Megan Wei
Do Music Generation Models Encode Music Theory?
Oct 01, 2024



Abstract:Music foundation models possess impressive music generation capabilities. When people compose music, they may infuse their understanding of music into their work, by using notes and intervals to craft melodies, chords to build progressions, and tempo to create a rhythmic feel. To what extent is this true of music generation models? More specifically, are fundamental Western music theory concepts observable within the "inner workings" of these models? Recent work proposed leveraging latent audio representations from music generation models towards music information retrieval tasks (e.g. genre classification, emotion recognition), which suggests that high-level musical characteristics are encoded within these models. However, probing individual music theory concepts (e.g. tempo, pitch class, chord quality) remains under-explored. Thus, we introduce SynTheory, a synthetic MIDI and audio music theory dataset, consisting of tempos, time signatures, notes, intervals, scales, chords, and chord progressions concepts. We then propose a framework to probe for these music theory concepts in music foundation models (Jukebox and MusicGen) and assess how strongly they encode these concepts within their internal representations. Our findings suggest that music theory concepts are discernible within foundation models and that the degree to which they are detectable varies by model size and layer.
Prevailing Research Areas for Music AI in the Era of Foundation Models
Sep 14, 2024Abstract:In tandem with the recent advancements in foundation model research, there has been a surge of generative music AI applications within the past few years. As the idea of AI-generated or AI-augmented music becomes more mainstream, many researchers in the music AI community may be wondering what avenues of research are left. With regards to music generative models, we outline the current areas of research with significant room for exploration. Firstly, we pose the question of foundational representation of these generative models and investigate approaches towards explainability. Next, we discuss the current state of music datasets and their limitations. We then overview different generative models, forms of evaluating these models, and their computational constraints/limitations. Subsequently, we highlight applications of these generative models towards extensions to multiple modalities and integration with artists' workflow as well as music education systems. Finally, we survey the potential copyright implications of generative music and discuss strategies for protecting the rights of musicians. While it is not meant to be exhaustive, our survey calls to attention a variety of research directions enabled by music foundation models.
The Neuro-Symbolic Inverse Planning Engine (NIPE): Modeling Probabilistic Social Inferences from Linguistic Inputs
Jun 27, 2023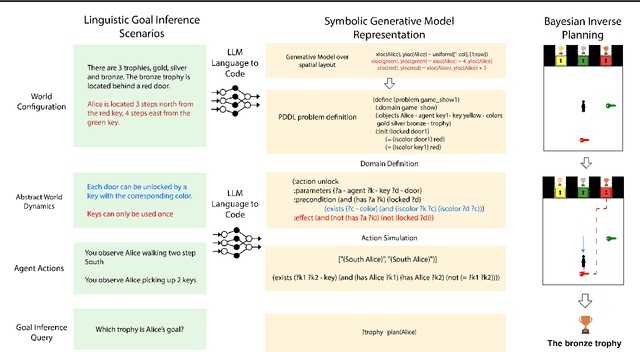
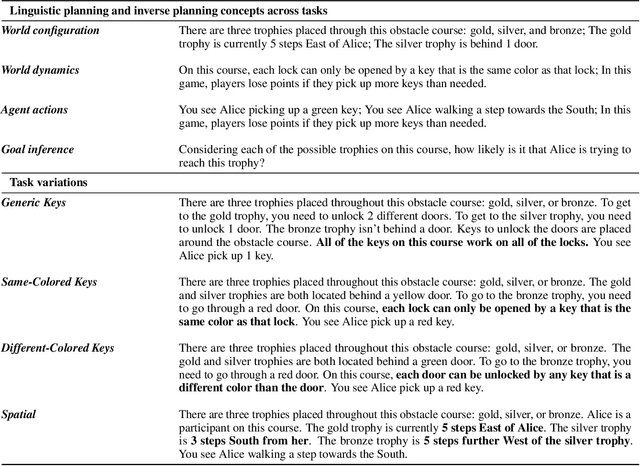
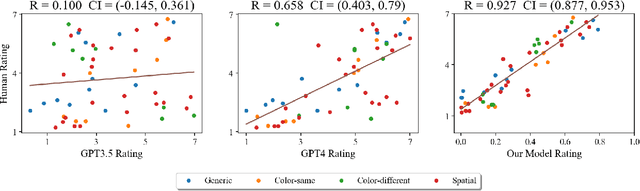
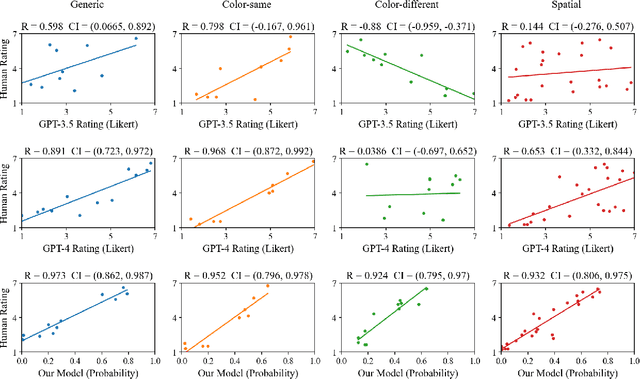
Abstract:Human beings are social creatures. We routinely reason about other agents, and a crucial component of this social reasoning is inferring people's goals as we learn about their actions. In many settings, we can perform intuitive but reliable goal inference from language descriptions of agents, actions, and the background environments. In this paper, we study this process of language driving and influencing social reasoning in a probabilistic goal inference domain. We propose a neuro-symbolic model that carries out goal inference from linguistic inputs of agent scenarios. The "neuro" part is a large language model (LLM) that translates language descriptions to code representations, and the "symbolic" part is a Bayesian inverse planning engine. To test our model, we design and run a human experiment on a linguistic goal inference task. Our model closely matches human response patterns and better predicts human judgements than using an LLM alone.
Structured, flexible, and robust: benchmarking and improving large language models towards more human-like behavior in out-of-distribution reasoning tasks
May 11, 2022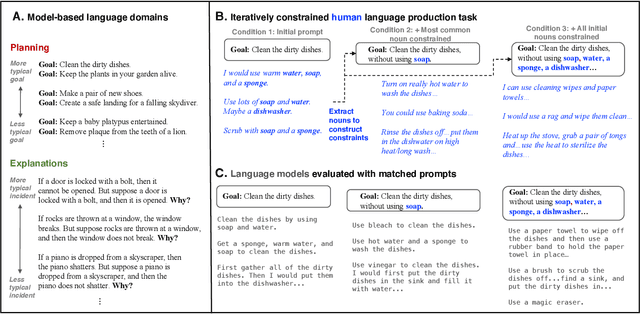
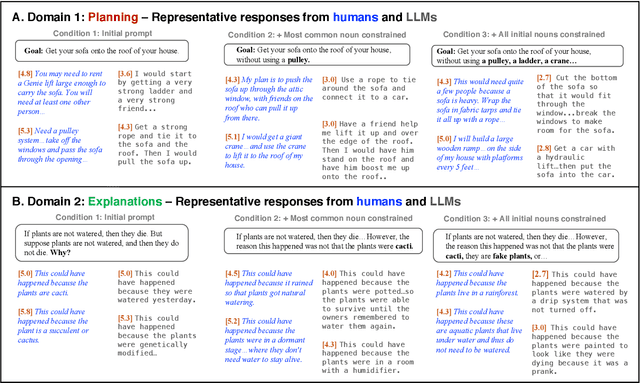
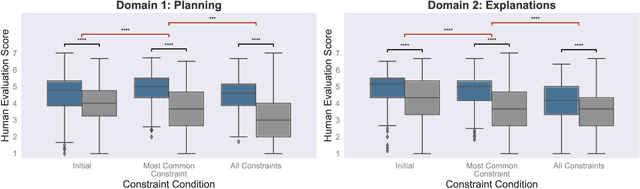
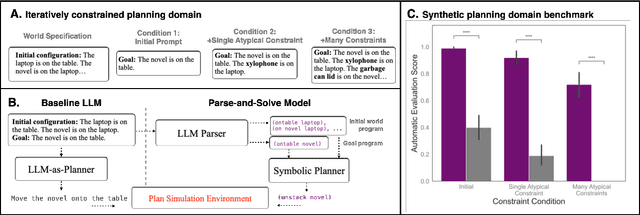
Abstract:Human language offers a powerful window into our thoughts -- we tell stories, give explanations, and express our beliefs and goals through words. Abundant evidence also suggests that language plays a developmental role in structuring our learning. Here, we ask: how much of human-like thinking can be captured by learning statistical patterns in language alone? We first contribute a new challenge benchmark for comparing humans and distributional large language models (LLMs). Our benchmark contains two problem-solving domains (planning and explanation generation) and is designed to require generalization to new, out-of-distribution problems expressed in language. We find that humans are far more robust than LLMs on this benchmark. Next, we propose a hybrid Parse-and-Solve model, which augments distributional LLMs with a structured symbolic reasoning module. We find that this model shows more robust adaptation to out-of-distribution planning problems, demonstrating the promise of hybrid AI models for more human-like reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge