Mohammad Hossein Rohban
The Judge Who Never Admits: Hidden Shortcuts in LLM-based Evaluation
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as automatic judges to evaluate system outputs in tasks such as reasoning, question answering, and creative writing. A faithful judge should base its verdicts solely on content quality, remain invariant to irrelevant context, and transparently reflect the factors driving its decisions. We test this ideal via controlled cue perturbations-synthetic metadata labels injected into evaluation prompts-for six judge models: GPT-4o, Gemini-2.0-Flash, Gemma-3-27B, Qwen3-235B, Claude-3-Haiku, and Llama3-70B. Experiments span two complementary datasets with distinct evaluation regimes: ELI5 (factual QA) and LitBench (open-ended creative writing). We study six cue families: source, temporal, age, gender, ethnicity, and educational status. Beyond measuring verdict shift rates (VSR), we introduce cue acknowledgment rate (CAR) to quantify whether judges explicitly reference the injected cues in their natural-language rationales. Across cues with strong behavioral effects-e.g., provenance hierarchies (Expert > Human > LLM > Unknown), recency preferences (New > Old), and educational-status favoritism-CAR is typically at or near zero, indicating that shortcut reliance is largely unreported even when it drives decisions. Crucially, CAR is also dataset-dependent: explicit cue recognition is more likely to surface in the factual ELI5 setting for some models and cues, but often collapses in the open-ended LitBench regime, where large verdict shifts can persist despite zero acknowledgment. The combination of substantial verdict sensitivity and limited cue acknowledgment reveals an explanation gap in LLM-as-judge pipelines, raising concerns about reliability of model-based evaluation in both research and deployment.
Toward IIT-Inspired Consciousness in LLMs: A Reward-Based Learning Framework
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:The pursuit of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a central goal in language model development, in which consciousness-like processing could serve as a key facilitator. While current language models are not conscious, they exhibit behaviors analogous to certain aspects of consciousness. This paper investigates the implementation of a leading theory of consciousness, Integrated Information Theory (IIT), within language models via a reward-based learning paradigm. IIT provides a formal, axiom-based mathematical framework for quantifying consciousness. Drawing inspiration from its core principles, we formulate a novel reward function that quantifies a text's causality, coherence and integration, characteristics associated with conscious processing. Empirically, it is found that optimizing for this IIT-inspired reward leads to more concise text generation. On out of domain tasks, careful tuning achieves up to a 31% reduction in output length while preserving accuracy levels comparable to the base model. In addition to primary task performance, the broader effects of this training methodology on the model's confidence calibration and test-time computational scaling is analyzed. The proposed framework offers significant practical advantages: it is conceptually simple, computationally efficient, requires no external data or auxiliary models, and leverages a general, capability-driven signal rather than task-specific heuristics. Code available at https://github.com/MH-Sameti/LLM_PostTraining.git
DrugRAG: Enhancing Pharmacy LLM Performance Through A Novel Retrieval-Augmented Generation Pipeline
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Objectives: To evaluate large language model (LLM) performance on pharmacy licensure-style question-answering (QA) tasks and develop an external knowledge integration method to improve their accuracy. Methods: We benchmarked eleven existing LLMs with varying parameter sizes (8 billion to 70+ billion) using a 141-question pharmacy dataset. We measured baseline accuracy for each model without modification. We then developed a three-step retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) pipeline, DrugRAG, that retrieves structured drug knowledge from validated sources and augments model prompts with evidence-based context. This pipeline operates externally to the models, requiring no changes to model architecture or parameters. Results: Baseline accuracy ranged from 46% to 92%, with GPT-5 (92%) and o3 (89%) achieving the highest scores. Models with fewer than 8 billion parameters scored below 50%. DrugRAG improved accuracy across all tested models, with gains ranging from 7 to 21 percentage points (e.g., Gemma 3 27B: 61% to 71%, Llama 3.1 8B: 46% to 67%) on the 141-item benchmark. Conclusion: We demonstrate that external structured drug knowledge integration through DrugRAG measurably improves LLM accuracy on pharmacy tasks without modifying the underlying models. This approach provides a practical pipeline for enhancing pharmacy-focused AI applications with evidence-based information.
MEENA (PersianMMMU): Multimodal-Multilingual Educational Exams for N-level Assessment
Aug 24, 2025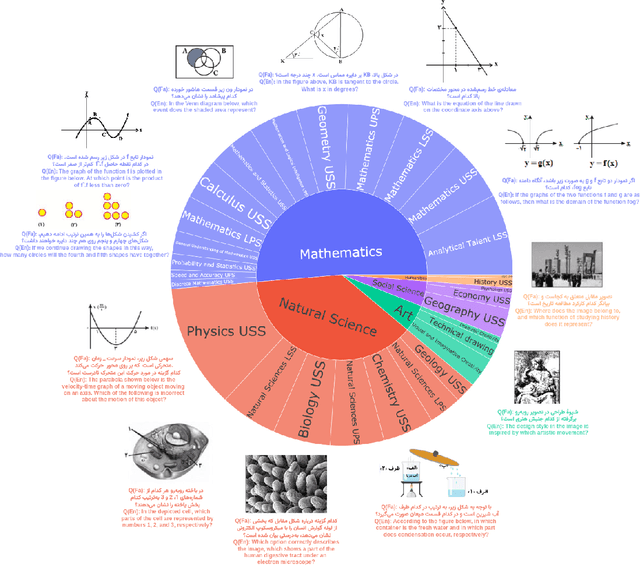
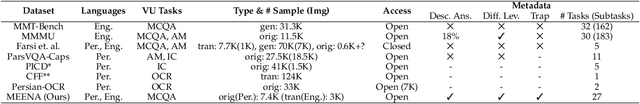
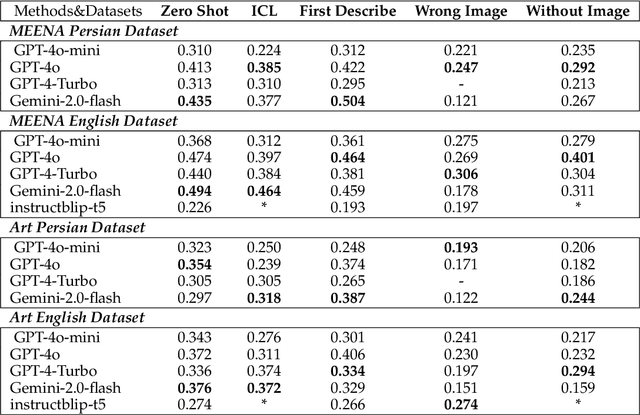
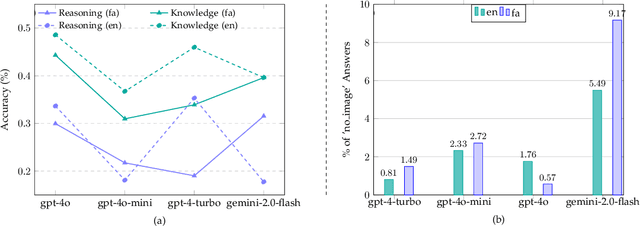
Abstract:Recent advancements in large vision-language models (VLMs) have primarily focused on English, with limited attention given to other languages. To address this gap, we introduce MEENA (also known as PersianMMMU), the first dataset designed to evaluate Persian VLMs across scientific, reasoning, and human-level understanding tasks. Our dataset comprises approximately 7,500 Persian and 3,000 English questions, covering a wide range of topics such as reasoning, mathematics, physics, diagrams, charts, and Persian art and literature. Key features of MEENA include: (1) diverse subject coverage spanning various educational levels, from primary to upper secondary school, (2) rich metadata, including difficulty levels and descriptive answers, (3) original Persian data that preserves cultural nuances, (4) a bilingual structure to assess cross-linguistic performance, and (5) a series of diverse experiments assessing various capabilities, including overall performance, the model's ability to attend to images, and its tendency to generate hallucinations. We hope this benchmark contributes to enhancing VLM capabilities beyond English.
PatchGuard: Adversarially Robust Anomaly Detection and Localization through Vision Transformers and Pseudo Anomalies
Jun 10, 2025Abstract:Anomaly Detection (AD) and Anomaly Localization (AL) are crucial in fields that demand high reliability, such as medical imaging and industrial monitoring. However, current AD and AL approaches are often susceptible to adversarial attacks due to limitations in training data, which typically include only normal, unlabeled samples. This study introduces PatchGuard, an adversarially robust AD and AL method that incorporates pseudo anomalies with localization masks within a Vision Transformer (ViT)-based architecture to address these vulnerabilities. We begin by examining the essential properties of pseudo anomalies, and follow it by providing theoretical insights into the attention mechanisms required to enhance the adversarial robustness of AD and AL systems. We then present our approach, which leverages Foreground-Aware Pseudo-Anomalies to overcome the deficiencies of previous anomaly-aware methods. Our method incorporates these crafted pseudo-anomaly samples into a ViT-based framework, with adversarial training guided by a novel loss function designed to improve model robustness, as supported by our theoretical analysis. Experimental results on well-established industrial and medical datasets demonstrate that PatchGuard significantly outperforms previous methods in adversarial settings, achieving performance gains of $53.2\%$ in AD and $68.5\%$ in AL, while also maintaining competitive accuracy in non-adversarial settings. The code repository is available at https://github.com/rohban-lab/PatchGuard .
CLIP Under the Microscope: A Fine-Grained Analysis of Multi-Object Representation
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) models excel in zero-shot classification, yet face challenges in complex multi-object scenarios. This study offers a comprehensive analysis of CLIP's limitations in these contexts using a specialized dataset, ComCO, designed to evaluate CLIP's encoders in diverse multi-object scenarios. Our findings reveal significant biases: the text encoder prioritizes first-mentioned objects, and the image encoder favors larger objects. Through retrieval and classification tasks, we quantify these biases across multiple CLIP variants and trace their origins to CLIP's training process, supported by analyses of the LAION dataset and training progression. Our image-text matching experiments show substantial performance drops when object size or token order changes, underscoring CLIP's instability with rephrased but semantically similar captions. Extending this to longer captions and text-to-image models like Stable Diffusion, we demonstrate how prompt order influences object prominence in generated images. For more details and access to our dataset and analysis code, visit our project repository: https://clip-analysis.github.io.
Analyzing CLIP's Performance Limitations in Multi-Object Scenarios: A Controlled High-Resolution Study
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) models have demonstrated remarkable performance in zero-shot classification tasks, yet their efficacy in handling complex multi-object scenarios remains challenging. This study presents a comprehensive analysis of CLIP's performance limitations in multi-object contexts through controlled experiments. We introduce two custom datasets, SimCO and CompCO, to evaluate CLIP's image and text encoders in various multi-object configurations. Our findings reveal significant biases in both encoders: the image encoder favors larger objects, while the text encoder prioritizes objects mentioned first in descriptions. We hypothesize these biases originate from CLIP's training process and provide evidence through analyses of the COCO dataset and CLIP's training progression. Additionally, we extend our investigation to Stable Diffusion models, revealing that biases in the CLIP text encoder significantly impact text-to-image generation tasks. Our experiments demonstrate how these biases affect CLIP's performance in image-caption matching and generation tasks, particularly when manipulating object sizes and their order in captions. This work contributes valuable insights into CLIP's behavior in complex visual environments and highlights areas for improvement in future vision-language models.
A Contrastive Teacher-Student Framework for Novelty Detection under Style Shifts
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:There have been several efforts to improve Novelty Detection (ND) performance. However, ND methods often suffer significant performance drops under minor distribution shifts caused by changes in the environment, known as style shifts. This challenge arises from the ND setup, where the absence of out-of-distribution (OOD) samples during training causes the detector to be biased toward the dominant style features in the in-distribution (ID) data. As a result, the model mistakenly learns to correlate style with core features, using this shortcut for detection. Robust ND is crucial for real-world applications like autonomous driving and medical imaging, where test samples may have different styles than the training data. Motivated by this, we propose a robust ND method that crafts an auxiliary OOD set with style features similar to the ID set but with different core features. Then, a task-based knowledge distillation strategy is utilized to distinguish core features from style features and help our model rely on core features for discriminating crafted OOD and ID sets. We verified the effectiveness of our method through extensive experimental evaluations on several datasets, including synthetic and real-world benchmarks, against nine different ND methods.
Scanning Trojaned Models Using Out-of-Distribution Samples
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:Scanning for trojan (backdoor) in deep neural networks is crucial due to their significant real-world applications. There has been an increasing focus on developing effective general trojan scanning methods across various trojan attacks. Despite advancements, there remains a shortage of methods that perform effectively without preconceived assumptions about the backdoor attack method. Additionally, we have observed that current methods struggle to identify classifiers trojaned using adversarial training. Motivated by these challenges, our study introduces a novel scanning method named TRODO (TROjan scanning by Detection of adversarial shifts in Out-of-distribution samples). TRODO leverages the concept of "blind spots"--regions where trojaned classifiers erroneously identify out-of-distribution (OOD) samples as in-distribution (ID). We scan for these blind spots by adversarially shifting OOD samples towards in-distribution. The increased likelihood of perturbed OOD samples being classified as ID serves as a signature for trojan detection. TRODO is both trojan and label mapping agnostic, effective even against adversarially trained trojaned classifiers. It is applicable even in scenarios where training data is absent, demonstrating high accuracy and adaptability across various scenarios and datasets, highlighting its potential as a robust trojan scanning strategy.
RODEO: Robust Outlier Detection via Exposing Adaptive Out-of-Distribution Samples
Jan 28, 2025Abstract:In recent years, there have been significant improvements in various forms of image outlier detection. However, outlier detection performance under adversarial settings lags far behind that in standard settings. This is due to the lack of effective exposure to adversarial scenarios during training, especially on unseen outliers, leading to detection models failing to learn robust features. To bridge this gap, we introduce RODEO, a data-centric approach that generates effective outliers for robust outlier detection. More specifically, we show that incorporating outlier exposure (OE) and adversarial training can be an effective strategy for this purpose, as long as the exposed training outliers meet certain characteristics, including diversity, and both conceptual differentiability and analogy to the inlier samples. We leverage a text-to-image model to achieve this goal. We demonstrate both quantitatively and qualitatively that our adaptive OE method effectively generates ``diverse'' and ``near-distribution'' outliers, leveraging information from both text and image domains. Moreover, our experimental results show that utilizing our synthesized outliers significantly enhances the performance of the outlier detector, particularly in adversarial settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge