Mohammad Shojafar
Secured Communication Schemes for UAVs in 5G: CRYSTALS-Kyber and IDS
Jan 31, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces a secure communication architecture for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) and ground stations in 5G networks, addressing critical challenges in network security. The proposed solution integrates the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) and CRYSTALS-Kyber for key encapsulation, offering a hybrid cryptographic approach. By incorporating CRYSTALS-Kyber, the framework mitigates vulnerabilities in ECC against quantum attacks, positioning it as a quantum-resistant alternative. The architecture is based on a server-client model, with UAVs functioning as clients and the ground station acting as the server. The system was rigorously evaluated in both VPN and 5G environments. Experimental results confirm that CRYSTALS-Kyber delivers strong protection against quantum threats with minimal performance overhead, making it highly suitable for UAVs with resource constraints. Moreover, the proposed architecture integrates an Artificial Intelligence (AI)-based Intrusion Detection System (IDS) to further enhance security. In performance evaluations, the IDS demonstrated strong results across multiple models with XGBoost, particularly in more demanding scenarios, outperforming other models with an accuracy of 97.33% and an AUC of 0.94. These findings underscore the potential of combining quantum-resistant encryption mechanisms with AI-driven IDS to create a robust, scalable, and secure communication framework for UAV networks, particularly within the high-performance requirements of 5G environments.
Multi-Agent Context Learning Strategy for Interference-Aware Beam Allocation in mmWave Vehicular Communications
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Millimeter wave (mmWave) has been recognized as one of key technologies for 5G and beyond networks due to its potential to enhance channel bandwidth and network capacity. The use of mmWave for various applications including vehicular communications has been extensively discussed. However, applying mmWave to vehicular communications faces challenges of high mobility nodes and narrow coverage along the mmWave beams. Due to high mobility in dense networks, overlapping beams can cause strong interference which leads to performance degradation. As a remedy, beam switching capability in mmWave can be utilized. Then, frequent beam switching and cell change become inevitable to manage interference, which increase computational and signalling complexity. In order to deal with the complexity in interference control, we develop a new strategy called Multi-Agent Context Learning (MACOL), which utilizes Contextual Bandit to manage interference while allocating mmWave beams to serve vehicles in the network. Our approach demonstrates that by leveraging knowledge of neighbouring beam status, the machine learning agent can identify and avoid potential interfering transmissions to other ongoing transmissions. Furthermore, we show that even under heavy traffic loads, our proposed MACOL strategy is able to maintain low interference levels at around 10%.
SETTI: A Self-supervised Adversarial Malware Detection Architecture in an IoT Environment
Apr 16, 2022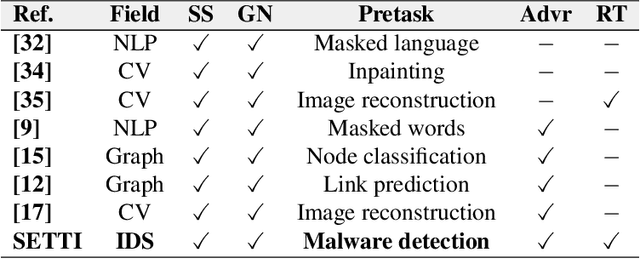
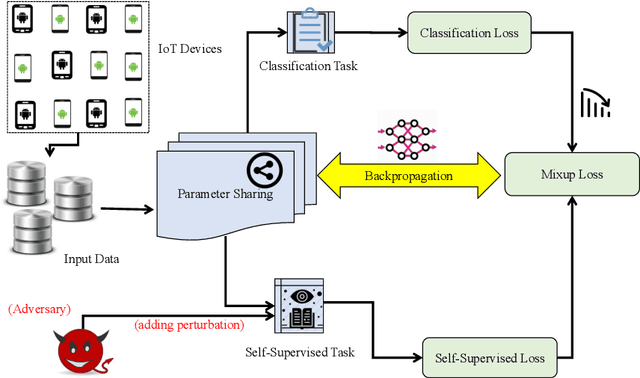
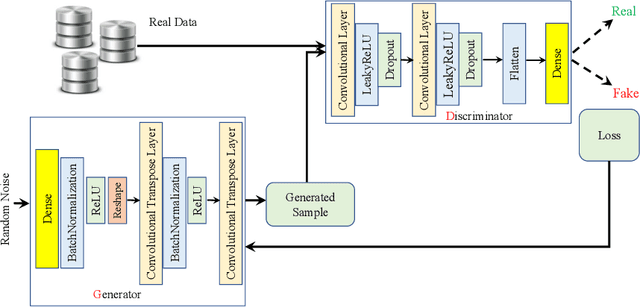
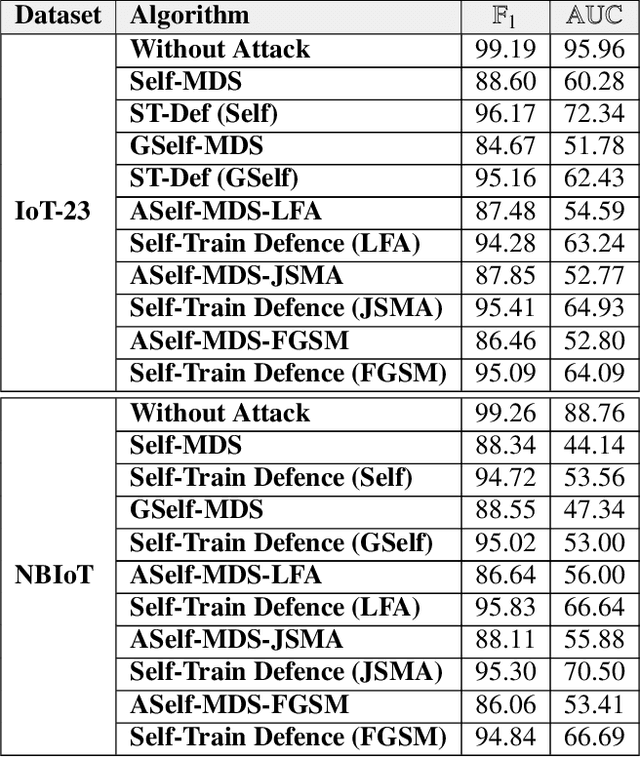
Abstract:In recent years, malware detection has become an active research topic in the area of Internet of Things (IoT) security. The principle is to exploit knowledge from large quantities of continuously generated malware. Existing algorithms practice available malware features for IoT devices and lack real-time prediction behaviors. More research is thus required on malware detection to cope with real-time misclassification of the input IoT data. Motivated by this, in this paper we propose an adversarial self-supervised architecture for detecting malware in IoT networks, SETTI, considering samples of IoT network traffic that may not be labeled. In the SETTI architecture, we design three self-supervised attack techniques, namely Self-MDS, GSelf-MDS and ASelf-MDS. The Self-MDS method considers the IoT input data and the adversarial sample generation in real-time. The GSelf-MDS builds a generative adversarial network model to generate adversarial samples in the self-supervised structure. Finally, ASelf-MDS utilizes three well-known perturbation sample techniques to develop adversarial malware and inject it over the self-supervised architecture. Also, we apply a defence method to mitigate these attacks, namely adversarial self-supervised training to protect the malware detection architecture against injecting the malicious samples. To validate the attack and defence algorithms, we conduct experiments on two recent IoT datasets: IoT23 and NBIoT. Comparison of the results shows that in the IoT23 dataset, the Self-MDS method has the most damaging consequences from the attacker's point of view by reducing the accuracy rate from 98% to 74%. In the NBIoT dataset, the ASelf-MDS method is the most devastating algorithm that can plunge the accuracy rate from 98% to 77%.
Deep Image: A precious image based deep learning method for online malware detection in IoT Environment
Apr 04, 2022
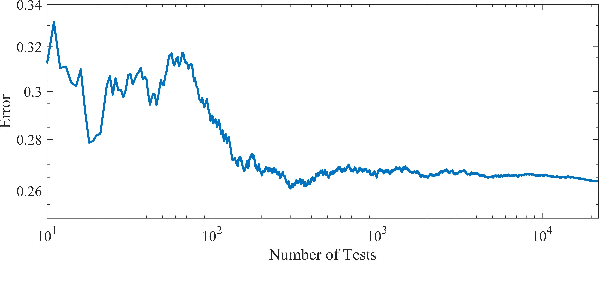
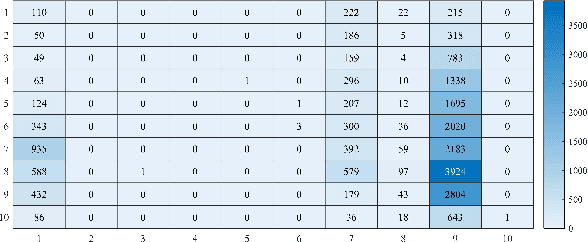
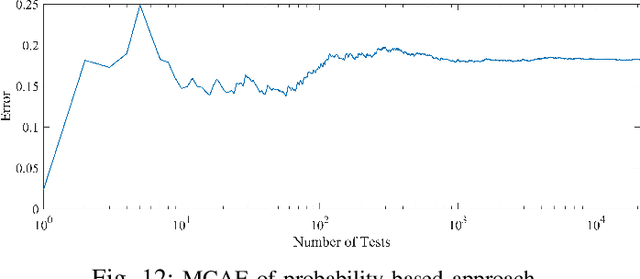
Abstract:The volume of malware and the number of attacks in IoT devices are rising everyday, which encourages security professionals to continually enhance their malware analysis tools. Researchers in the field of cyber security have extensively explored the usage of sophisticated analytics and the efficiency of malware detection. With the introduction of new malware kinds and attack routes, security experts confront considerable challenges in developing efficient malware detection and analysis solutions. In this paper, a different view of malware analysis is considered and the risk level of each sample feature is computed, and based on that the risk level of that sample is calculated. In this way, a criterion is introduced that is used together with accuracy and FPR criteria for malware analysis in IoT environment. In this paper, three malware detection methods based on visualization techniques called the clustering approach, the probabilistic approach, and the deep learning approach are proposed. Then, in addition to the usual machine learning criteria namely accuracy and FPR, a proposed criterion based on the risk of samples has also been used for comparison, with the results showing that the deep learning approach performed better in detecting malware
Similarity-based Android Malware Detection Using Hamming Distance of Static Binary Features
Aug 13, 2019
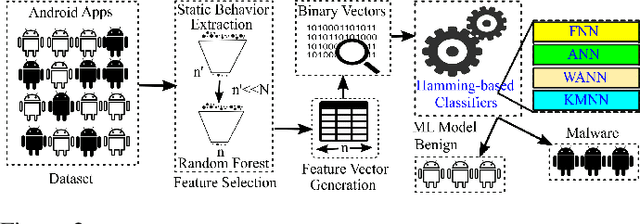
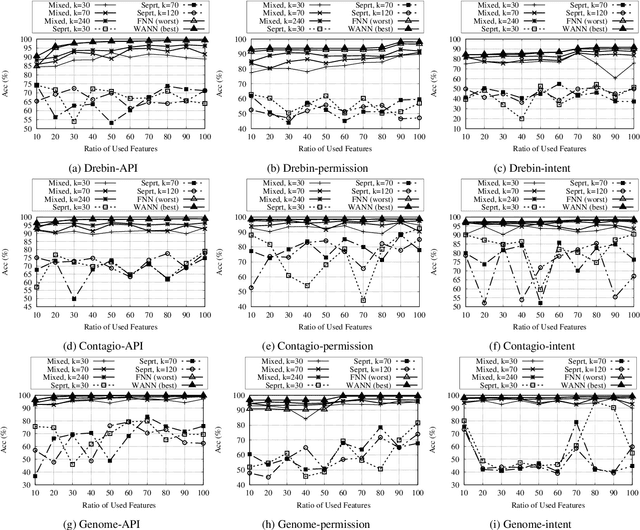
Abstract:In this paper, we develop four malware detection methods using Hamming distance to find similarity between samples which are first nearest neighbors (FNN), all nearest neighbors (ANN), weighted all nearest neighbors (WANN), and k-medoid based nearest neighbors (KMNN). In our proposed methods, we can trigger the alarm if we detect an Android app is malicious. Hence, our solutions help us to avoid the spread of detected malware on a broader scale. We provide a detailed description of the proposed detection methods and related algorithms. We include an extensive analysis to asses the suitability of our proposed similarity-based detection methods. In this way, we perform our experiments on three datasets, including benign and malware Android apps like Drebin, Contagio, and Genome. Thus, to corroborate the actual effectiveness of our classifier, we carry out performance comparisons with some state-of-the-art classification and malware detection algorithms, namely Mixed and Separated solutions, the program dissimilarity measure based on entropy (PDME) and the FalDroid algorithms. We test our experiments in a different type of features: API, intent, and permission features on these three datasets. The results confirm that accuracy rates of proposed algorithms are more than 90% and in some cases (i.e., considering API features) are more than 99%, and are comparable with existing state-of-the-art solutions.
On Defending Against Label Flipping Attacks on Malware Detection Systems
Aug 13, 2019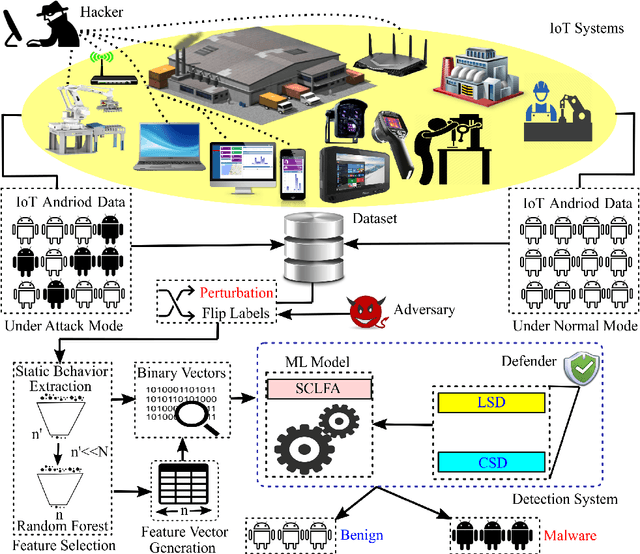
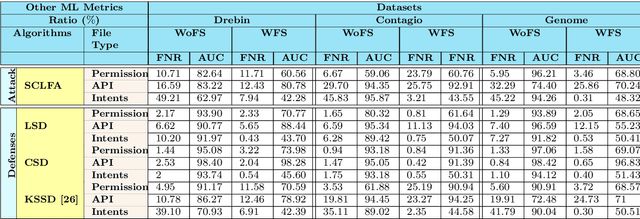
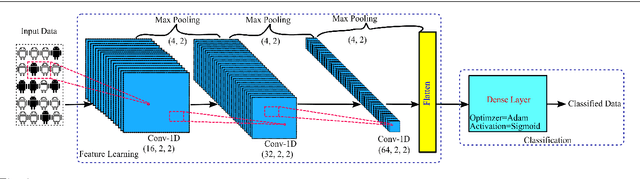

Abstract:Label manipulation attacks are a subclass of data poisoning attacks in adversarial machine learning used against different applications, such as malware detection. These types of attacks represent a serious threat to detection systems in environments having high noise rate or uncertainty, such as complex networks and Internet of Thing (IoT). Recent work in the literature has suggested using the $K$-Nearest Neighboring (KNN) algorithm to defend against such attacks. However, such an approach can suffer from low to wrong detection accuracy. In this paper, we design an architecture to tackle the Android malware detection problem in IoT systems. We develop an attack mechanism based on Silhouette clustering method, modified for mobile Android platforms. We proposed two Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)-type deep learning algorithms against this \emph{Silhouette Clustering-based Label Flipping Attack (SCLFA)}. We show the effectiveness of these two defense algorithms - \emph{Label-based Semi-supervised Defense (LSD)} and \emph{clustering-based Semi-supervised Defense (CSD)} - in correcting labels being attacked. We evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithms by varying the various machine learning parameters on three Android datasets: Drebin, Contagio, and Genome and three types of features: API, intent, and permission. Our evaluation shows that using random forest feature selection and varying ratios of features can result in an improvement of up to 19\% accuracy when compared with the state-of-the-art method in the literature.
Can Machine Learning Model with Static Features be Fooled: an Adversarial Machine Learning Approach
Apr 20, 2019



Abstract:The widespread adoption of smartphones dramatically increases the risk of attacks and the spread of mobile malware, especially on the Android platform. Machine learning based solutions have been already used as a tool to supersede signature based anti-malware systems. However, malware authors leverage attributes from malicious and legitimate samples to estimate statistical difference in-order to create adversarial examples. Hence, to evaluate the vulnerability of machine learning algorithms in malware detection, we propose five different attack scenarios to perturb malicious applications (apps). By doing this, the classification algorithm inappropriately fits discriminant function on the set of data points, eventually yielding a higher misclassification rate. Further, to distinguish the adversarial examples from benign samples, we propose two defense mechanisms to counter attacks. To validate our attacks and solutions, we test our model on three different benchmark datasets. We also test our methods using various classifier algorithms and compare them with the state-of-the-art data poisoning method using the Jacobian matrix. Promising results show that generated adversarial samples can evade detection with a very high probability. Additionally, evasive variants generated by our attacks models when used to harden the developed anti-malware system improves the detection rate.
FeatureAnalytics: An approach to derive relevant attributes for analyzing Android Malware
Sep 17, 2018
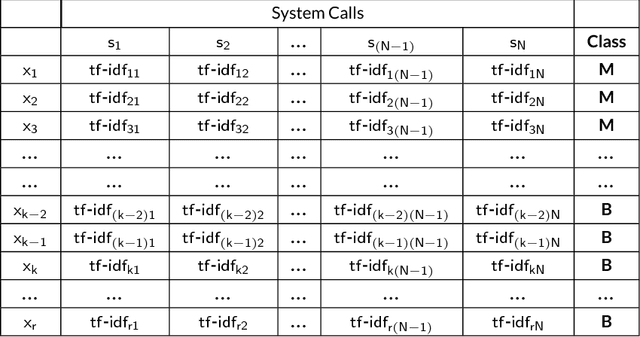
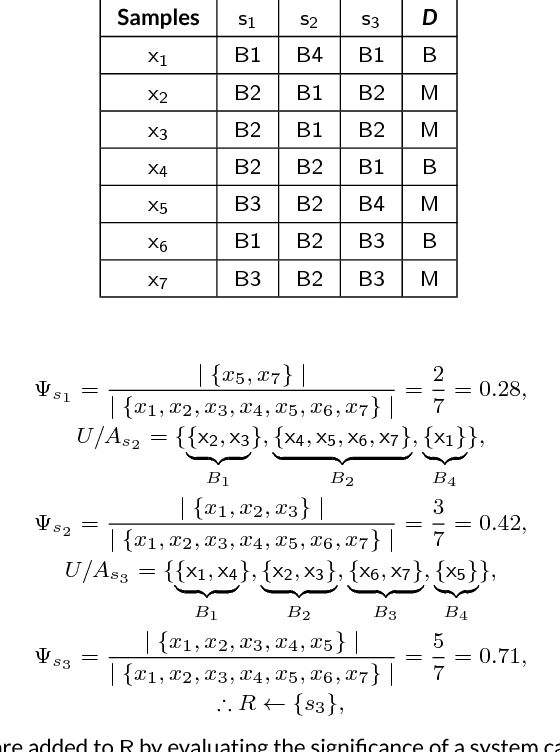
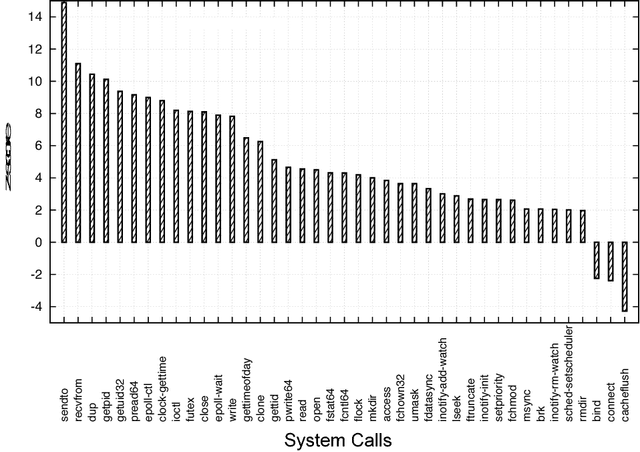
Abstract:Ever increasing number of Android malware, has always been a concern for cybersecurity professionals. Even though plenty of anti-malware solutions exist, a rational and pragmatic approach for the same is rare and has to be inspected further. In this paper, we propose a novel two-set feature selection approach based on Rough Set and Statistical Test named as RSST to extract relevant system calls. To address the problem of higher dimensional attribute set, we derived suboptimal system call space by applying the proposed feature selection method to maximize the separability between malware and benign samples. Comprehensive experiments conducted on a dataset consisting of 3500 samples with 30 RSST derived essential system calls resulted in an accuracy of 99.9%, Area Under Curve (AUC) of 1.0, with 1% False Positive Rate (FPR). However, other feature selectors (Information Gain, CFsSubsetEval, ChiSquare, FreqSel and Symmetric Uncertainty) used in the domain of malware analysis resulted in the accuracy of 95.5% with 8.5% FPR. Besides, empirical analysis of RSST derived system calls outperform other attributes such as permissions, opcodes, API, methods, call graphs, Droidbox attributes and network traces.
Hybrid Genetic Algorithm for Cloud Computing Applications
Apr 22, 2014

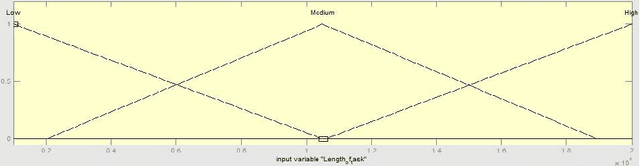
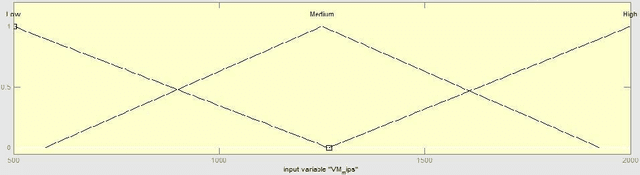
Abstract:In this paper with the aid of genetic algorithm and fuzzy theory, we present a hybrid job scheduling approach, which considers the load balancing of the system and reduces total execution time and execution cost. We try to modify the standard Genetic algorithm and to reduce the iteration of creating population with the aid of fuzzy theory. The main goal of this research is to assign the jobs to the resources with considering the VM MIPS and length of jobs. The new algorithm assigns the jobs to the resources with considering the job length and resources capacities. We evaluate the performance of our approach with some famous cloud scheduling models. The results of the experiments show the efficiency of the proposed approach in term of execution time, execution cost and average Degree of Imbalance (DI).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge