Alper Yildirim
CoRe-Net: Co-Operational Regressor Network with Progressive Transfer Learning for Blind Radar Signal Restoration
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Real-world radar signals are frequently corrupted by various artifacts, including sensor noise, echoes, interference, and intentional jamming, differing in type, severity, and duration. This pilot study introduces a novel model, called Co-Operational Regressor Network (CoRe-Net) for blind radar signal restoration, designed to address such limitations and drawbacks. CoRe-Net replaces adversarial training with a novel cooperative learning strategy, leveraging the complementary roles of its Apprentice Regressor (AR) and Master Regressor (MR). The AR restores radar signals corrupted by various artifacts, while the MR evaluates the quality of the restoration and provides immediate and task-specific feedback, ensuring stable and efficient learning. The AR, therefore, has the advantage of both self-learning and assistive learning by the MR. The proposed model has been extensively evaluated over the benchmark Blind Radar Signal Restoration (BRSR) dataset, which simulates diverse real-world artifact scenarios. Under the fair experimental setup, this study shows that the CoRe-Net surpasses the Op-GANs over a 1 dB mean SNR improvement. To further boost the performance gain, this study proposes multi-pass restoration by cascaded CoRe-Nets trained with a novel paradigm called Progressive Transfer Learning (PTL), which enables iterative refinement, thus achieving an additional 2 dB mean SNR enhancement. Multi-pass CoRe-Net training by PTL consistently yields incremental performance improvements through successive restoration passes whilst highlighting CoRe-Net ability to handle such a complex and varying blend of artifacts.
BRSR-OpGAN: Blind Radar Signal Restoration using Operational Generative Adversarial Network
Jul 18, 2024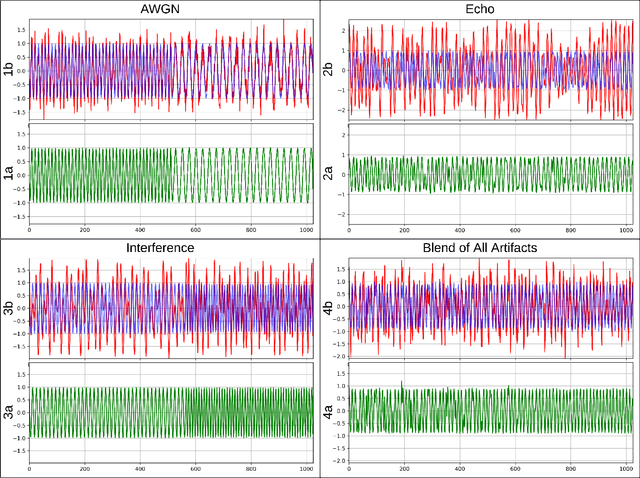
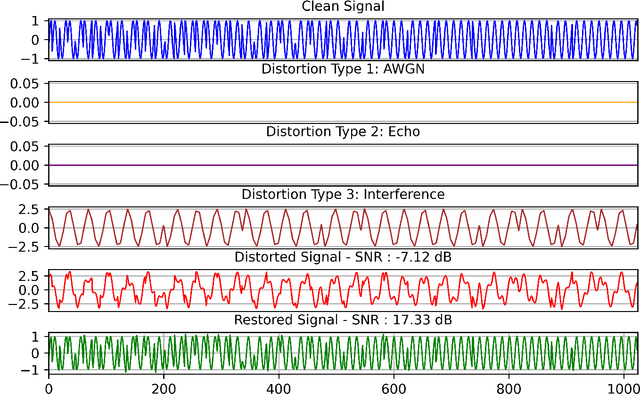
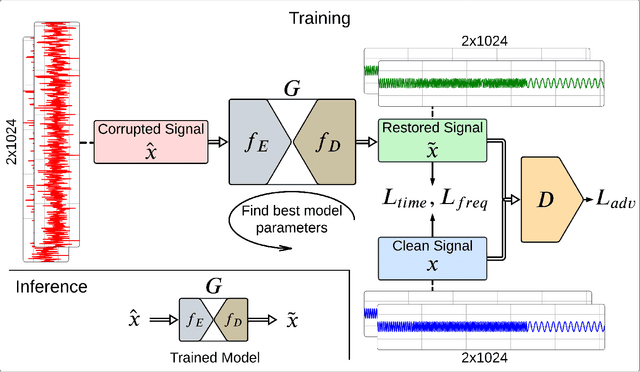
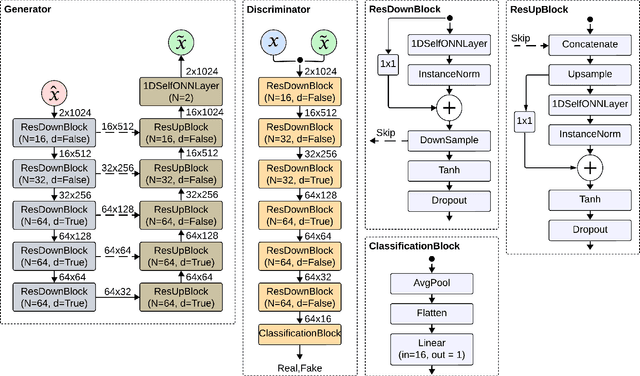
Abstract:Objective: Many studies on radar signal restoration in the literature focus on isolated restoration problems, such as denoising over a certain type of noise, while ignoring other types of artifacts. Additionally, these approaches usually assume a noisy environment with a limited set of fixed signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) levels. However, real-world radar signals are often corrupted by a blend of artifacts, including but not limited to unwanted echo, sensor noise, intentional jamming, and interference, each of which can vary in type, severity, and duration. This study introduces Blind Radar Signal Restoration using an Operational Generative Adversarial Network (BRSR-OpGAN), which uses a dual domain loss in the temporal and spectral domains. This approach is designed to improve the quality of radar signals, regardless of the diversity and intensity of the corruption. Methods: The BRSR-OpGAN utilizes 1D Operational GANs, which use a generative neuron model specifically optimized for blind restoration of corrupted radar signals. This approach leverages GANs' flexibility to adapt dynamically to a wide range of artifact characteristics. Results: The proposed approach has been extensively evaluated using a well-established baseline and a newly curated extended dataset called the Blind Radar Signal Restoration (BRSR) dataset. This dataset was designed to simulate real-world conditions and includes a variety of artifacts, each varying in severity. The evaluation shows an average SNR improvement over 15.1 dB and 14.3 dB for the baseline and BRSR datasets, respectively. Finally, even on resource-constrained platforms, the proposed approach can be applied in real-time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge