Mira Slavcheva
Defurnishing with X-Ray Vision: Joint Removal of Furniture from Panoramas and Mesh
Jun 06, 2025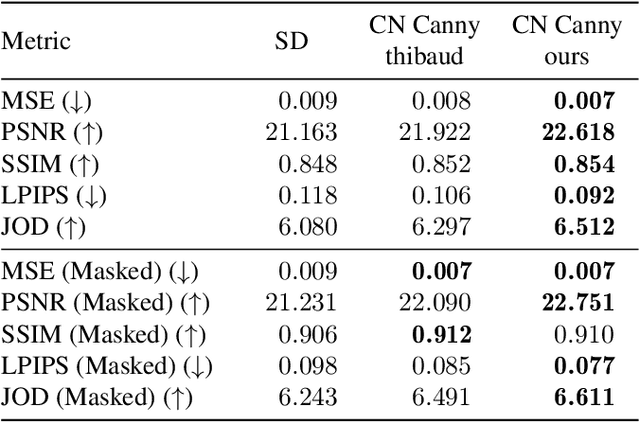
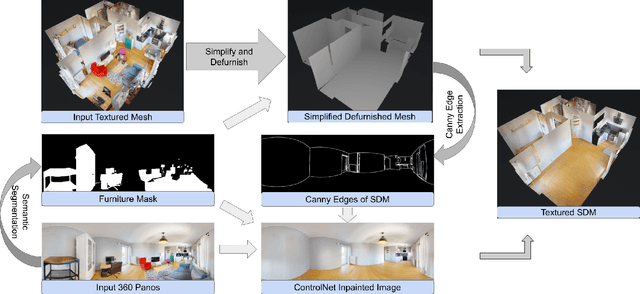
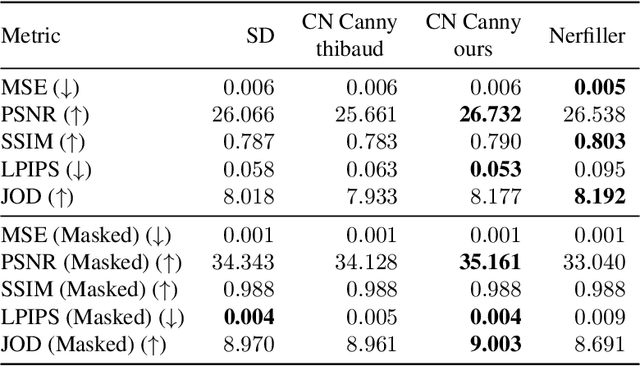
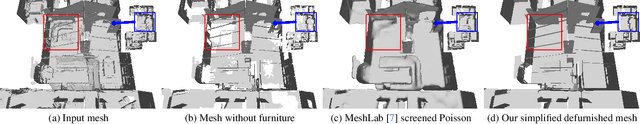
Abstract:We present a pipeline for generating defurnished replicas of indoor spaces represented as textured meshes and corresponding multi-view panoramic images. To achieve this, we first segment and remove furniture from the mesh representation, extend planes, and fill holes, obtaining a simplified defurnished mesh (SDM). This SDM acts as an ``X-ray'' of the scene's underlying structure, guiding the defurnishing process. We extract Canny edges from depth and normal images rendered from the SDM. We then use these as a guide to remove the furniture from panorama images via ControlNet inpainting. This control signal ensures the availability of global geometric information that may be hidden from a particular panoramic view by the furniture being removed. The inpainted panoramas are used to texture the mesh. We show that our approach produces higher quality assets than methods that rely on neural radiance fields, which tend to produce blurry low-resolution images, or RGB-D inpainting, which is highly susceptible to hallucinations.
An Empty Room is All We Want: Automatic Defurnishing of Indoor Panoramas
May 06, 2024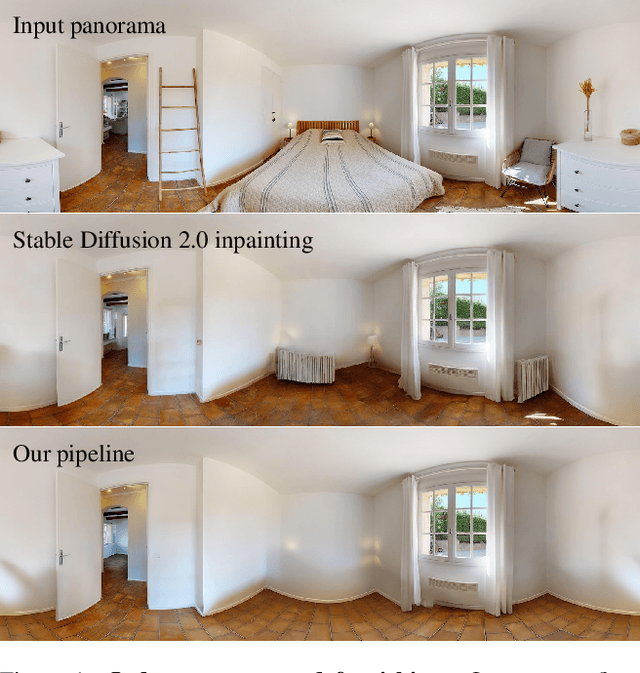
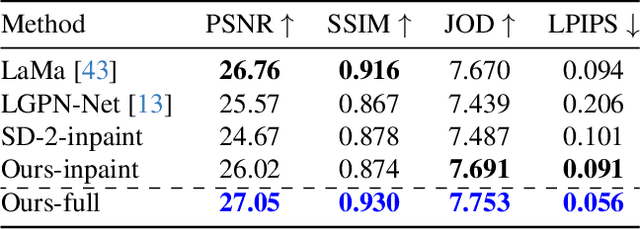
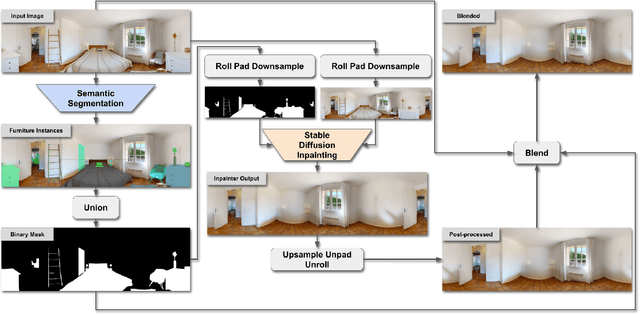

Abstract:We propose a pipeline that leverages Stable Diffusion to improve inpainting results in the context of defurnishing -- the removal of furniture items from indoor panorama images. Specifically, we illustrate how increased context, domain-specific model fine-tuning, and improved image blending can produce high-fidelity inpaints that are geometrically plausible without needing to rely on room layout estimation. We demonstrate qualitative and quantitative improvements over other furniture removal techniques.
Self-supervised Neural Articulated Shape and Appearance Models
May 17, 2022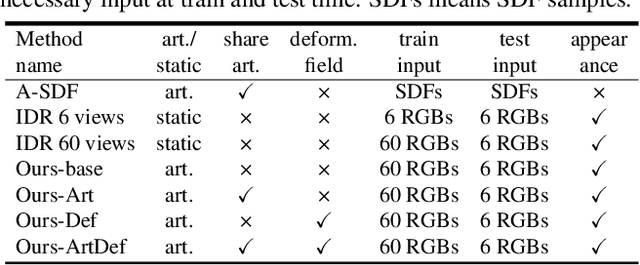
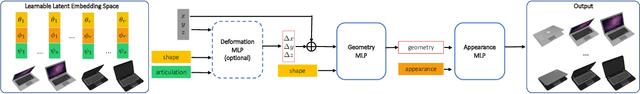
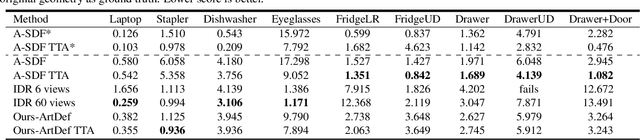
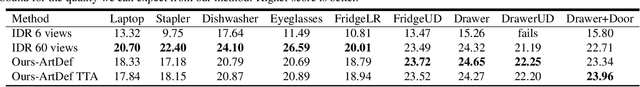
Abstract:Learning geometry, motion, and appearance priors of object classes is important for the solution of a large variety of computer vision problems. While the majority of approaches has focused on static objects, dynamic objects, especially with controllable articulation, are less explored. We propose a novel approach for learning a representation of the geometry, appearance, and motion of a class of articulated objects given only a set of color images as input. In a self-supervised manner, our novel representation learns shape, appearance, and articulation codes that enable independent control of these semantic dimensions. Our model is trained end-to-end without requiring any articulation annotations. Experiments show that our approach performs well for different joint types, such as revolute and prismatic joints, as well as different combinations of these joints. Compared to state of the art that uses direct 3D supervision and does not output appearance, we recover more faithful geometry and appearance from 2D observations only. In addition, our representation enables a large variety of applications, such as few-shot reconstruction, the generation of novel articulations, and novel view-synthesis.
Neural 3D Video Synthesis
Mar 03, 2021



Abstract:We propose a novel approach for 3D video synthesis that is able to represent multi-view video recordings of a dynamic real-world scene in a compact, yet expressive representation that enables high-quality view synthesis and motion interpolation. Our approach takes the high quality and compactness of static neural radiance fields in a new direction: to a model-free, dynamic setting. At the core of our approach is a novel time-conditioned neural radiance fields that represents scene dynamics using a set of compact latent codes. To exploit the fact that changes between adjacent frames of a video are typically small and locally consistent, we propose two novel strategies for efficient training of our neural network: 1) An efficient hierarchical training scheme, and 2) an importance sampling strategy that selects the next rays for training based on the temporal variation of the input videos. In combination, these two strategies significantly boost the training speed, lead to fast convergence of the training process, and enable high quality results. Our learned representation is highly compact and able to represent a 10 second 30 FPS multi-view video recording by 18 cameras with a model size of just 28MB. We demonstrate that our method can render high-fidelity wide-angle novel views at over 1K resolution, even for highly complex and dynamic scenes. We perform an extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluation that shows that our approach outperforms the current state of the art. We include additional video and information at: https://neural-3d-video.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge