systems. This highlights the promise of the proposed device heterogeneity handling techniques for enabling a wide deployment of deep learning-based localization systems over different devices.
DeepCell: A Ubiquitous Accurate Provider-side Cellular-based Localization
Jul 24, 2024Abstract:Although outdoor localization is already available to the general public and businesses through the wide spread use of the GPS, it is not supported by low-end phones, requires a direct line of sight to satellites and can drain phone battery quickly. The current fingerprinting solutions can provide high-accuracy localization but are based on the client side. This limits their ubiquitous deployment and accuracy. In this paper, we introduce DeepCell: a provider-side fingerprinting localization system that can provide high accuracy localization for any cell phone. To build its fingerprint, DeepCell leverages the unlabeled cellular measurements recorded by the cellular provider while opportunistically synchronizing with selected client devices to get location labels. The fingerprint is then used to train a deep neural network model that is harnessed for localization. To achieve this goal, DeepCell need to address a number of challenges including using unlabeled data from the provider side, handling noise and sparsity, scaling the data to large areas, and finally providing enough data that is required for training deep models without overhead. Evaluation of DeepCell in a typical realistic environment shows that it can achieve a consistent median accuracy of 29m. This accuracy outperforms the state-of-the-art client-based cellular-based systems by more than 75.4%. In addition, the same accuracy is extended to low-end phones.
A Novel Framework for Brain Tumor Detection Based on Convolutional Variational Generative Models
Feb 20, 2022



Abstract:Brain tumor detection can make the difference between life and death. Recently, deep learning-based brain tumor detection techniques have gained attention due to their higher performance. However, obtaining the expected performance of such deep learning-based systems requires large amounts of classified images to train the deep models. Obtaining such data is usually boring, time-consuming, and can easily be exposed to human mistakes which hinder the utilization of such deep learning approaches. This paper introduces a novel framework for brain tumor detection and classification. The basic idea is to generate a large synthetic MRI images dataset that reflects the typical pattern of the brain MRI images from a small class-unbalanced collected dataset. The resulted dataset is then used for training a deep model for detection and classification. Specifically, we employ two types of deep models. The first model is a generative model to capture the distribution of the important features in a set of small class-unbalanced brain MRI images. Then by using this distribution, the generative model can synthesize any number of brain MRI images for each class. Hence, the system can automatically convert a small unbalanced dataset to a larger balanced one. The second model is the classifier that is trained using the large balanced dataset to detect brain tumors in MRI images. The proposed framework acquires an overall detection accuracy of 96.88% which highlights the promise of the proposed framework as an accurate low-overhead brain tumor detection system.
Autofocusing Optimal Search Algorithm for a Telescope System
Jul 09, 2021



Abstract:Focus accuracy affects the quality of the astronomical observations. Auto-focusing is necessary for imaging systems designed for astronomical observations. The automatic focus system searches for the best focus position by using a proposed search algorithm. The search algorithm uses the image's focus levels as its objective function in the search process. This paper aims to study the performance of several search algorithms to select a suitable one. The proper search algorithm will be used to develop an automatic focus system for Kottamia Astronomical Observatory (KAO). The optimal search algorithm is selected by applying several search algorithms into five sequences of star-clusters observations. Then, their performance is evaluated based on two criteria, which are accuracy and number of steps. The experimental results show that the Binary search is the optimal search algorithm.
DeepLoc: A Ubiquitous Accurate and Low-Overhead Outdoor Cellular Localization System
Jun 25, 2021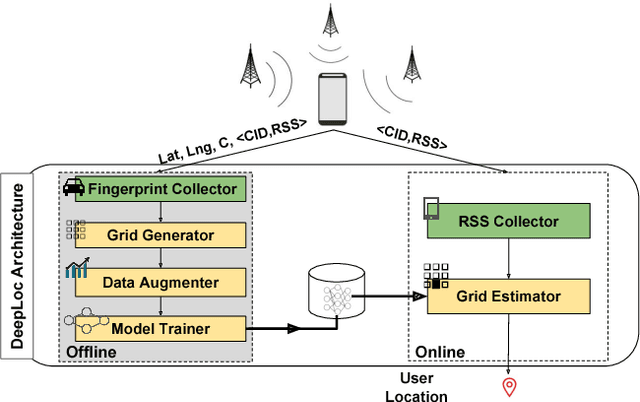
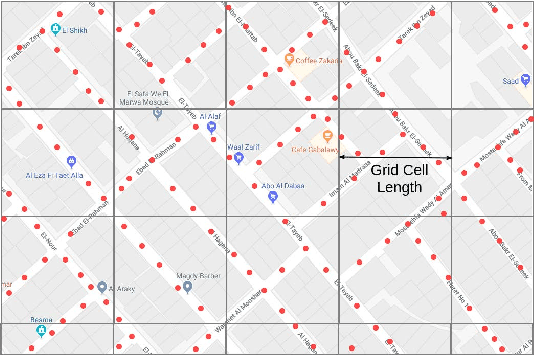
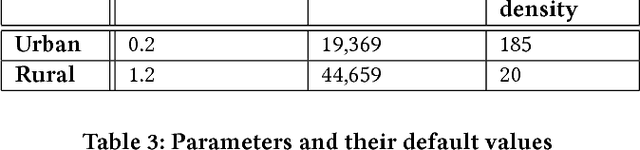
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed fast growth in outdoor location-based services. While GPS is considered a ubiquitous localization system, it is not supported by low-end phones, requires direct line of sight to the satellites, and can drain the phone battery quickly. In this paper, we propose DeepLoc: a deep learning-based outdoor localization system that obtains GPS-like localization accuracy without its limitations. In particular, DeepLoc leverages the ubiquitous cellular signals received from the different cell towers heard by the mobile device as hints to localize it. To do that, crowd-sensed geo-tagged received signal strength information coming from different cell towers is used to train a deep model that is used to infer the user's position. As part of DeepLoc design, we introduce modules to address a number of practical challenges including scaling the data collection to large areas, handling the inherent noise in the cellular signal and geo-tagged data, as well as providing enough data that is required for deep learning models with low-overhead. We implemented DeepLoc on different Android devices. Evaluation results in realistic urban and rural environments show that DeepLoc can achieve a median localization accuracy within 18.8m in urban areas and within 15.7m in rural areas. This accuracy outperforms the state-of-the-art cellular-based systems by more than 470% and comes with 330% savings in power compared to the GPS. This highlights the promise of DeepLoc as a ubiquitous accurate and low-overhead localization system.
The Effect of Ground Truth Accuracy on the Evaluation of Localization Systems
Jun 25, 2021



Abstract:The ability to accurately evaluate the performance of location determination systems is crucial for many applications. Typically, the performance of such systems is obtained by comparing ground truth locations with estimated locations. However, these ground truth locations are usually obtained by clicking on a map or using other worldwide available technologies like GPS. This introduces ground truth errors that are due to the marking process, map distortions, or inherent GPS inaccuracy. In this paper, we present a theoretical framework for analyzing the effect of ground truth errors on the evaluation of localization systems. Based on that, we design two algorithms for computing the real algorithmic error from the validation error and marking/map ground truth errors, respectively. We further establish bounds on different performance metrics. Validation of our theoretical assumptions and analysis using real data collected in a typical environment shows the ability of our theoretical framework to correct the estimated error of a localization algorithm in the presence of ground truth errors. Specifically, our marking error algorithm matches the real error CDF within 4%, and our map error algorithm provides a more accurate estimate of the median/tail error by 150%/72% when the map is shifted by 6m.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge