Ahmad Shapiro
HALT: Hallucination Assessment via Log-probs as Time series
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Hallucinations remain a major obstacle for large language models (LLMs), especially in safety-critical domains. We present HALT (Hallucination Assessment via Log-probs as Time series), a lightweight hallucination detector that leverages only the top-20 token log-probabilities from LLM generations as a time series. HALT uses a gated recurrent unit model combined with entropy-based features to learn model calibration bias, providing an extremely efficient alternative to large encoders. Unlike white-box approaches, HALT does not require access to hidden states or attention maps, relying only on output log-probabilities. Unlike black-box approaches, it operates on log-probs rather than surface-form text, which enables stronger domain generalization and compatibility with proprietary LLMs without requiring access to internal weights. To benchmark performance, we introduce HUB (Hallucination detection Unified Benchmark), which consolidates prior datasets into ten capabilities covering both reasoning tasks (Algorithmic, Commonsense, Mathematical, Symbolic, Code Generation) and general purpose skills (Chat, Data-to-Text, Question Answering, Summarization, World Knowledge). While being 30x smaller, HALT outperforms Lettuce, a fine-tuned modernBERT-base encoder, achieving a 60x speedup gain on HUB. HALT and HUB together establish an effective framework for hallucination detection across diverse LLM capabilities.
AlexU-AIC at Arabic Hate Speech 2022: Contrast to Classify
Jul 18, 2022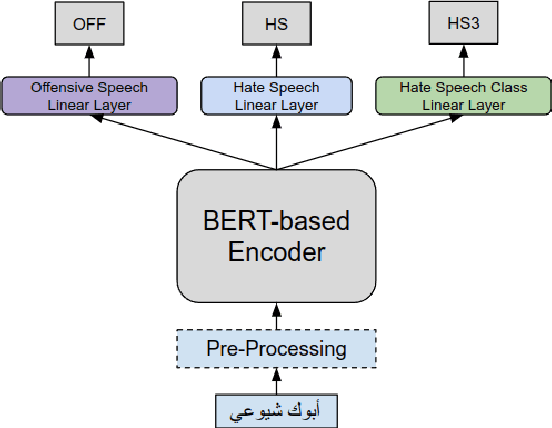
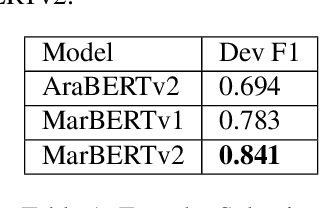
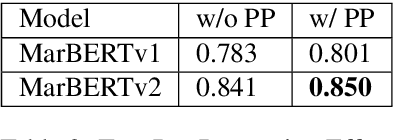
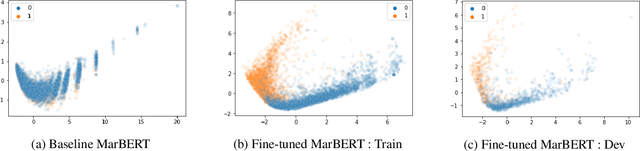
Abstract:Online presence on social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter has become a daily habit for internet users. Despite the vast amount of services the platforms offer for their users, users suffer from cyber-bullying, which further leads to mental abuse and may escalate to cause physical harm to individuals or targeted groups. In this paper, we present our submission to the Arabic Hate Speech 2022 Shared Task Workshop (OSACT5 2022) using the associated Arabic Twitter dataset. The shared task consists of 3 sub-tasks, sub-task A focuses on detecting whether the tweet is offensive or not. Then, For offensive Tweets, sub-task B focuses on detecting whether the tweet is hate speech or not. Finally, For hate speech Tweets, sub-task C focuses on detecting the fine-grained type of hate speech among six different classes. Transformer models proved their efficiency in classification tasks, but with the problem of over-fitting when fine-tuned on a small or an imbalanced dataset. We overcome this limitation by investigating multiple training paradigms such as Contrastive learning and Multi-task learning along with Classification fine-tuning and an ensemble of our top 5 performers. Our proposed solution achieved 0.841, 0.817, and 0.476 macro F1-average in sub-tasks A, B, and C respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge