Mohamed Amine Ketata
Joint Relational Database Generation via Graph-Conditional Diffusion Models
May 22, 2025Abstract:Building generative models for relational databases (RDBs) is important for applications like privacy-preserving data release and augmenting real datasets. However, most prior work either focuses on single-table generation or relies on autoregressive factorizations that impose a fixed table order and generate tables sequentially. This approach limits parallelism, restricts flexibility in downstream applications like missing value imputation, and compounds errors due to commonly made conditional independence assumptions. We propose a fundamentally different approach: jointly modeling all tables in an RDB without imposing any order. By using a natural graph representation of RDBs, we propose the Graph-Conditional Relational Diffusion Model (GRDM). GRDM leverages a graph neural network to jointly denoise row attributes and capture complex inter-table dependencies. Extensive experiments on six real-world RDBs demonstrate that our approach substantially outperforms autoregressive baselines in modeling multi-hop inter-table correlations and achieves state-of-the-art performance on single-table fidelity metrics.
Lift Your Molecules: Molecular Graph Generation in Latent Euclidean Space
Jun 15, 2024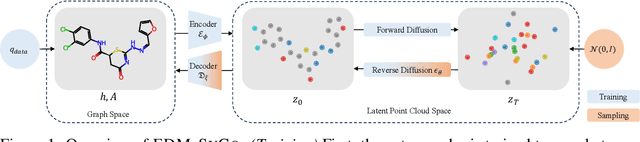
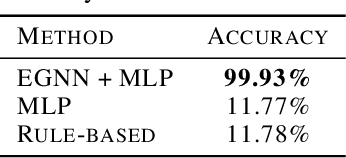
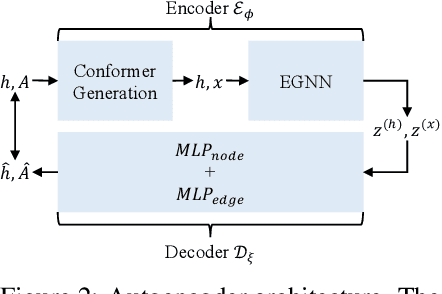
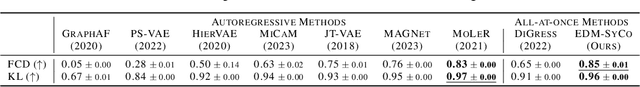
Abstract:We introduce a new framework for molecular graph generation with 3D molecular generative models. Our Synthetic Coordinate Embedding (SyCo) framework maps molecular graphs to Euclidean point clouds via synthetic conformer coordinates and learns the inverse map using an E(n)-Equivariant Graph Neural Network (EGNN). The induced point cloud-structured latent space is well-suited to apply existing 3D molecular generative models. This approach simplifies the graph generation problem - without relying on molecular fragments nor autoregressive decoding - into a point cloud generation problem followed by node and edge classification tasks. Further, we propose a novel similarity-constrained optimization scheme for 3D diffusion models based on inpainting and guidance. As a concrete implementation of our framework, we develop EDM-SyCo based on the E(3) Equivariant Diffusion Model (EDM). EDM-SyCo achieves state-of-the-art performance in distribution learning of molecular graphs, outperforming the best non-autoregressive methods by more than 30% on ZINC250K and 16% on the large-scale GuacaMol dataset while improving conditional generation by up to 3.9 times.
Uncertainty Estimation for Molecules: Desiderata and Methods
Jun 20, 2023


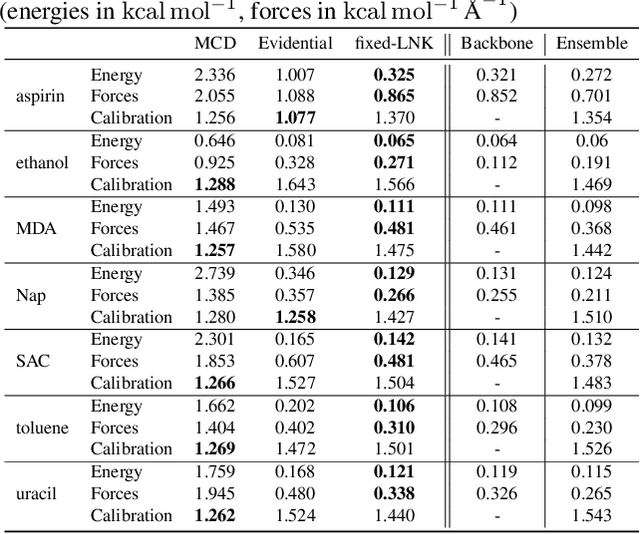
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are promising surrogates for quantum mechanical calculations as they establish unprecedented low errors on collections of molecular dynamics (MD) trajectories. Thanks to their fast inference times they promise to accelerate computational chemistry applications. Unfortunately, despite low in-distribution (ID) errors, such GNNs might be horribly wrong for out-of-distribution (OOD) samples. Uncertainty estimation (UE) may aid in such situations by communicating the model's certainty about its prediction. Here, we take a closer look at the problem and identify six key desiderata for UE in molecular force fields, three 'physics-informed' and three 'application-focused' ones. To overview the field, we survey existing methods from the field of UE and analyze how they fit to the set desiderata. By our analysis, we conclude that none of the previous works satisfies all criteria. To fill this gap, we propose Localized Neural Kernel (LNK) a Gaussian Process (GP)-based extension to existing GNNs satisfying the desiderata. In our extensive experimental evaluation, we test four different UE with three different backbones and two datasets. In out-of-equilibrium detection, we find LNK yielding up to 2.5 and 2.1 times lower errors in terms of AUC-ROC score than dropout or evidential regression-based methods while maintaining high predictive performance.
DiffDock-PP: Rigid Protein-Protein Docking with Diffusion Models
Apr 08, 2023



Abstract:Understanding how proteins structurally interact is crucial to modern biology, with applications in drug discovery and protein design. Recent machine learning methods have formulated protein-small molecule docking as a generative problem with significant performance boosts over both traditional and deep learning baselines. In this work, we propose a similar approach for rigid protein-protein docking: DiffDock-PP is a diffusion generative model that learns to translate and rotate unbound protein structures into their bound conformations. We achieve state-of-the-art performance on DIPS with a median C-RMSD of 4.85, outperforming all considered baselines. Additionally, DiffDock-PP is faster than all search-based methods and generates reliable confidence estimates for its predictions. Our code is publicly available at $\texttt{https://github.com/ketatam/DiffDock-PP}$
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge