Robust Peak Detection for Holter ECGs by Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Sep 30, 2021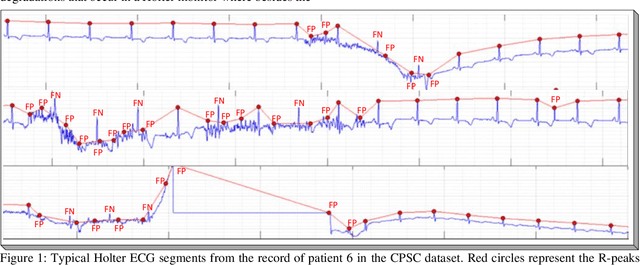
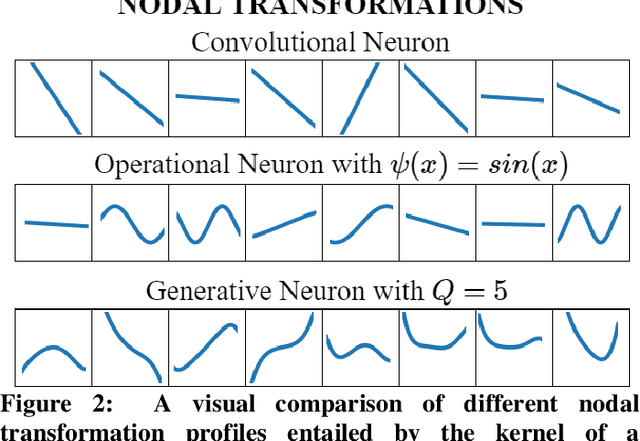
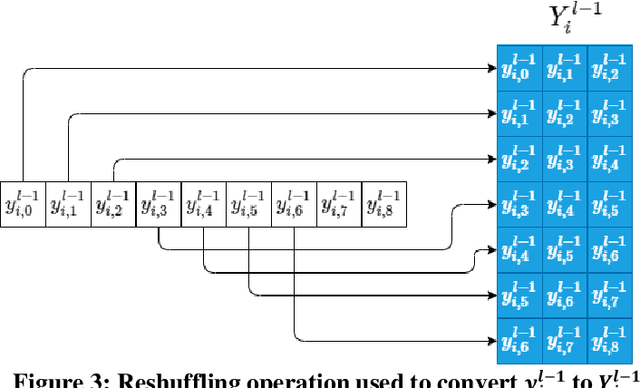
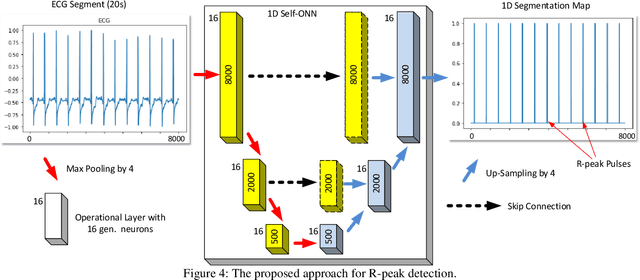
Although numerous R-peak detectors have been proposed in the literature, their robustness and performance levels may significantly deteriorate in low quality and noisy signals acquired from mobile ECG sensors such as Holter monitors. Recently, this issue has been addressed by deep 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) that have achieved state-of-the-art performance levels in Holter monitors; however, they pose a high complexity level that requires special parallelized hardware setup for real-time processing. On the other hand, their performance deteriorates when a compact network configuration is used instead. This is an expected outcome as recent studies have demonstrated that the learning performance of CNNs is limited due to their strictly homogenous configuration with the sole linear neuron model. This has been addressed by Operational Neural Networks (ONNs) with their heterogenous network configuration encapsulating neurons with various non-linear operators. In this study, to further boost the peak detection performance along with an elegant computational efficiency, we propose 1D Self-Organized Operational Neural Networks (Self-ONNs) with generative neurons. The most crucial advantage of 1D Self-ONNs over the ONNs is their self-organization capability that voids the need to search for the best operator set per neuron since each generative neuron has the ability to create the optimal operator during training. The experimental results over the China Physiological Signal Challenge-2020 (CPSC) dataset with more than one million ECG beats show that the proposed 1D Self-ONNs can significantly surpass the state-of-the-art deep CNN with less computational complexity. Results demonstrate that the proposed solution achieves 99.10% F1-score, 99.79% sensitivity, and 98.42% positive predictivity in the CPSC dataset which is the best R-peak detection performance ever achieved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge