Michael Uder
Adapted Foundation Models for Breast MRI Triaging in Contrast-Enhanced and Non-Contrast Enhanced Protocols
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has high sensitivity for breast cancer detection, but interpretation is time-consuming. Artificial intelligence may aid in pre-screening. Purpose: To evaluate the DINOv2-based Medical Slice Transformer (MST) for ruling out significant findings (Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System [BI-RADS] >=4) in contrast-enhanced and non-contrast-enhanced abbreviated breast MRI. Materials and Methods: This institutional review board approved retrospective study included 1,847 single-breast MRI examinations (377 BI-RADS >=4) from an in-house dataset and 924 from an external validation dataset (Duke). Four abbreviated protocols were tested: T1-weighted early subtraction (T1sub), diffusion-weighted imaging with b=1500 s/mm2 (DWI1500), DWI1500+T2-weighted (T2w), and T1sub+T2w. Performance was assessed at 90%, 95%, and 97.5% sensitivity using five-fold cross-validation and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) analysis. AUC differences were compared with the DeLong test. False negatives were characterized, and attention maps of true positives were rated in the external dataset. Results: A total of 1,448 female patients (mean age, 49 +/- 12 years) were included. T1sub+T2w achieved an AUC of 0.77 +/- 0.04; DWI1500+T2w, 0.74 +/- 0.04 (p=0.15). At 97.5% sensitivity, T1sub+T2w had the highest specificity (19% +/- 7%), followed by DWI1500+T2w (17% +/- 11%). Missed lesions had a mean diameter <10 mm at 95% and 97.5% thresholds for both T1sub and DWI1500, predominantly non-mass enhancements. External validation yielded an AUC of 0.77, with 88% of attention maps rated good or moderate. Conclusion: At 97.5% sensitivity, the MST framework correctly triaged cases without BI-RADS >=4, achieving 19% specificity for contrast-enhanced and 17% for non-contrast-enhanced MRI. Further research is warranted before clinical implementation.
PoCaP Corpus: A Multimodal Dataset for Smart Operating Room Speech Assistant using Interventional Radiology Workflow Analysis
Jun 24, 2022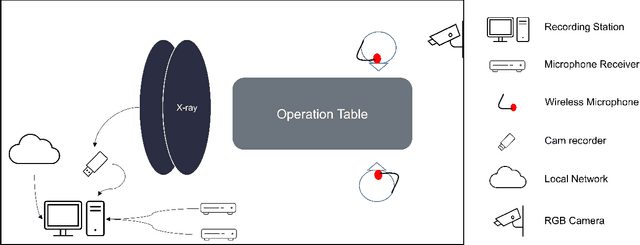
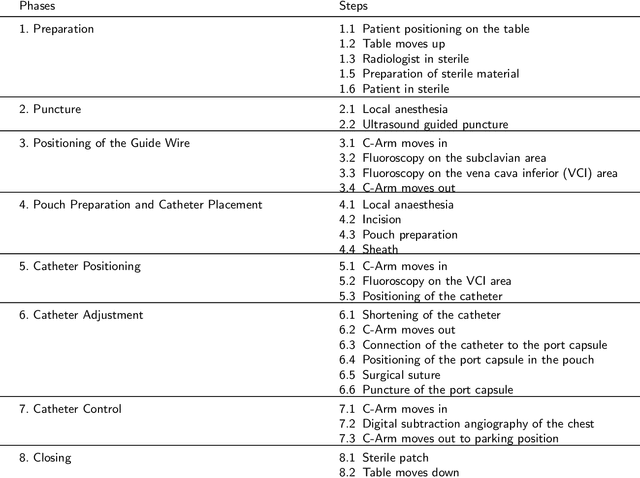
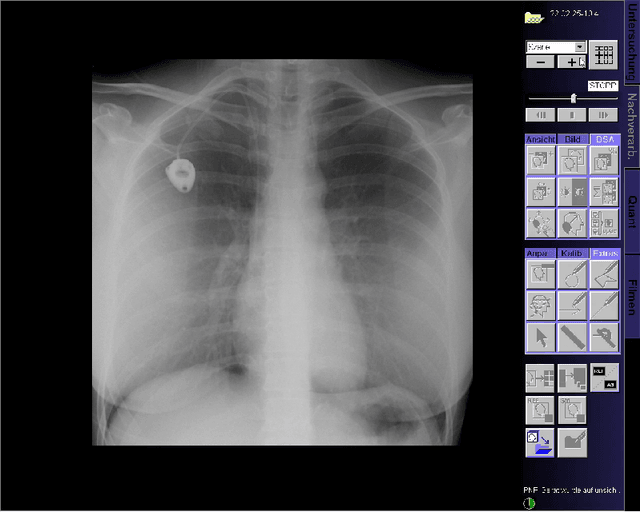
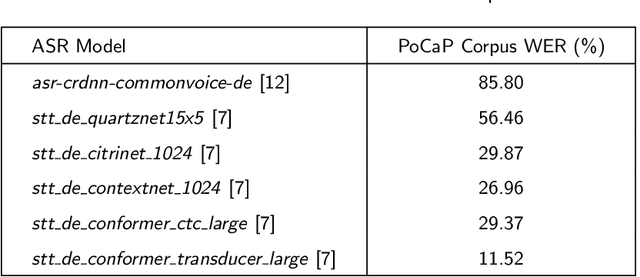
Abstract:This paper presents a new multimodal interventional radiology dataset, called PoCaP (Port Catheter Placement) Corpus. This corpus consists of speech and audio signals in German, X-ray images, and system commands collected from 31 PoCaP interventions by six surgeons with average duration of 81.4 $\pm$ 41.0 minutes. The corpus aims to provide a resource for developing a smart speech assistant in operating rooms. In particular, it may be used to develop a speech controlled system that enables surgeons to control the operation parameters such as C-arm movements and table positions. In order to record the dataset, we acquired consent by the institutional review board and workers council in the University Hospital Erlangen and by the patients for data privacy. We describe the recording set-up, data structure, workflow and preprocessing steps, and report the first PoCaP Corpus speech recognition analysis results with 11.52 $\%$ word error rate using pretrained models. The findings suggest that the data has the potential to build a robust command recognition system and will allow the development of a novel intervention support systems using speech and image processing in the medical domain.
Deep learning for brain metastasis detection and segmentation in longitudinal MRI data
Dec 28, 2021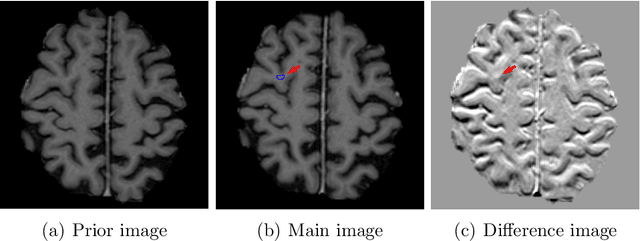
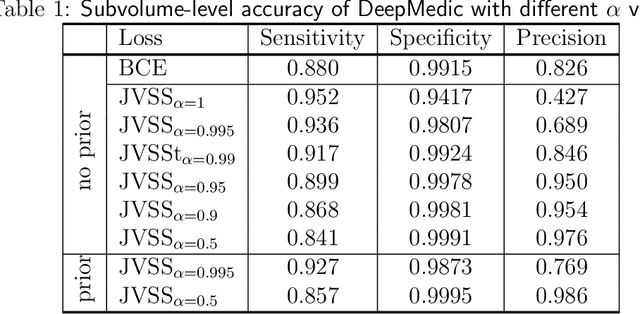
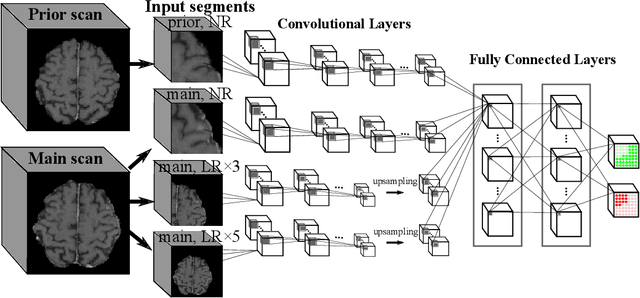
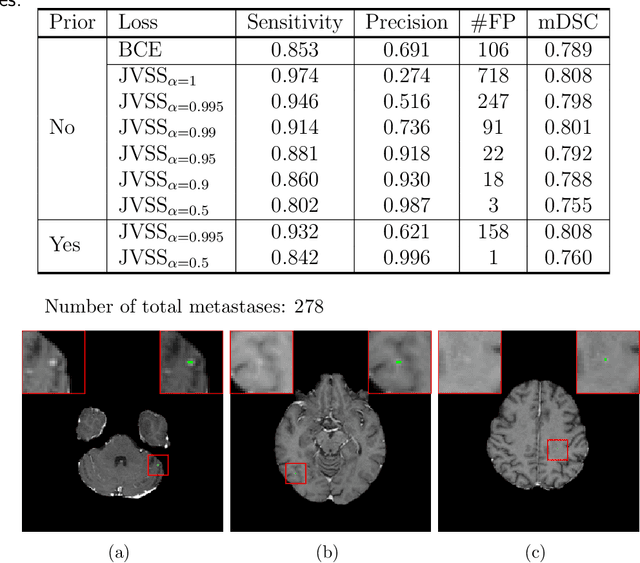
Abstract:Brain metastases occur frequently in patients with metastatic cancer. Early and accurate detection of brain metastases is very essential for treatment planning and prognosis in radiation therapy. To improve brain metastasis detection performance with deep learning, a custom detection loss called volume-level sensitivity-specificity (VSS) is proposed, which rates individual metastasis detection sensitivity and specificity in (sub-)volume levels. As sensitivity and precision are always a trade-off in a metastasis level, either a high sensitivity or a high precision can be achieved by adjusting the weights in the VSS loss without decline in dice score coefficient for segmented metastases. To reduce metastasis-like structures being detected as false positive metastases, a temporal prior volume is proposed as an additional input of the neural network. Our proposed VSS loss improves the sensitivity of brain metastasis detection, increasing the sensitivity from 86.7% to 95.5%. Alternatively, it improves the precision from 68.8% to 97.8%. With the additional temporal prior volume, about 45% of the false positive metastases are reduced in the high sensitivity model and the precision reaches 99.6% for the high specificity model. The mean dice coefficient for all metastases is about 0.81. With the ensemble of the high sensitivity and high specificity models, on average only 1.5 false positive metastases per patient needs further check, while the majority of true positive metastases are confirmed. The ensemble learning is able to distinguish high confidence true positive metastases from metastases candidates that require special expert review or further follow-up, being particularly well-fit to the requirements of expert support in real clinical practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge