Max Eichler
Document Structure in Long Document Transformers
Jan 31, 2024
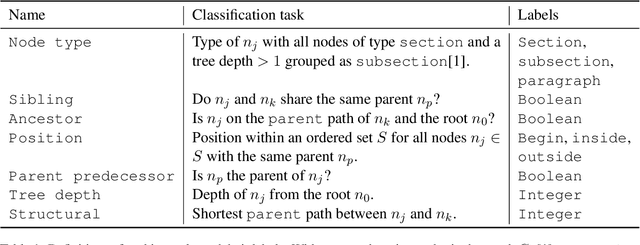

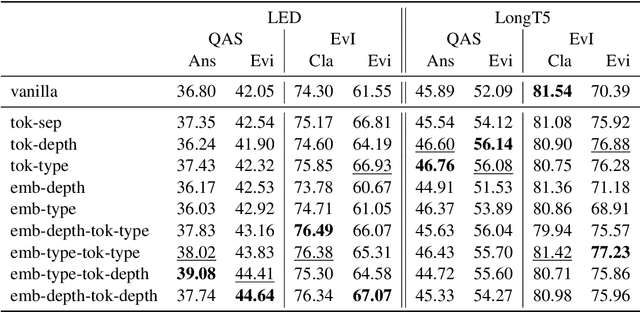
Abstract:Long documents often exhibit structure with hierarchically organized elements of different functions, such as section headers and paragraphs. Despite the omnipresence of document structure, its role in natural language processing (NLP) remains opaque. Do long-document Transformer models acquire an internal representation of document structure during pre-training? How can structural information be communicated to a model after pre-training, and how does it influence downstream performance? To answer these questions, we develop a novel suite of probing tasks to assess structure-awareness of long-document Transformers, propose general-purpose structure infusion methods, and evaluate the effects of structure infusion on QASPER and Evidence Inference, two challenging long-document NLP tasks. Results on LED and LongT5 suggest that they acquire implicit understanding of document structure during pre-training, which can be further enhanced by structure infusion, leading to improved end-task performance. To foster research on the role of document structure in NLP modeling, we make our data and code publicly available.
Revise and Resubmit: An Intertextual Model of Text-based Collaboration in Peer Review
Apr 22, 2022



Abstract:Peer review is a key component of the publishing process in most fields of science. The increasing submission rates put a strain on reviewing quality and efficiency, motivating the development of applications to support the reviewing and editorial work. While existing NLP studies focus on the analysis of individual texts, editorial assistance often requires modeling interactions between pairs of texts -- yet general frameworks and datasets to support this scenario are missing. Relationships between texts are the core object of the intertextuality theory -- a family of approaches in literary studies not yet operationalized in NLP. Inspired by prior theoretical work, we propose the first intertextual model of text-based collaboration, which encompasses three major phenomena that make up a full iteration of the review-revise-and-resubmit cycle: pragmatic tagging, linking and long-document version alignment. While peer review is used across the fields of science and publication formats, existing datasets solely focus on conference-style review in computer science. Addressing this, we instantiate our proposed model in the first annotated multi-domain corpus in journal-style post-publication open peer review, and provide detailed insights into the practical aspects of intertextual annotation. Our resource is a major step towards multi-domain, fine-grained applications of NLP in editorial support for peer review, and our intertextual framework paves the path for general-purpose modeling of text-based collaboration.
UKP-SQUARE: An Online Platform for Question Answering Research
Mar 28, 2022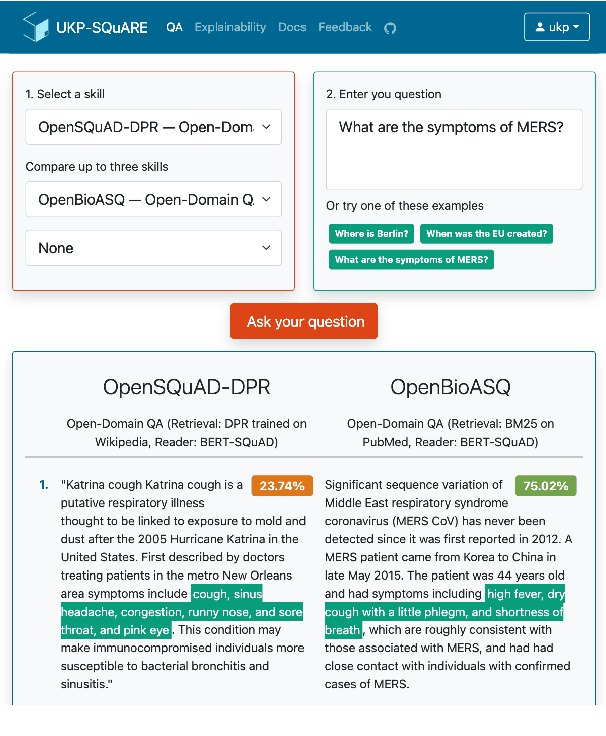
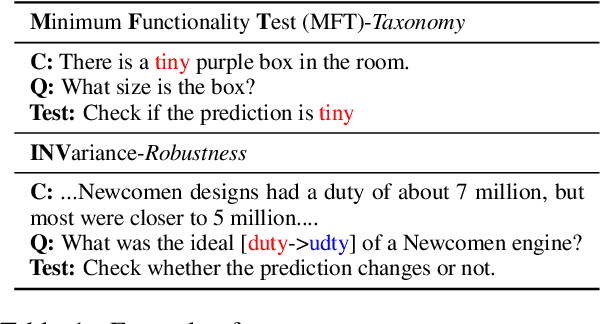
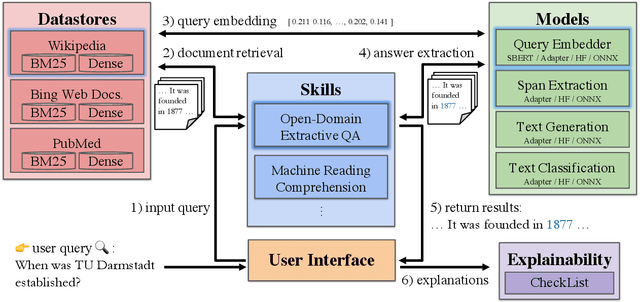
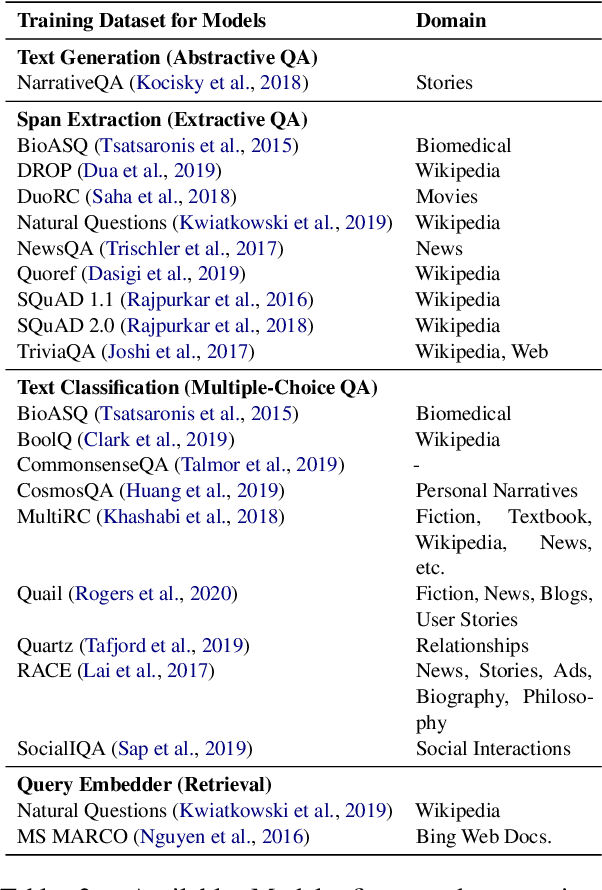
Abstract:Recent advances in NLP and information retrieval have given rise to a diverse set of question answering tasks that are of different formats (e.g., extractive, abstractive), require different model architectures (e.g., generative, discriminative), and setups (e.g., with or without retrieval). Despite having a large number of powerful, specialized QA pipelines (which we refer to as Skills) that consider a single domain, model or setup, there exists no framework where users can easily explore and compare such pipelines and can extend them according to their needs. To address this issue, we present UKP-SQUARE, an extensible online QA platform for researchers which allows users to query and analyze a large collection of modern Skills via a user-friendly web interface and integrated behavioural tests. In addition, QA researchers can develop, manage, and share their custom Skills using our microservices that support a wide range of models (Transformers, Adapters, ONNX), datastores and retrieval techniques (e.g., sparse and dense). UKP-SQUARE is available on https://square.ukp-lab.de.
LINSPECTOR WEB: A Multilingual Probing Suite for Word Representations
Sep 02, 2019



Abstract:We present LINSPECTOR WEB, an open source multilingual inspector to analyze word representations. Our system provides researchers working in low-resource settings with an easily accessible web based probing tool to gain quick insights into their word embeddings especially outside of the English language. To do this we employ 16 simple linguistic probing tasks such as gender, case marking, and tense for a diverse set of 28 languages. We support probing of static word embeddings along with pretrained AllenNLP models that are commonly used for NLP downstream tasks such as named entity recognition, natural language inference and dependency parsing. The results are visualized in a polar chart and also provided as a table. LINSPECTOR WEB is available as an offline tool or at https://linspector.ukp.informatik.tu-darmstadt.de.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge