Mohamed Maher
Microsoft ATL Cairo
Simply Trainable Nearest Neighbour Machine Translation with GPU Inference
Jul 29, 2024Abstract:Nearest neighbor machine translation is a successful approach for fast domain adaption, which interpolates the pre-trained transformers with domain-specific token-level k-nearest-neighbor (kNN) retrieval without retraining. Despite kNN MT's success, searching large reference corpus and fixed interpolation between the kNN and pre-trained model led to computational complexity and translation quality challenges. Among other papers, Dai et al. proposed methods to obtain a small number of reference samples dynamically for which they introduced a distance-aware interpolation method using an equation that includes free parameters. This paper proposes a simply trainable nearest neighbor machine translation and carry out inference experiments on GPU. Similar to Dai et al., we first adaptively construct a small datastore for each input sentence. Second, we train a single-layer network for the interpolation coefficient between the knnMT and pre-trained result to automatically interpolate in different domains. Experimental results on different domains show that our proposed method either improves or sometimes maintain the translation quality of methods in Dai et al. while being automatic. In addition, our GPU inference results demonstrate that knnMT can be integrated into GPUs with a drop of only 5% in terms of speed.
Language Tokens: A Frustratingly Simple Approach Improves Zero-Shot Performance of Multilingual Translation
Aug 11, 2022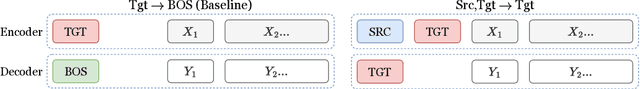
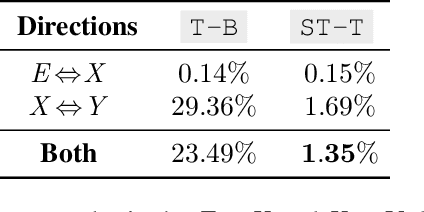
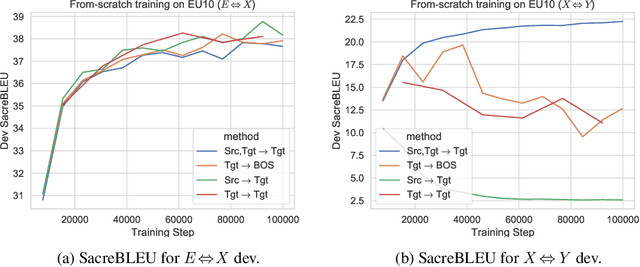
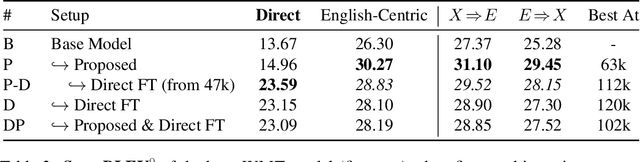
Abstract:This paper proposes a simple yet effective method to improve direct (X-to-Y) translation for both cases: zero-shot and when direct data is available. We modify the input tokens at both the encoder and decoder to include signals for the source and target languages. We show a performance gain when training from scratch, or finetuning a pretrained model with the proposed setup. In the experiments, our method shows nearly 10.0 BLEU points gain on in-house datasets depending on the checkpoint selection criteria. In a WMT evaluation campaign, From-English performance improves by 4.17 and 2.87 BLEU points, in the zero-shot setting, and when direct data is available for training, respectively. While X-to-Y improves by 1.29 BLEU over the zero-shot baseline, and 0.44 over the many-to-many baseline. In the low-resource setting, we see a 1.5~1.7 point improvement when finetuning on X-to-Y domain data.
AutoMLBench: A Comprehensive Experimental Evaluation of Automated Machine Learning Frameworks
Apr 18, 2022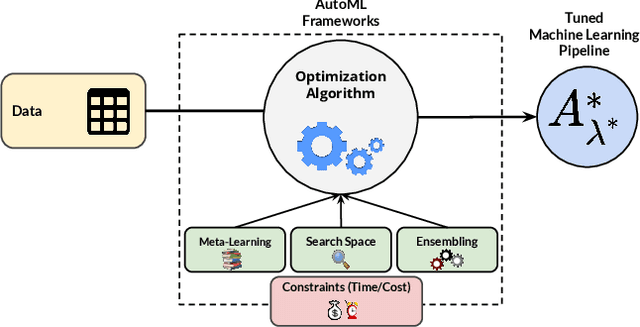
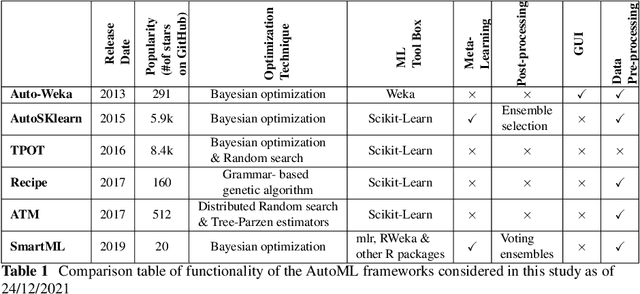
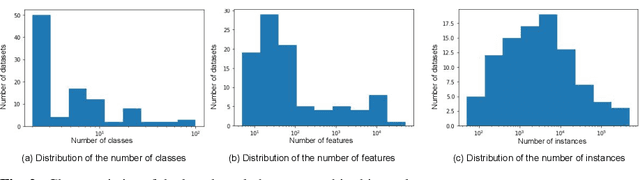
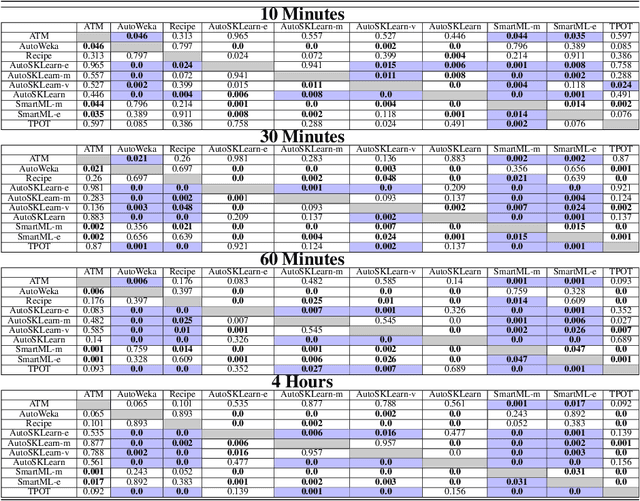
Abstract:Nowadays, machine learning is playing a crucial role in harnessing the power of the massive amounts of data that we are currently producing every day in our digital world. With the booming demand for machine learning applications, it has been recognized that the number of knowledgeable data scientists can not scale with the growing data volumes and application needs in our digital world. In response to this demand, several automated machine learning (AutoML) techniques and frameworks have been developed to fill the gap of human expertise by automating the process of building machine learning pipelines. In this study, we present a comprehensive evaluation and comparison of the performance characteristics of six popular AutoML frameworks, namely, Auto-Weka, AutoSKlearn, TPOT, Recipe, ATM, and SmartML across 100 data sets from established AutoML benchmark suites. Our experimental evaluation considers different aspects for its comparison including the performance impact of several design decisions including time budget, size of search space, meta-learning, and ensemble construction. The results of our study reveal various interesting insights that can significantly guide and impact the design of AutoML frameworks.
Instance-based Label Smoothing For Better Calibrated Classification Networks
Oct 11, 2021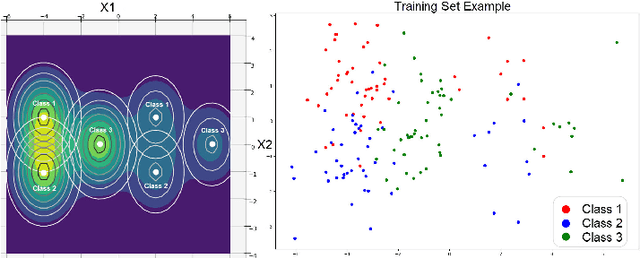
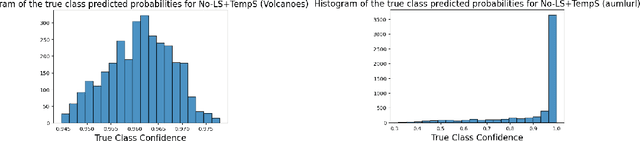
Abstract:Label smoothing is widely used in deep neural networks for multi-class classification. While it enhances model generalization and reduces overconfidence by aiming to lower the probability for the predicted class, it distorts the predicted probabilities of other classes resulting in poor class-wise calibration. Another method for enhancing model generalization is self-distillation where the predictions of a teacher network trained with one-hot labels are used as the target for training a student network. We take inspiration from both label smoothing and self-distillation and propose two novel instance-based label smoothing approaches, where a teacher network trained with hard one-hot labels is used to determine the amount of per class smoothness applied to each instance. The assigned smoothing factor is non-uniformly distributed along with the classes according to their similarity with the actual class. Our methods show better generalization and calibration over standard label smoothing on various deep neural architectures and image classification datasets.
Automated Machine Learning: State-of-The-Art and Open Challenges
Jun 11, 2019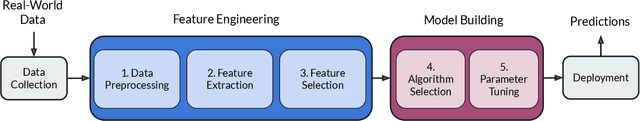
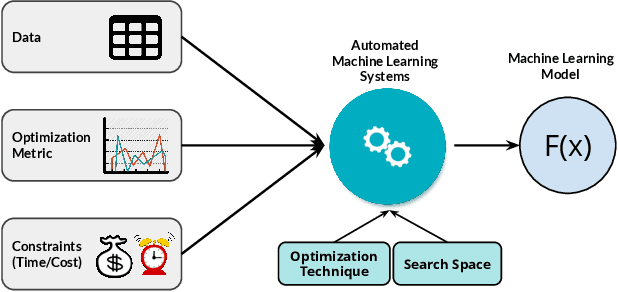
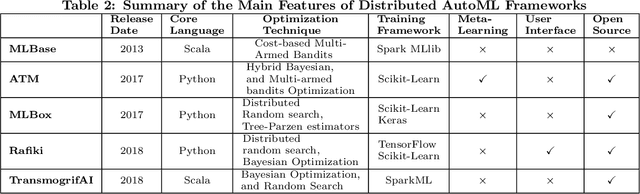
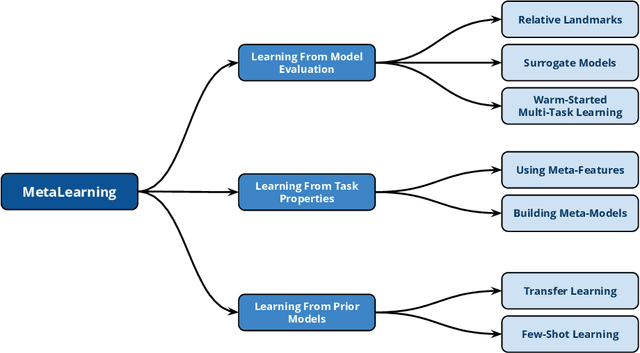
Abstract:With the continuous and vast increase in the amount of data in our digital world, it has been acknowledged that the number of knowledgeable data scientists can not scale to address these challenges. Thus, there was a crucial need for automating the process of building good machine learning models. In the last few years, several techniques and frameworks have been introduced to tackle the challenge of automating the process of Combined Algorithm Selection and Hyper-parameter tuning (CASH) in the machine learning domain. The main aim of these techniques is to reduce the role of the human in the loop and fill the gap for non-expert machine learning users by playing the role of the domain expert. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey for the state-of-the-art efforts in tackling the CASH problem. In addition, we highlight the research work of automating the other steps of the full complex machine learning pipeline (AutoML) from data understanding till model deployment. Furthermore, we provide comprehensive coverage for the various tools and frameworks that have been introduced in this domain. Finally, we discuss some of the research directions and open challenges that need to be addressed in order to achieve the vision and goals of the AutoML process.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge