Marwan Torki
Speak the Art: A Direct Speech to Image Generation Framework
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Direct speech-to-image generation has recently shown promising results. However, compared to text-to-image generation, there is still a large gap to enclose. Current approaches use two stages to tackle this task: speech encoding network and image generative adversarial network (GAN). The speech encoding networks in these approaches produce embeddings that do not capture sufficient linguistic information to semantically represent the input speech. GANs suffer from issues such as non-convergence, mode collapse, and diminished gradient, which result in unstable model parameters, limited sample diversity, and ineffective generator learning, respectively. To address these weaknesses, we introduce a framework called \textbf{Speak the Art (STA)} which consists of a speech encoding network and a VQ-Diffusion network conditioned on speech embeddings. To improve speech embeddings, the speech encoding network is supervised by a large pre-trained image-text model during training. Replacing GANs with diffusion leads to more stable training and the generation of diverse images. Additionally, we investigate the feasibility of extending our framework to be multilingual. As a proof of concept, we trained our framework with two languages: English and Arabic. Finally, we show that our results surpass state-of-the-art models by a large margin.
Utilizing Multi-step Loss for Single Image Reflection Removal
Dec 11, 2024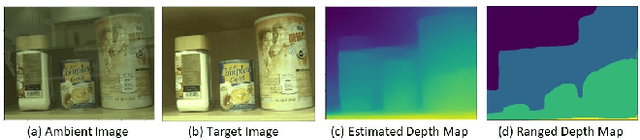
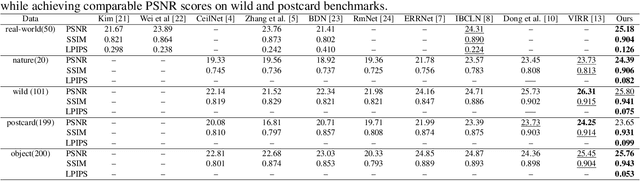
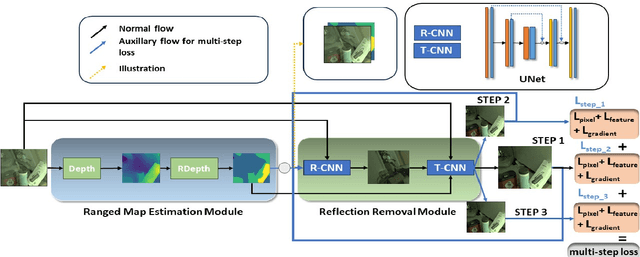

Abstract:Image reflection removal is crucial for restoring image quality. Distorted images can negatively impact tasks like object detection and image segmentation. In this paper, we present a novel approach for image reflection removal using a single image. Instead of focusing on model architecture, we introduce a new training technique that can be generalized to image-to-image problems, with input and output being similar in nature. This technique is embodied in our multi-step loss mechanism, which has proven effective in the reflection removal task. Additionally, we address the scarcity of reflection removal training data by synthesizing a high-quality, non-linear synthetic dataset called RefGAN using Pix2Pix GAN. This dataset significantly enhances the model's ability to learn better patterns for reflection removal. We also utilize a ranged depth map, extracted from the depth estimation of the ambient image, as an auxiliary feature, leveraging its property of lacking depth estimations for reflections. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on the SIR^2 benchmark and other real-world datasets, proving its effectiveness by outperforming other state-of-the-art models.
DiffuPT: Class Imbalance Mitigation for Glaucoma Detection via Diffusion Based Generation and Model Pretraining
Dec 04, 2024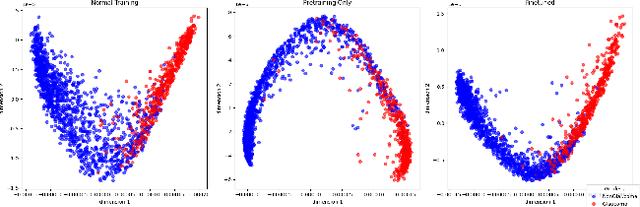
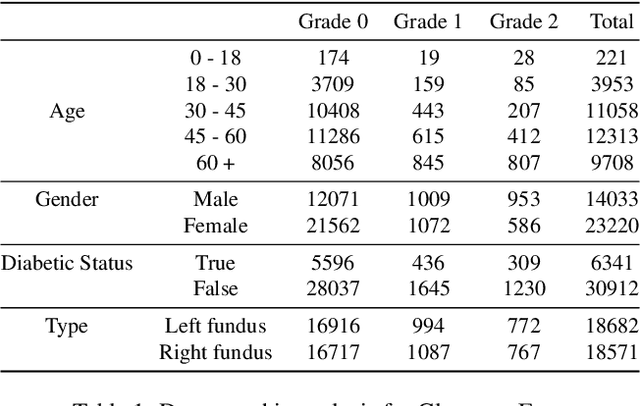

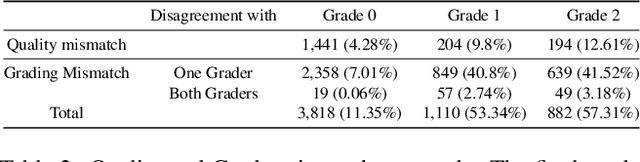
Abstract:Glaucoma is a progressive optic neuropathy characterized by structural damage to the optic nerve head and functional changes in the visual field. Detecting glaucoma early is crucial to preventing loss of eyesight. However, medical datasets often suffer from class imbalances, making detection more difficult for deep-learning algorithms. We use a generative-based framework to enhance glaucoma diagnosis, specifically addressing class imbalance through synthetic data generation. In addition, we collected the largest national dataset for glaucoma detection to support our study. The imbalance between normal and glaucomatous cases leads to performance degradation of classifier models. By combining our proposed framework leveraging diffusion models with a pretraining approach, we created a more robust classifier training process. This training process results in a better-performing classifier. The proposed approach shows promising results in improving the harmonic mean (sensitivity and specificity) and AUC for the roc for the glaucoma classifier. We report an improvement in the harmonic mean metric from 89.09% to 92.59% on the test set of our national dataset. We examine our method against other methods to overcome imbalance through extensive experiments. We report similar improvements on the AIROGS dataset. This study highlights that diffusion-based generation can be of great importance in tackling class imbalances in medical datasets to improve diagnostic performance.
C2F-CHART: A Curriculum Learning Approach to Chart Classification
Sep 07, 2024Abstract:In scientific research, charts are usually the primary method for visually representing data. However, the accessibility of charts remains a significant concern. In an effort to improve chart understanding pipelines, we focus on optimizing the chart classification component. We leverage curriculum learning, which is inspired by the human learning process. In this paper, we introduce a novel training approach for chart classification that utilizes coarse-to-fine curriculum learning. Our approach, which we name C2F-CHART (for coarse-to-fine) exploits inter-class similarities to create learning tasks of varying difficulty levels. We benchmark our method on the ICPR 2022 CHART-Infographics UB UNITEC PMC dataset, outperforming the state-of-the-art results.
Temporal Divide-and-Conquer Anomaly Actions Localization in Semi-Supervised Videos with Hierarchical Transformer
Aug 24, 2024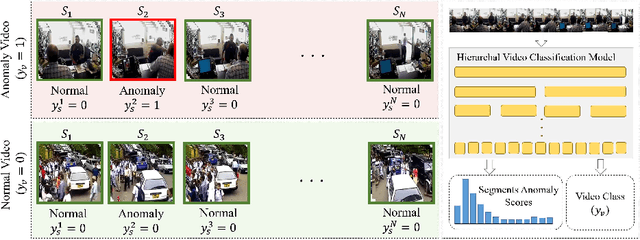
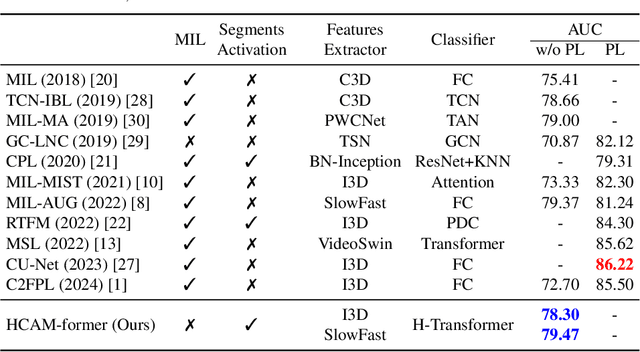
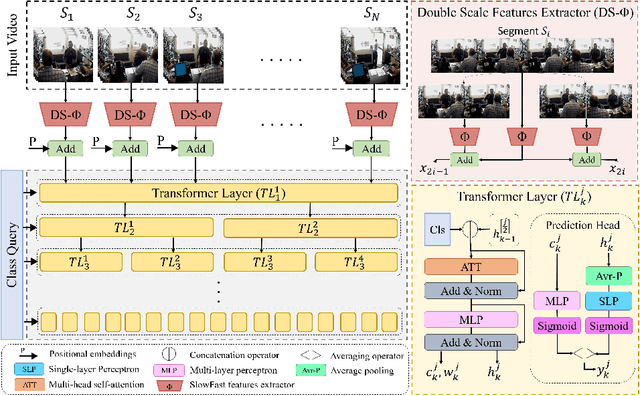
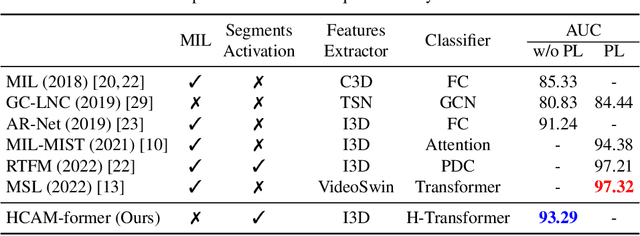
Abstract:Anomaly action detection and localization play an essential role in security and advanced surveillance systems. However, due to the tremendous amount of surveillance videos, most of the available data for the task is unlabeled or semi-labeled with the video class known, but the location of the anomaly event is unknown. In this work, we target anomaly localization in semi-supervised videos. While the mainstream direction in addressing this task is focused on segment-level multi-instance learning and the generation of pseudo labels, we aim to explore a promising yet unfulfilled direction to solve the problem by learning the temporal relations within videos in order to locate anomaly events. To this end, we propose a hierarchical transformer model designed to evaluate the significance of observed actions in anomalous videos with a divide-and-conquer strategy along the temporal axis. Our approach segments a parent video hierarchically into multiple temporal children instances and measures the influence of the children nodes in classifying the abnormality of the parent video. Evaluating our model on two well-known anomaly detection datasets, UCF-crime and ShanghaiTech, proves its ability to interpret the observed actions within videos and localize the anomalous ones. Our proposed approach outperforms previous works relying on segment-level multiple-instance learning approaches while reaching a promising performance compared to the more recent pseudo-labeling-based approaches.
Toward Flare-Free Images: A Survey
Oct 22, 2023



Abstract:Lens flare is a common image artifact that can significantly degrade image quality and affect the performance of computer vision systems due to a strong light source pointing at the camera. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the multifaceted domain of lens flare, encompassing its underlying physics, influencing factors, types, and characteristics. It delves into the complex optics of flare formation, arising from factors like internal reflection, scattering, diffraction, and dispersion within the camera lens system. The diverse categories of flare are explored, including scattering, reflective, glare, orb, and starburst types. Key properties such as shape, color, and localization are analyzed. The numerous factors impacting flare appearance are discussed, spanning light source attributes, lens features, camera settings, and scene content. The survey extensively covers the wide range of methods proposed for flare removal, including hardware optimization strategies, classical image processing techniques, and learning-based methods using deep learning. It not only describes pioneering flare datasets created for training and evaluation purposes but also how they were created. Commonly employed performance metrics such as PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS are explored. Challenges posed by flare's complex and data-dependent characteristics are highlighted. The survey provides insights into best practices, limitations, and promising future directions for flare removal research. Reviewing the state-of-the-art enables an in-depth understanding of the inherent complexities of the flare phenomenon and the capabilities of existing solutions. This can inform and inspire new innovations for handling lens flare artifacts and improving visual quality across various applications.
AlexU-AIC at Arabic Hate Speech 2022: Contrast to Classify
Jul 18, 2022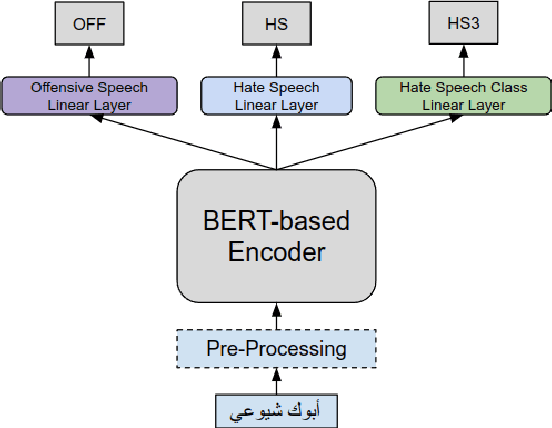
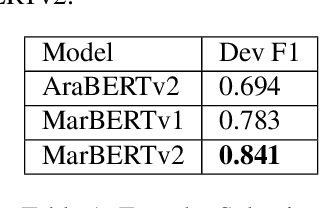
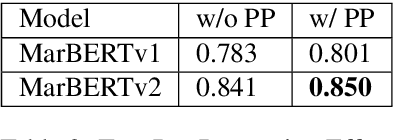
Abstract:Online presence on social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter has become a daily habit for internet users. Despite the vast amount of services the platforms offer for their users, users suffer from cyber-bullying, which further leads to mental abuse and may escalate to cause physical harm to individuals or targeted groups. In this paper, we present our submission to the Arabic Hate Speech 2022 Shared Task Workshop (OSACT5 2022) using the associated Arabic Twitter dataset. The shared task consists of 3 sub-tasks, sub-task A focuses on detecting whether the tweet is offensive or not. Then, For offensive Tweets, sub-task B focuses on detecting whether the tweet is hate speech or not. Finally, For hate speech Tweets, sub-task C focuses on detecting the fine-grained type of hate speech among six different classes. Transformer models proved their efficiency in classification tasks, but with the problem of over-fitting when fine-tuned on a small or an imbalanced dataset. We overcome this limitation by investigating multiple training paradigms such as Contrastive learning and Multi-task learning along with Classification fine-tuning and an ensemble of our top 5 performers. Our proposed solution achieved 0.841, 0.817, and 0.476 macro F1-average in sub-tasks A, B, and C respectively.
DeepLoc: A Ubiquitous Accurate and Low-Overhead Outdoor Cellular Localization System
Jun 25, 2021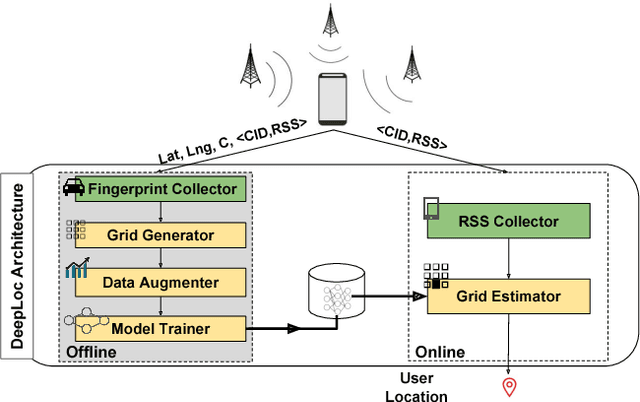
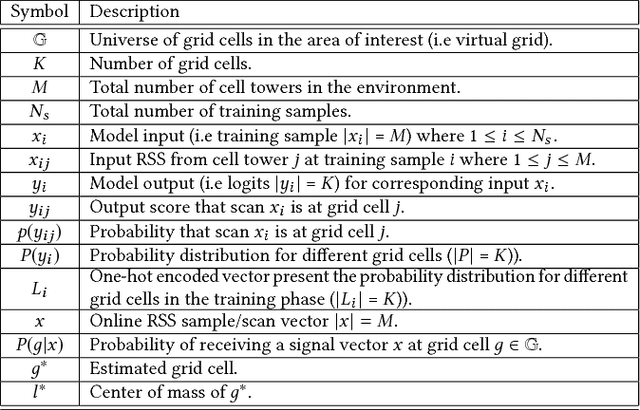
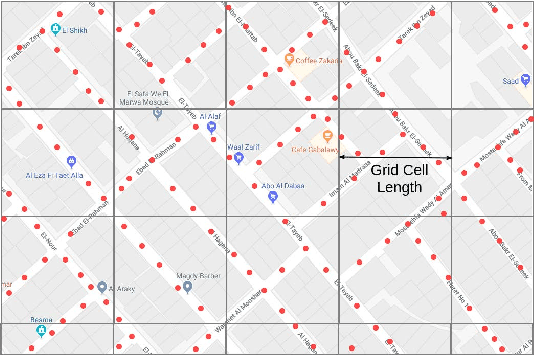
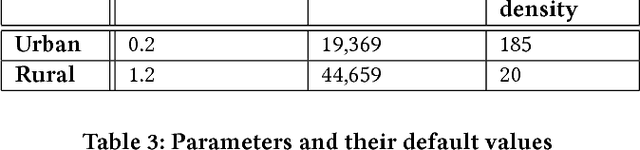
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed fast growth in outdoor location-based services. While GPS is considered a ubiquitous localization system, it is not supported by low-end phones, requires direct line of sight to the satellites, and can drain the phone battery quickly. In this paper, we propose DeepLoc: a deep learning-based outdoor localization system that obtains GPS-like localization accuracy without its limitations. In particular, DeepLoc leverages the ubiquitous cellular signals received from the different cell towers heard by the mobile device as hints to localize it. To do that, crowd-sensed geo-tagged received signal strength information coming from different cell towers is used to train a deep model that is used to infer the user's position. As part of DeepLoc design, we introduce modules to address a number of practical challenges including scaling the data collection to large areas, handling the inherent noise in the cellular signal and geo-tagged data, as well as providing enough data that is required for deep learning models with low-overhead. We implemented DeepLoc on different Android devices. Evaluation results in realistic urban and rural environments show that DeepLoc can achieve a median localization accuracy within 18.8m in urban areas and within 15.7m in rural areas. This accuracy outperforms the state-of-the-art cellular-based systems by more than 470% and comes with 330% savings in power compared to the GPS. This highlights the promise of DeepLoc as a ubiquitous accurate and low-overhead localization system.
Seeded Laplaican: An Eigenfunction Solution for Scribble Based Interactive Image Segmentation
Aug 27, 2017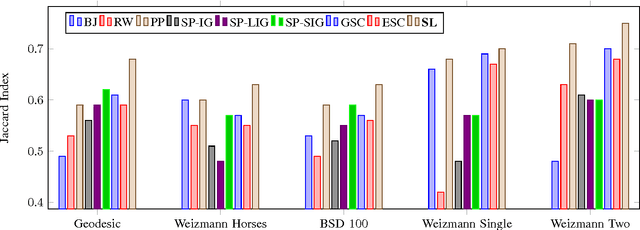
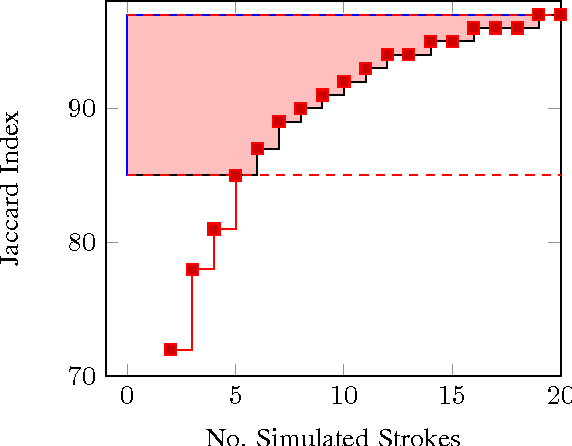
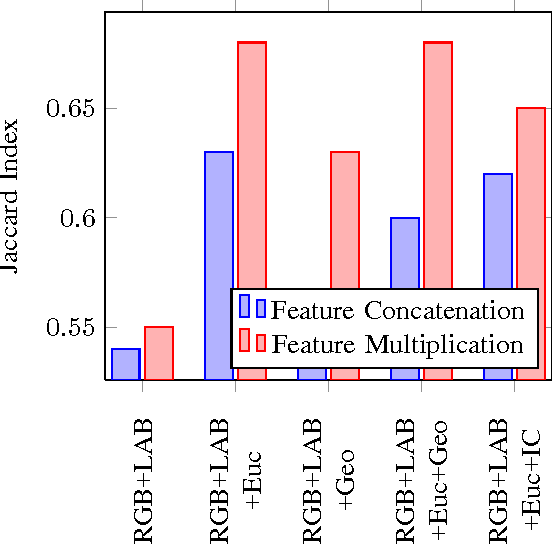
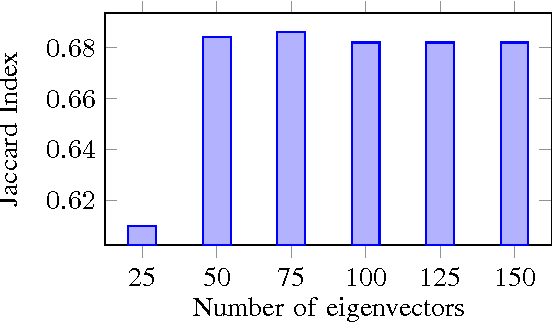
Abstract:In this paper, we cast the scribble-based interactive image segmentation as a semi-supervised learning problem. Our novel approach alleviates the need to solve an expensive generalized eigenvector problem by approximating the eigenvectors using efficiently computed eigenfunctions. The smoothness operator defined on feature densities at the limit n tends to infinity recovers the exact eigenvectors of the graph Laplacian, where n is the number of nodes in the graph. To further reduce the computational complexity without scarifying our accuracy, we select pivots pixels from user annotations. In our experiments, we evaluate our approach using both human scribble and "robot user" annotations to guide the foreground/background segmentation. We developed a new unbiased collection of five annotated images datasets to standardize the evaluation procedure for any scribble-based segmentation method. We experimented with several variations, including different feature vectors, pivot count and the number of eigenvectors. Experiments are carried out on datasets that contain a wide variety of natural images. We achieve better qualitative and quantitative results compared to state-of-the-art interactive segmentation algorithms.
Linear-time Online Action Detection From 3D Skeletal Data Using Bags of Gesturelets
Dec 28, 2015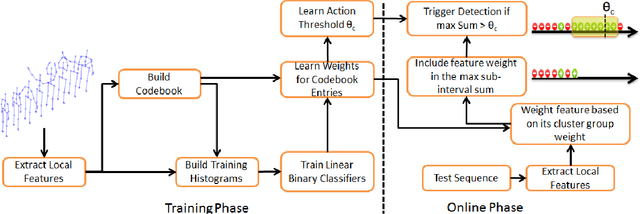
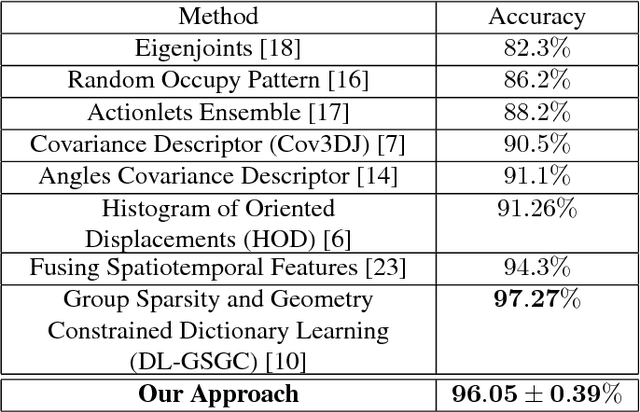
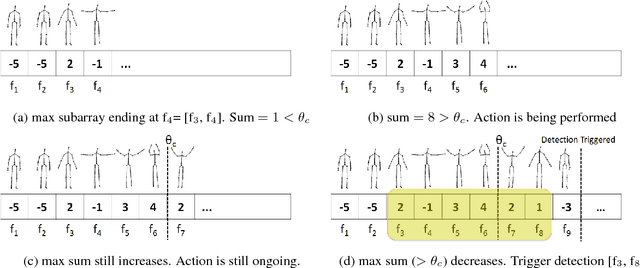

Abstract:Sliding window is one direct way to extend a successful recognition system to handle the more challenging detection problem. While action recognition decides only whether or not an action is present in a pre-segmented video sequence, action detection identifies the time interval where the action occurred in an unsegmented video stream. Sliding window approaches for action detection can however be slow as they maximize a classifier score over all possible sub-intervals. Even though new schemes utilize dynamic programming to speed up the search for the optimal sub-interval, they require offline processing on the whole video sequence. In this paper, we propose a novel approach for online action detection based on 3D skeleton sequences extracted from depth data. It identifies the sub-interval with the maximum classifier score in linear time. Furthermore, it is invariant to temporal scale variations and is suitable for real-time applications with low latency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge