Muhammad Uzair Zahid
CoRe-Net: Co-Operational Regressor Network with Progressive Transfer Learning for Blind Radar Signal Restoration
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Real-world radar signals are frequently corrupted by various artifacts, including sensor noise, echoes, interference, and intentional jamming, differing in type, severity, and duration. This pilot study introduces a novel model, called Co-Operational Regressor Network (CoRe-Net) for blind radar signal restoration, designed to address such limitations and drawbacks. CoRe-Net replaces adversarial training with a novel cooperative learning strategy, leveraging the complementary roles of its Apprentice Regressor (AR) and Master Regressor (MR). The AR restores radar signals corrupted by various artifacts, while the MR evaluates the quality of the restoration and provides immediate and task-specific feedback, ensuring stable and efficient learning. The AR, therefore, has the advantage of both self-learning and assistive learning by the MR. The proposed model has been extensively evaluated over the benchmark Blind Radar Signal Restoration (BRSR) dataset, which simulates diverse real-world artifact scenarios. Under the fair experimental setup, this study shows that the CoRe-Net surpasses the Op-GANs over a 1 dB mean SNR improvement. To further boost the performance gain, this study proposes multi-pass restoration by cascaded CoRe-Nets trained with a novel paradigm called Progressive Transfer Learning (PTL), which enables iterative refinement, thus achieving an additional 2 dB mean SNR enhancement. Multi-pass CoRe-Net training by PTL consistently yields incremental performance improvements through successive restoration passes whilst highlighting CoRe-Net ability to handle such a complex and varying blend of artifacts.
BRSR-OpGAN: Blind Radar Signal Restoration using Operational Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 18, 2024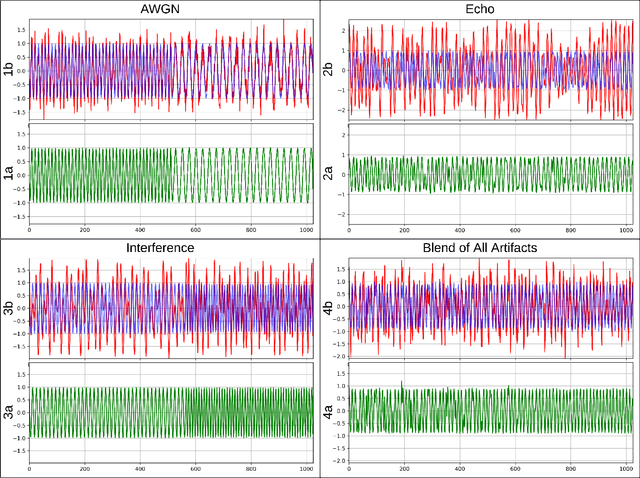
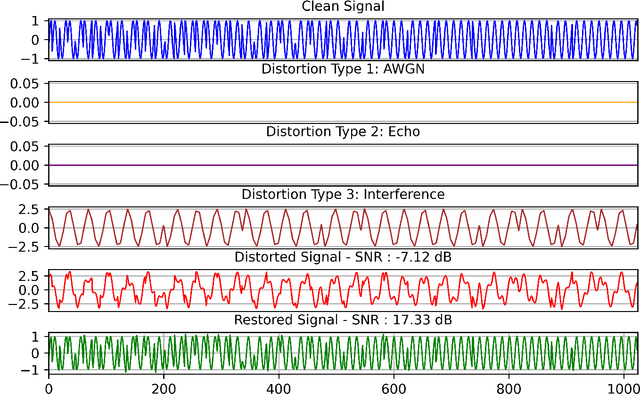
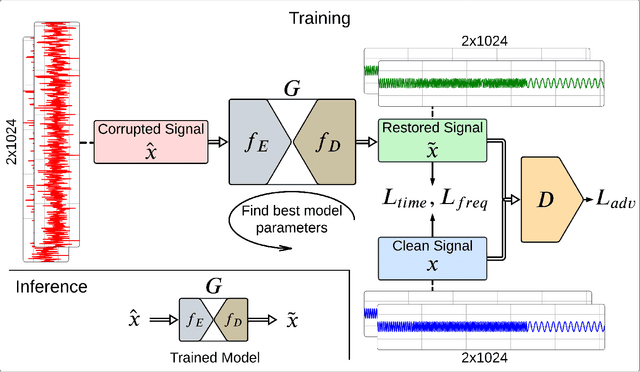
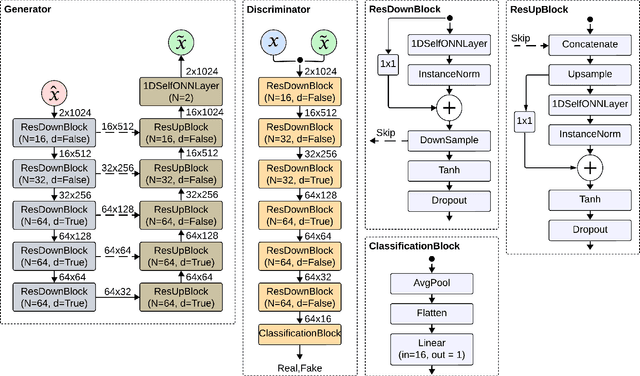
Abstract:Objective: Many studies on radar signal restoration in the literature focus on isolated restoration problems, such as denoising over a certain type of noise, while ignoring other types of artifacts. Additionally, these approaches usually assume a noisy environment with a limited set of fixed signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels. However, real-world radar signals are often corrupted by a blend of artifacts, including but not limited to unwanted echo, sensor noise, intentional jamming, and interference, each of which can vary in type, severity, and duration. This study introduces Blind Radar Signal Restoration using an Operational Generative Adversarial Network (BRSR-OpGAN), which uses a dual domain loss in the temporal and spectral domains. This approach is designed to improve the quality of radar signals, regardless of the diversity and intensity of the corruption. Methods: The BRSR-OpGAN utilizes 1D Operational GANs, which use a generative neuron model specifically optimized for blind restoration of corrupted radar signals. This approach leverages GANs' flexibility to adapt dynamically to a wide range of artifact characteristics. Results: The proposed approach has been extensively evaluated using a well-established baseline and a newly curated extended dataset called the Blind Radar Signal Restoration (BRSR) dataset. This dataset was designed to simulate real-world conditions and includes a variety of artifacts, each varying in severity. The evaluation shows an average SNR improvement over 15.1 dB and 14.3 dB for the baseline and BRSR datasets, respectively. Finally, even on resource-constrained platforms, the proposed approach can be applied in real-time.
Refining Myocardial Infarction Detection: A Novel Multi-Modal Composite Kernel Strategy in One-Class Classification
Feb 09, 2024


Abstract:Early detection of myocardial infarction (MI), a critical condition arising from coronary artery disease (CAD), is vital to prevent further myocardial damage. This study introduces a novel method for early MI detection using a one-class classification (OCC) algorithm in echocardiography. Our study overcomes the challenge of limited echocardiography data availability by adopting a novel approach based on Multi-modal Subspace Support Vector Data Description. The proposed technique involves a specialized MI detection framework employing multi-view echocardiography incorporating a composite kernel in the non-linear projection trick, fusing Gaussian and Laplacian sigmoid functions. Additionally, we enhance the update strategy of the projection matrices by adapting maximization for both or one of the modalities in the optimization process. Our method boosts MI detection capability by efficiently transforming features extracted from echocardiography data into an optimized lower-dimensional subspace. The OCC model trained specifically on target class instances from the comprehensive HMC-QU dataset that includes multiple echocardiography views indicates a marked improvement in MI detection accuracy. Our findings reveal that our proposed multi-view approach achieves a geometric mean of 71.24\%, signifying a substantial advancement in echocardiography-based MI diagnosis and offering more precise and efficient diagnostic tools.
Global ECG Classification by Self-Operational Neural Networks with Feature Injection
Apr 07, 2022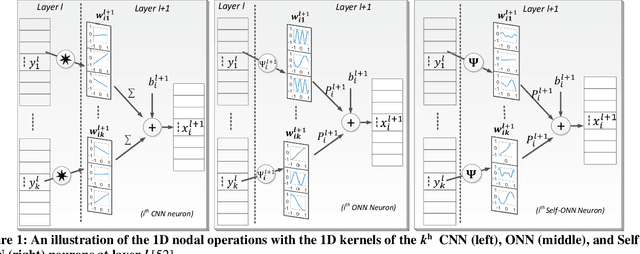
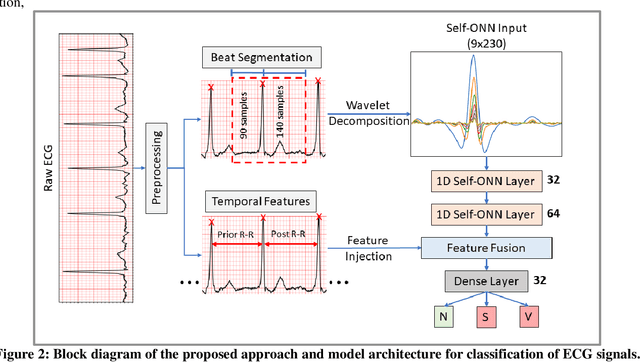
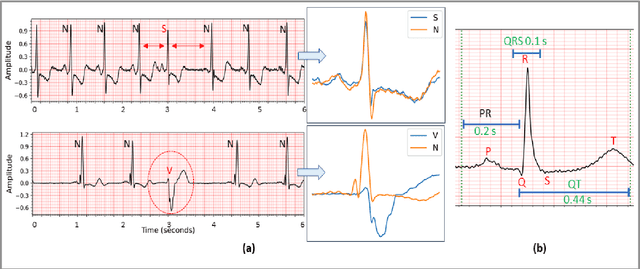
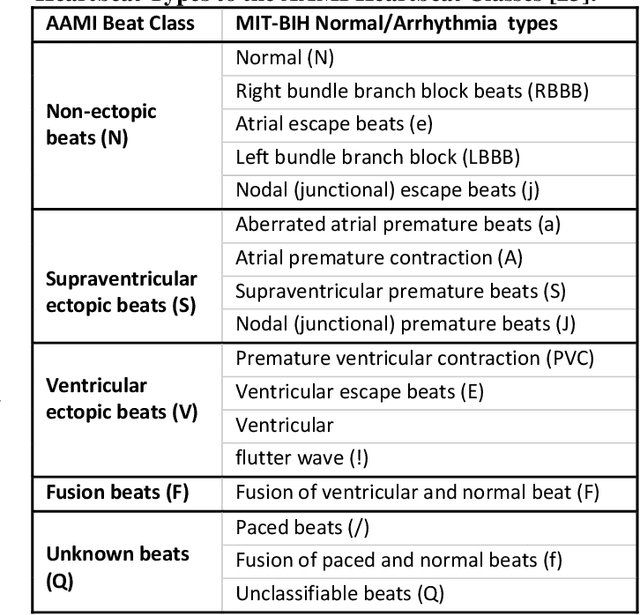
Abstract:Objective: Global (inter-patient) ECG classification for arrhythmia detection over Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is a challenging task for both humans and machines. The main reason is the significant variations of both normal and arrhythmic ECG patterns among patients. Automating this process with utmost accuracy is, therefore, highly desirable due to the advent of wearable ECG sensors. However, even with numerous deep learning approaches proposed recently, there is still a notable gap in the performance of global and patient-specific ECG classification performances. This study proposes a novel approach to narrow this gap and propose a real-time solution with shallow and compact 1D Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks (Self-ONNs). Methods: In this study, we propose a novel approach for inter-patient ECG classification using a compact 1D Self-ONN by exploiting morphological and timing information in heart cycles. We used 1D Self-ONN layers to automatically learn morphological representations from ECG data, enabling us to capture the shape of the ECG waveform around the R peaks. We further inject temporal features based on RR interval for timing characterization. The classification layers can thus benefit from both temporal and learned features for the final arrhythmia classification. Results: Using the MIT-BIH arrhythmia benchmark database, the proposed method achieves the highest classification performance ever achieved, i.e., 99.21% precision, 99.10% recall, and 99.15% F1-score for normal (N) segments; 82.19% precision, 82.50% recall, and 82.34% F1-score for the supra-ventricular ectopic beat (SVEBs); and finally, 94.41% precision, 96.10% recall, and 95.2% F1-score for the ventricular-ectopic beats (VEBs).
Robust Peak Detection for Holter ECGs by Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks
Sep 30, 2021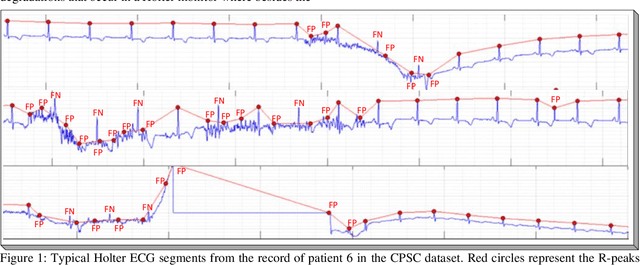
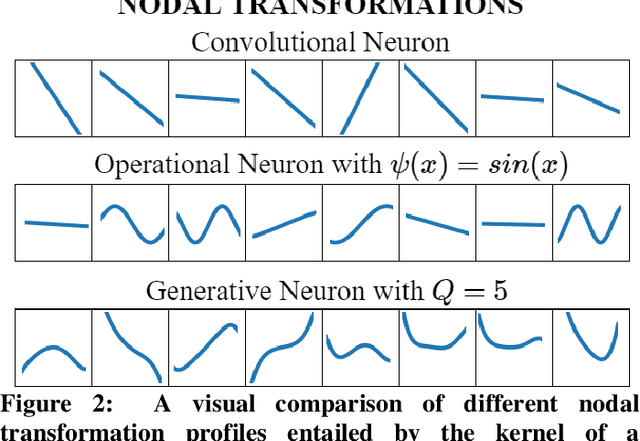
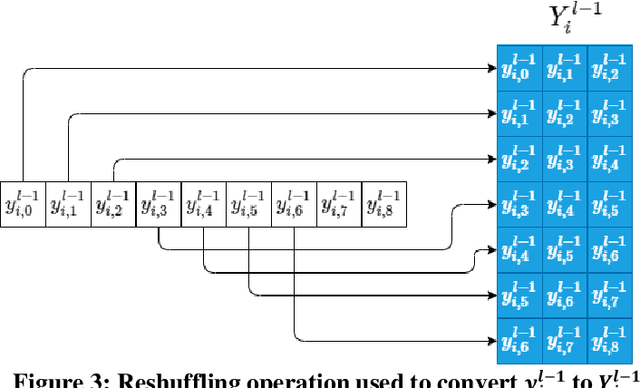
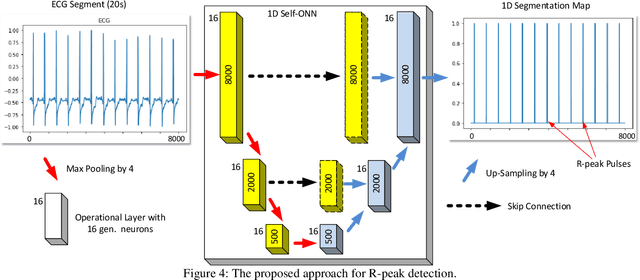
Abstract:Although numerous R-peak detectors have been proposed in the literature, their robustness and performance levels may significantly deteriorate in low quality and noisy signals acquired from mobile ECG sensors such as Holter monitors. Recently, this issue has been addressed by deep 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that have achieved state-of-the-art performance levels in Holter monitors; however, they pose a high complexity level that requires special parallelized hardware setup for real-time processing. On the other hand, their performance deteriorates when a compact network configuration is used instead. This is an expected outcome as recent studies have demonstrated that the learning performance of CNNs is limited due to their strictly homogenous configuration with the sole linear neuron model. This has been addressed by Operational Neural Networks (ONNs) with their heterogenous network configuration encapsulating neurons with various non-linear operators. In this study, to further boost the peak detection performance along with an elegant computational efficiency, we propose 1D Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks (Self-ONNs) with generative neurons. The most crucial advantage of 1D Self-ONNs over the ONNs is their self-organization capability that voids the need to search for the best operator set per neuron since each generative neuron has the ability to create the optimal operator during training. The experimental results over the China Physiological Signal Challenge-2020 (CPSC) dataset with more than one million ECG beats show that the proposed 1D Self-ONNs can significantly surpass the state-of-the-art deep CNN with less computational complexity. Results demonstrate that the proposed solution achieves 99.10% F1-score, 99.79% sensitivity, and 98.42% positive predictivity in the CPSC dataset which is the best R-peak detection performance ever achieved.
Robust R-Peak Detection in Low-Quality Holter ECGs using 1D Convolutional Neural Network
Dec 29, 2020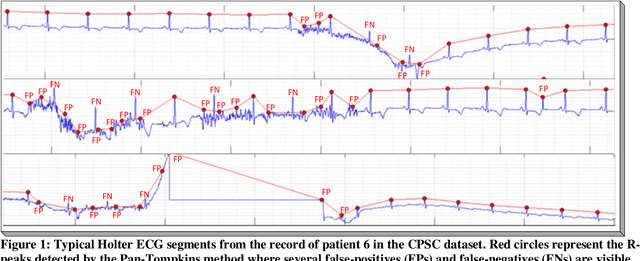
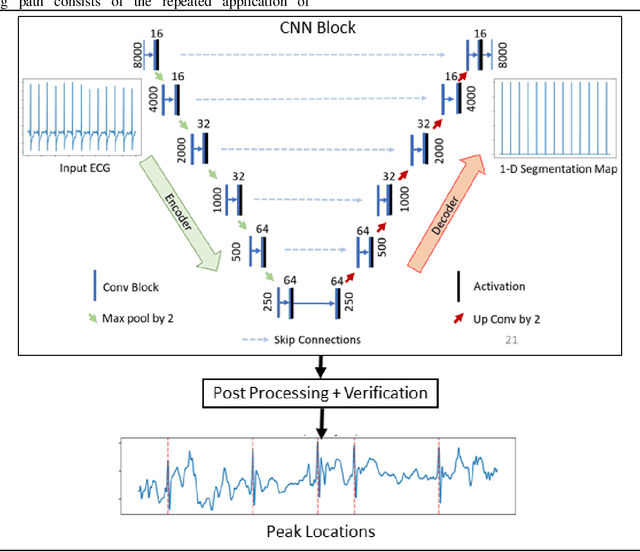
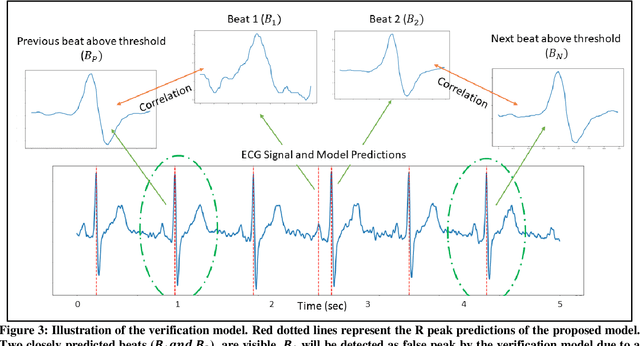
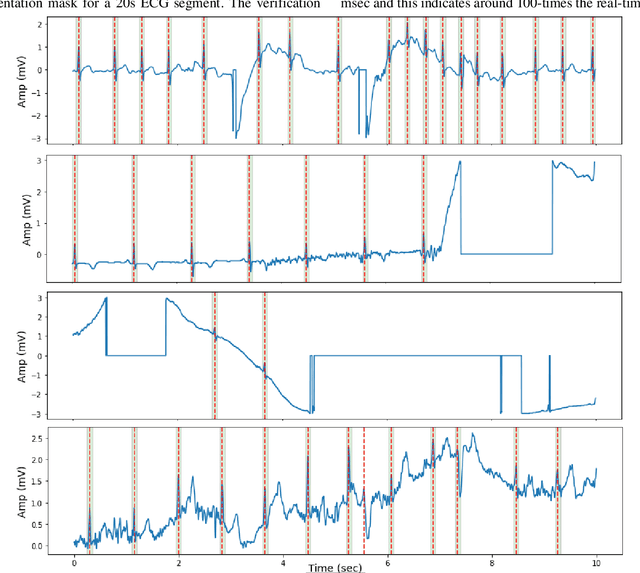
Abstract:Noise and low quality of ECG signals acquired from Holter or wearable devices deteriorate the accuracy and robustness of R-peak detection algorithms. This paper presents a generic and robust system for R-peak detection in Holter ECG signals. While many proposed algorithms have successfully addressed the problem of ECG R-peak detection, there is still a notable gap in the performance of these detectors on such low-quality ECG records. Therefore, in this study, a novel implementation of the 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is used integrated with a verification model to reduce the number of false alarms. This CNN architecture consists of an encoder block and a corresponding decoder block followed by a sample-wise classification layer to construct the 1D segmentation map of R- peaks from the input ECG signal. Once the proposed model has been trained, it can solely be used to detect R-peaks possibly in a single channel ECG data stream quickly and accurately, or alternatively, such a solution can be conveniently employed for real-time monitoring on a lightweight portable device. The model is tested on two open-access ECG databases: The China Physiological Signal Challenge (2020) database (CPSC-DB) with more than one million beats, and the commonly used MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database (MIT-DB). Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed systematic approach achieves 99.30% F1-score, 99.69% recall, and 98.91% precision in CPSC-DB, which is the best R-peak detection performance ever achieved. Compared to all competing methods, the proposed approach can reduce the false-positives and false-negatives in Holter ECG signals by more than 54% and 82%, respectively. Results also demonstrate similar or better performance than most competing algorithms on MIT-DB with 99.83% F1-score, 99.85% recall, and 99.82% precision.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge