Mingyuan Liu
TongSIM: A General Platform for Simulating Intelligent Machines
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:As artificial intelligence (AI) rapidly advances, especially in multimodal large language models (MLLMs), research focus is shifting from single-modality text processing to the more complex domains of multimodal and embodied AI. Embodied intelligence focuses on training agents within realistic simulated environments, leveraging physical interaction and action feedback rather than conventionally labeled datasets. Yet, most existing simulation platforms remain narrowly designed, each tailored to specific tasks. A versatile, general-purpose training environment that can support everything from low-level embodied navigation to high-level composite activities, such as multi-agent social simulation and human-AI collaboration, remains largely unavailable. To bridge this gap, we introduce TongSIM, a high-fidelity, general-purpose platform for training and evaluating embodied agents. TongSIM offers practical advantages by providing over 100 diverse, multi-room indoor scenarios as well as an open-ended, interaction-rich outdoor town simulation, ensuring broad applicability across research needs. Its comprehensive evaluation framework and benchmarks enable precise assessment of agent capabilities, such as perception, cognition, decision-making, human-robot cooperation, and spatial and social reasoning. With features like customized scenes, task-adaptive fidelity, diverse agent types, and dynamic environmental simulation, TongSIM delivers flexibility and scalability for researchers, serving as a unified platform that accelerates training, evaluation, and advancement toward general embodied intelligence.
Sparsity- and Hybridity-Inspired Visual Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Medical Diagnosis
May 28, 2024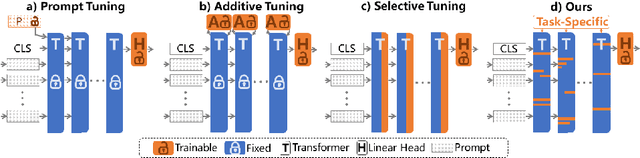
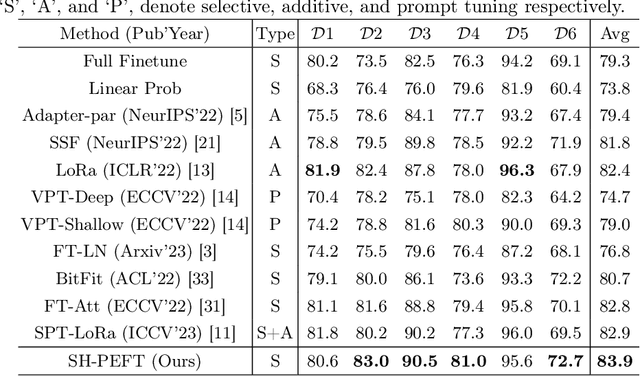
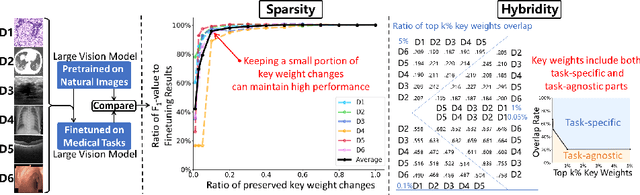
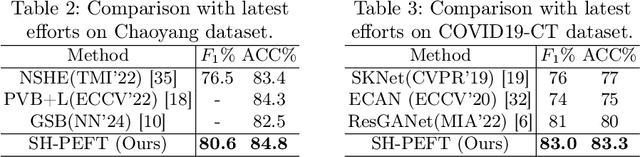
Abstract:The success of Large Vision Models (LVMs) is accompanied by vast data volumes, which are prohibitively expensive in medical diagnosis.To address this, recent efforts exploit Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT), which trains a small number of weights while freezing the rest.However, they typically assign trainable weights to the same positions in LVMs in a heuristic manner, regardless of task differences, making them suboptimal for professional applications like medical diagnosis.To address this, we statistically reveal the nature of sparsity and hybridity during diagnostic-targeted fine-tuning, i.e., a small portion of key weights significantly impacts performance, and these key weights are hybrid, including both task-specific and task-agnostic parts.Based on this, we propose a novel Sparsity- and Hybridity-inspired Parameter Efficient Fine-Tuning (SH-PEFT).It selects and trains a small portion of weights based on their importance, which is innovatively estimated by hybridizing both task-specific and task-agnostic strategies.Validated on six medical datasets of different modalities, we demonstrate that SH-PEFT achieves state-of-the-art performance in transferring LVMs to medical diagnosis in terms of accuracy. By tuning around 0.01% number of weights, it outperforms full model fine-tuning.Moreover, SH-PEFT also achieves comparable performance to other models deliberately optimized for specific medical tasks.Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of each design and reveal that large model transfer holds great potential in medical diagnosis.
Streamlined Photoacoustic Image Processing with Foundation Models: A Training-Free Solution
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:Foundation models have rapidly evolved and have achieved significant accomplishments in computer vision tasks. Specifically, the prompt mechanism conveniently allows users to integrate image prior information into the model, making it possible to apply models without any training. Therefore, we propose a method based on foundation models and zero training to solve the tasks of photoacoustic (PA) image segmentation. We employed the segment anything model (SAM) by setting simple prompts and integrating the model's outputs with prior knowledge of the imaged objects to accomplish various tasks, including: (1) removing the skin signal in three-dimensional PA image rendering; (2) dual speed-of-sound reconstruction, and (3) segmentation of finger blood vessels. Through these demonstrations, we have concluded that deep learning can be directly applied in PA imaging without the requirement for network design and training. This potentially allows for a hands-on, convenient approach to achieving efficient and accurate segmentation of PA images. This letter serves as a comprehensive tutorial, facilitating the mastery of the technique through the provision of code and sample datasets.
Learning Large Margin Sparse Embeddings for Open Set Medical Diagnosis
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:Fueled by deep learning, computer-aided diagnosis achieves huge advances. However, out of controlled lab environments, algorithms could face multiple challenges. Open set recognition (OSR), as an important one, states that categories unseen in training could appear in testing. In medical fields, it could derive from incompletely collected training datasets and the constantly emerging new or rare diseases. OSR requires an algorithm to not only correctly classify known classes, but also recognize unknown classes and forward them to experts for further diagnosis. To tackle OSR, we assume that known classes could densely occupy small parts of the embedding space and the remaining sparse regions could be recognized as unknowns. Following it, we propose Open Margin Cosine Loss (OMCL) unifying two mechanisms. The former, called Margin Loss with Adaptive Scale (MLAS), introduces angular margin for reinforcing intra-class compactness and inter-class separability, together with an adaptive scaling factor to strengthen the generalization capacity. The latter, called Open-Space Suppression (OSS), opens the classifier by recognizing sparse embedding space as unknowns using proposed feature space descriptors. Besides, since medical OSR is still a nascent field, two publicly available benchmark datasets are proposed for comparison. Extensive ablation studies and feature visualization demonstrate the effectiveness of each design. Compared with state-of-the-art methods, MLAS achieves superior performances, measured by ACC, AUROC, and OSCR.
Gland Instance Segmentation Using Deep Multichannel Neural Networks
Nov 23, 2017



Abstract:Objective: A new image instance segmentation method is proposed to segment individual glands (instances) in colon histology images. This process is challenging since the glands not only need to be segmented from a complex background, they must also be individually identified. Methods: We leverage the idea of image-to-image prediction in recent deep learning by designing an algorithm that automatically exploits and fuses complex multichannel information - regional, location, and boundary cues - in gland histology images. Our proposed algorithm, a deep multichannel framework, alleviates heavy feature design due to the use of convolutional neural networks and is able to meet multifarious requirements by altering channels. Results: Compared with methods reported in the 2015 MICCAI Gland Segmentation Challenge and other currently prevalent instance segmentation methods, we observe state-of-the-art results based on the evaluation metrics. Conclusion: The proposed deep multichannel algorithm is an effective method for gland instance segmentation. Significance: The generalization ability of our model not only enable the algorithm to solve gland instance segmentation problems, but the channel is also alternative that can be replaced for a specific task.
* arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:1607.04889
Gland Instance Segmentation by Deep Multichannel Neural Networks
Jul 19, 2016



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new image instance segmentation method that segments individual glands (instances) in colon histology images. This is a task called instance segmentation that has recently become increasingly important. The problem is challenging since not only do the glands need to be segmented from the complex background, they are also required to be individually identified. Here we leverage the idea of image-to-image prediction in recent deep learning by building a framework that automatically exploits and fuses complex multichannel information, regional, location and boundary patterns in gland histology images. Our proposed system, deep multichannel framework, alleviates heavy feature design due to the use of convolutional neural networks and is able to meet multifarious requirement by altering channels. Compared to methods reported in the 2015 MICCAI Gland Segmentation Challenge and other currently prevalent methods of instance segmentation, we observe state-of-the-art results based on a number of evaluation metrics.
Gland Instance Segmentation by Deep Multichannel Side Supervision
Jul 14, 2016



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new image instance segmentation method that segments individual glands (instances) in colon histology images. This is a task called instance segmentation that has recently become increasingly important. The problem is challenging since not only do the glands need to be segmented from the complex background, they are also required to be individually identified. Here we leverage the idea of image-to-image prediction in recent deep learning by building a framework that automatically exploits and fuses complex multichannel information, regional and boundary patterns, with side supervision (deep supervision on side responses) in gland histology images. Our proposed system, deep multichannel side supervision (DMCS), alleviates heavy feature design due to the use of convolutional neural networks guided by side supervision. Compared to methods reported in the 2015 MICCAI Gland Segmentation Challenge, we observe state-of-the-art results based on a number of evaluation metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge