Michal Marcinkiewicz
ScaleFold: Reducing AlphaFold Initial Training Time to 10 Hours
Apr 17, 2024



Abstract:AlphaFold2 has been hailed as a breakthrough in protein folding. It can rapidly predict protein structures with lab-grade accuracy. However, its implementation does not include the necessary training code. OpenFold is the first trainable public reimplementation of AlphaFold. AlphaFold training procedure is prohibitively time-consuming, and gets diminishing benefits from scaling to more compute resources. In this work, we conducted a comprehensive analysis on the AlphaFold training procedure based on Openfold, identified that inefficient communications and overhead-dominated computations were the key factors that prevented the AlphaFold training from effective scaling. We introduced ScaleFold, a systematic training method that incorporated optimizations specifically for these factors. ScaleFold successfully scaled the AlphaFold training to 2080 NVIDIA H100 GPUs with high resource utilization. In the MLPerf HPC v3.0 benchmark, ScaleFold finished the OpenFold benchmark in 7.51 minutes, shown over $6\times$ speedup than the baseline. For training the AlphaFold model from scratch, ScaleFold completed the pretraining in 10 hours, a significant improvement over the seven days required by the original AlphaFold pretraining baseline.
Optimized U-Net for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Oct 07, 2021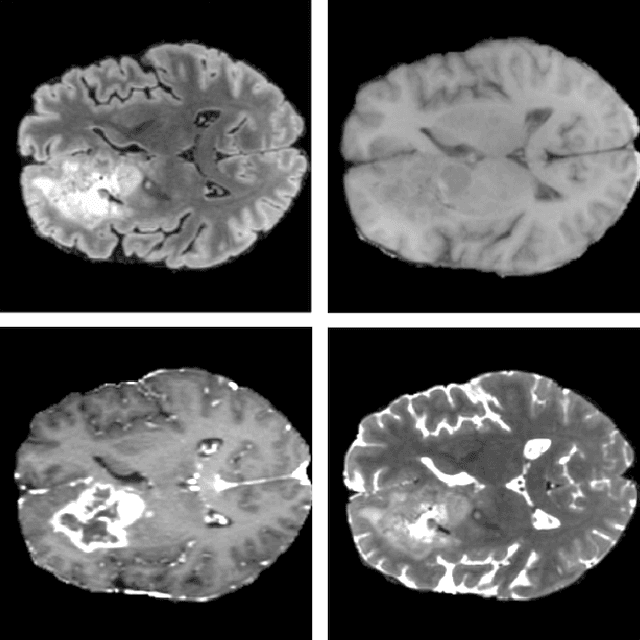
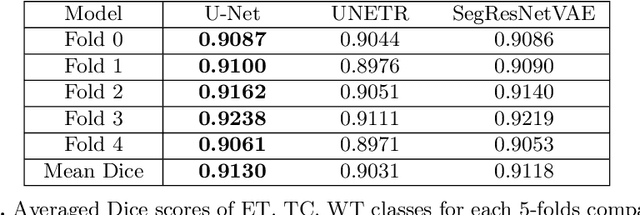
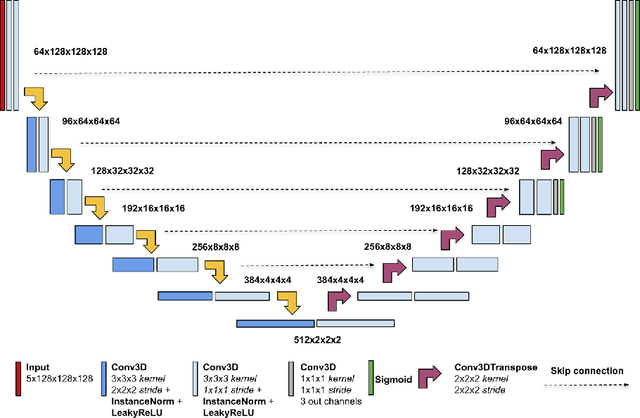
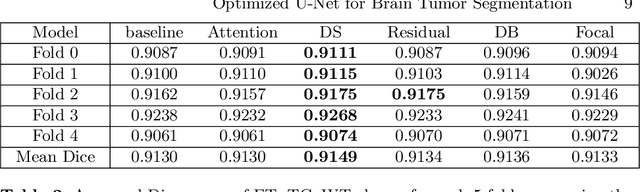
Abstract:We propose an optimized U-Net architecture for a brain \mbox{tumor} segmentation task in the BraTS21 Challenge. To find the \mbox{optimal} model architecture and learning schedule we ran an extensive ablation study to test: deep supervision loss, Focal loss, decoder attention, drop block, and residual connections. Additionally, we have searched for the optimal depth of the U-Net and number of convolutional channels. Our solution was the winner of the challenge validation phase, with the normalized statistical ranking score of 0.267 and mean Dice score of 0.8855
Fully-automated deep learning-powered system for DCE-MRI analysis of brain tumors
Jul 18, 2019



Abstract:Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) plays an important role in diagnosis and grading of brain tumor. Although manual DCE biomarker extraction algorithms boost the diagnostic yield of DCE-MRI by providing quantitative information on tumor prognosis and prediction, they are time-consuming and prone to human error. In this paper, we propose a fully-automated, end-to-end system for DCE-MRI analysis of brain tumors. Our deep learning-powered technique does not require any user interaction, it yields reproducible results, and it is rigorously validated against benchmark (BraTS'17 for tumor segmentation, and a test dataset released by the Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers Alliance for the contrast-concentration fitting) and clinical (44 low-grade glioma patients) data. Also, we introduce a cubic model of the vascular input function used for pharmacokinetic modeling which significantly decreases the fitting error when compared with the state of the art, alongside a real-time algorithm for determination of the vascular input region. An extensive experimental study, backed up with statistical tests, showed that our system delivers state-of-the-art results (in terms of segmentation accuracy and contrast-concentration fitting) while requiring less than 3 minutes to process an entire input DCE-MRI study using a single GPU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge