Mengfei Du
RoboBrain 2.0 Technical Report
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.0, our latest generation of embodied vision-language foundation models, designed to unify perception, reasoning, and planning for complex embodied tasks in physical environments. It comes in two variants: a lightweight 7B model and a full-scale 32B model, featuring a heterogeneous architecture with a vision encoder and a language model. Despite its compact size, RoboBrain 2.0 achieves strong performance across a wide spectrum of embodied reasoning tasks. On both spatial and temporal benchmarks, the 32B variant achieves leading results, surpassing prior open-source and proprietary models. In particular, it supports key real-world embodied AI capabilities, including spatial understanding (e.g., affordance prediction, spatial referring, trajectory forecasting) and temporal decision-making (e.g., closed-loop interaction, multi-agent long-horizon planning, and scene graph updating). This report details the model architecture, data construction, multi-stage training strategies, infrastructure and practical applications. We hope RoboBrain 2.0 advances embodied AI research and serves as a practical step toward building generalist embodied agents. The code, checkpoint and benchmark are available at https://superrobobrain.github.io.
Seed1.5-VL Technical Report
May 11, 2025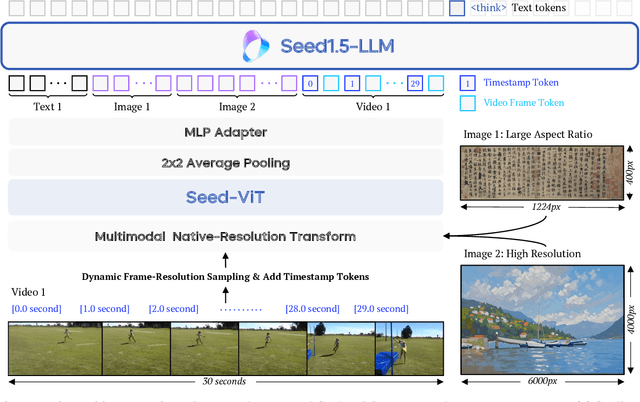

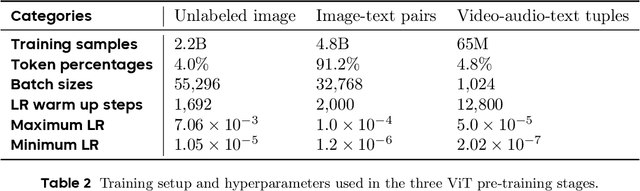
Abstract:We present Seed1.5-VL, a vision-language foundation model designed to advance general-purpose multimodal understanding and reasoning. Seed1.5-VL is composed with a 532M-parameter vision encoder and a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) LLM of 20B active parameters. Despite its relatively compact architecture, it delivers strong performance across a wide spectrum of public VLM benchmarks and internal evaluation suites, achieving the state-of-the-art performance on 38 out of 60 public benchmarks. Moreover, in agent-centric tasks such as GUI control and gameplay, Seed1.5-VL outperforms leading multimodal systems, including OpenAI CUA and Claude 3.7. Beyond visual and video understanding, it also demonstrates strong reasoning abilities, making it particularly effective for multimodal reasoning challenges such as visual puzzles. We believe these capabilities will empower broader applications across diverse tasks. In this report, we mainly provide a comprehensive review of our experiences in building Seed1.5-VL across model design, data construction, and training at various stages, hoping that this report can inspire further research. Seed1.5-VL is now accessible at https://www.volcengine.com/ (Volcano Engine Model ID: doubao-1-5-thinking-vision-pro-250428)
Qwen2-VL: Enhancing Vision-Language Model's Perception of the World at Any Resolution
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:We present the Qwen2-VL Series, an advanced upgrade of the previous Qwen-VL models that redefines the conventional predetermined-resolution approach in visual processing. Qwen2-VL introduces the Naive Dynamic Resolution mechanism, which enables the model to dynamically process images of varying resolutions into different numbers of visual tokens. This approach allows the model to generate more efficient and accurate visual representations, closely aligning with human perceptual processes. The model also integrates Multimodal Rotary Position Embedding (M-RoPE), facilitating the effective fusion of positional information across text, images, and videos. We employ a unified paradigm for processing both images and videos, enhancing the model's visual perception capabilities. To explore the potential of large multimodal models, Qwen2-VL investigates the scaling laws for large vision-language models (LVLMs). By scaling both the model size-with versions at 2B, 8B, and 72B parameters-and the amount of training data, the Qwen2-VL Series achieves highly competitive performance. Notably, the Qwen2-VL-72B model achieves results comparable to leading models such as GPT-4o and Claude3.5-Sonnet across various multimodal benchmarks, outperforming other generalist models. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/QwenLM/Qwen2-VL}.
EmbSpatial-Bench: Benchmarking Spatial Understanding for Embodied Tasks with Large Vision-Language Models
Jun 09, 2024



Abstract:The recent rapid development of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) has indicated their potential for embodied tasks.However, the critical skill of spatial understanding in embodied environments has not been thoroughly evaluated, leaving the gap between current LVLMs and qualified embodied intelligence unknown. Therefore, we construct EmbSpatial-Bench, a benchmark for evaluating embodied spatial understanding of LVLMs.The benchmark is automatically derived from embodied scenes and covers 6 spatial relationships from an egocentric perspective.Experiments expose the insufficient capacity of current LVLMs (even GPT-4V). We further present EmbSpatial-SFT, an instruction-tuning dataset designed to improve LVLMs' embodied spatial understanding.
DELAN: Dual-Level Alignment for Vision-and-Language Navigation by Cross-Modal Contrastive Learning
Apr 02, 2024



Abstract:Vision-and-Language navigation (VLN) requires an agent to navigate in unseen environment by following natural language instruction. For task completion, the agent needs to align and integrate various navigation modalities, including instruction, observation and navigation history. Existing works primarily concentrate on cross-modal attention at the fusion stage to achieve this objective. Nevertheless, modality features generated by disparate uni-encoders reside in their own spaces, leading to a decline in the quality of cross-modal fusion and decision. To address this problem, we propose a Dual-levEL AligNment (DELAN) framework by cross-modal contrastive learning. This framework is designed to align various navigation-related modalities before fusion, thereby enhancing cross-modal interaction and action decision-making. Specifically, we divide the pre-fusion alignment into dual levels: instruction-history level and landmark-observation level according to their semantic correlations. We also reconstruct a dual-level instruction for adaptation to the dual-level alignment. As the training signals for pre-fusion alignment are extremely limited, self-supervised contrastive learning strategies are employed to enforce the matching between different modalities. Our approach seamlessly integrates with the majority of existing models, resulting in improved navigation performance on various VLN benchmarks, including R2R, R4R, RxR and CVDN.
ReForm-Eval: Evaluating Large Vision Language Models via Unified Re-Formulation of Task-Oriented Benchmarks
Oct 17, 2023



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed remarkable progress in the development of large vision-language models (LVLMs). Benefiting from the strong language backbones and efficient cross-modal alignment strategies, LVLMs exhibit surprising capabilities to perceive visual signals and perform visually grounded reasoning. However, the capabilities of LVLMs have not been comprehensively and quantitatively evaluate. Most existing multi-modal benchmarks require task-oriented input-output formats, posing great challenges to automatically assess the free-form text output of LVLMs. To effectively leverage the annotations available in existing benchmarks and reduce the manual effort required for constructing new benchmarks, we propose to re-formulate existing benchmarks into unified LVLM-compatible formats. Through systematic data collection and reformulation, we present the ReForm-Eval benchmark, offering substantial data for evaluating various capabilities of LVLMs. Based on ReForm-Eval, we conduct extensive experiments, thoroughly analyze the strengths and weaknesses of existing LVLMs, and identify the underlying factors. Our benchmark and evaluation framework will be open-sourced as a cornerstone for advancing the development of LVLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge