Maximilian Springenberg
DiffScale: Continuous Downscaling and Bias Correction of Subseasonal Wind Speed Forecasts using Diffusion Models
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Renewable resources are strongly dependent on local and large-scale weather situations. Skillful subseasonal to seasonal (S2S) forecasts -- beyond two weeks and up to two months -- can offer significant socioeconomic advantages to the energy sector. This study aims to enhance wind speed predictions using a diffusion model with classifier-free guidance to downscale S2S forecasts of surface wind speed. We propose DiffScale, a diffusion model that super-resolves spatial information for continuous downscaling factors and lead times. Leveraging weather priors as guidance for the generative process of diffusion models, we adopt the perspective of conditional probabilities on sampling super-resolved S2S forecasts. We aim to directly estimate the density associated with the target S2S forecasts at different spatial resolutions and lead times without auto-regression or sequence prediction, resulting in an efficient and flexible model. Synthetic experiments were designed to super-resolve wind speed S2S forecasts from the European Center for Medium-Range Weather Forecast (ECMWF) from a coarse resolution to a finer resolution of ERA5 reanalysis data, which serves as a high-resolution target. The innovative aspect of DiffScale lies in its flexibility to downscale arbitrary scaling factors, enabling it to generalize across various grid resolutions and lead times -without retraining the model- while correcting model errors, making it a versatile tool for improving S2S wind speed forecasts. We achieve a significant improvement in prediction quality, outperforming baselines up to week 3.
Generative Fractional Diffusion Models
Oct 26, 2023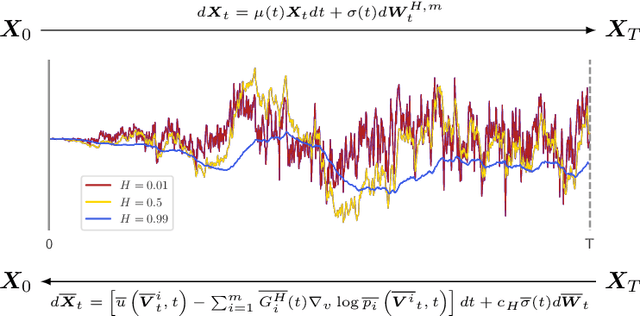

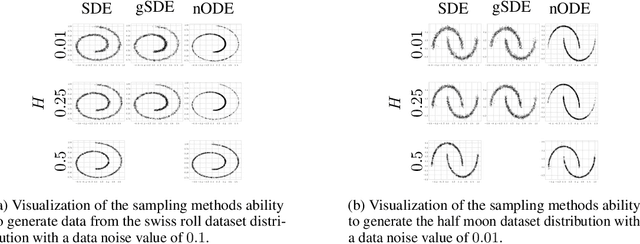

Abstract:We generalize the continuous time framework for score-based generative models from an underlying Brownian motion (BM) to an approximation of fractional Brownian motion (FBM). We derive a continuous reparameterization trick and the reverse time model by representing FBM as a stochastic integral over a family of Ornstein-Uhlenbeck processes to define generative fractional diffusion models (GFDM) with driving noise converging to a non-Markovian process of infinite quadratic variation. The Hurst index $H\in(0,1)$ of FBM enables control of the roughness of the distribution transforming path. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to build a generative model upon a stochastic process with infinite quadratic variation.
From CNNs to Vision Transformers -- A Comprehensive Evaluation of Deep Learning Models for Histopathology
Apr 11, 2022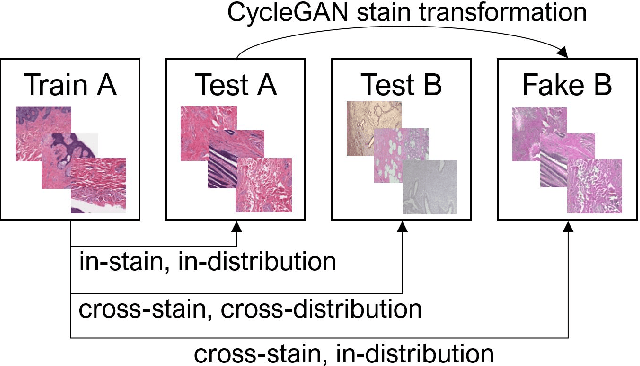



Abstract:While machine learning is currently transforming the field of histopathology, the domain lacks a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art models based on essential but complementary quality requirements beyond a mere classification accuracy. In order to fill this gap, we conducted an extensive evaluation by benchmarking a wide range of classification models, including recent vision transformers, convolutional neural networks and hybrid models comprising transformer and convolutional models. We thoroughly tested the models on five widely used histopathology datasets containing whole slide images of breast, gastric, and colorectal cancer and developed a novel approach using an image-to-image translation model to assess the robustness of a cancer classification model against stain variations. Further, we extended existing interpretability methods to previously unstudied models and systematically reveal insights of the models' classification strategies that allow for plausibility checks and systematic comparisons. The study resulted in specific model recommendations for practitioners as well as putting forward a general methodology to quantify a model's quality according to complementary requirements that can be transferred to future model architectures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge