Matti Pietikainen
From BoW to CNN: Two Decades of Texture Representation for Texture Classification
Oct 03, 2018



Abstract:Texture is a fundamental characteristic of many types of images, and texture representation is one of the essential and challenging problems in computer vision and pattern recognition which has attracted extensive research attention. Since 2000, texture representations based on Bag of Words (BoW) and on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have been extensively studied with impressive performance. Given this period of remarkable evolution, this paper aims to present a comprehensive survey of advances in texture representation over the last two decades. More than 200 major publications are cited in this survey covering different aspects of the research, which includes (i) problem description; (ii) recent advances in the broad categories of BoW-based, CNN-based and attribute-based methods; and (iii) evaluation issues, specifically benchmark datasets and state of the art results. In retrospect of what has been achieved so far, the survey discusses open challenges and directions for future research.
A Global Alignment Kernel based Approach for Group-level Happiness Intensity Estimation
Sep 03, 2018


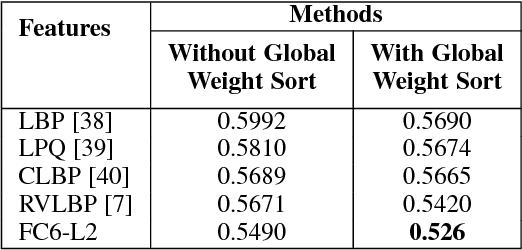
Abstract:With the progress in automatic human behavior understanding, analysing the perceived affect of multiple people has been recieved interest in affective computing community. Unlike conventional facial expression analysis, this paper primarily focuses on analysing the behaviour of multiple people in an image. The proposed method is based on support vector regression with the combined global alignment kernels (GAKs) to estimate the happiness intensity of a group of people. We first exploit Riesz-based volume local binary pattern (RVLBP) and deep convolutional neural network (CNN) based features for characterizing facial images. Furthermore, we propose to use the GAK for RVLBP and deep CNN features, respectively for explicitly measuring the similarity of two group-level images. Specifically, we exploit the global weight sort scheme to sort the face images from group-level image according to their spatial weights, making an efficient data structure to GAK. Lastly, we propose Multiple kernel learning based on three combination strategies for combining two respective GAKs based on RVLBP and deep CNN features, such that enhancing the discriminative ability of each GAK. Intensive experiments are performed on the challenging group-level happiness intensity database, namely HAPPEI. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach achieves promising performance for group happiness intensity analysis, when compared with the recent state-of-the-art methods.
Analyzing the Affect of a Group of People Using Multi-modal Framework
Oct 13, 2016



Abstract:Millions of images on the web enable us to explore images from social events such as a family party, thus it is of interest to understand and model the affect exhibited by a group of people in images. But analysis of the affect expressed by multiple people is challenging due to varied indoor and outdoor settings, and interactions taking place between various numbers of people. A few existing works on Group-level Emotion Recognition (GER) have investigated on face-level information. Due to the challenging environments, face may not provide enough information to GER. Relatively few studies have investigated multi-modal GER. Therefore, we propose a novel multi-modal approach based on a new feature description for understanding emotional state of a group of people in an image. In this paper, we firstly exploit three kinds of rich information containing face, upperbody and scene in a group-level image. Furthermore, in order to integrate multiple person's information in a group-level image, we propose an information aggregation method to generate three features for face, upperbody and scene, respectively. We fuse face, upperbody and scene information for robustness of GER against the challenging environments. Intensive experiments are performed on two challenging group-level emotion databases to investigate the role of face, upperbody and scene as well as multi-modal framework. Experimental results demonstrate that our framework achieves very promising performance for GER.
Spontaneous Facial Micro-Expression Recognition using Discriminative Spatiotemporal Local Binary Pattern with an Improved Integral Projection
Aug 07, 2016



Abstract:Recently, there are increasing interests in inferring mirco-expression from facial image sequences. Due to subtle facial movement of micro-expressions, feature extraction has become an important and critical issue for spontaneous facial micro-expression recognition. Recent works usually used spatiotemporal local binary pattern for micro-expression analysis. However, the commonly used spatiotemporal local binary pattern considers dynamic texture information to represent face images while misses the shape attribute of face images. On the other hand, their works extracted the spatiotemporal features from the global face regions, which ignore the discriminative information between two micro-expression classes. The above-mentioned problems seriously limit the application of spatiotemporal local binary pattern on micro-expression recognition. In this paper, we propose a discriminative spatiotemporal local binary pattern based on an improved integral projection to resolve the problems of spatiotemporal local binary pattern for micro-expression recognition. Firstly, we develop an improved integral projection for preserving the shape attribute of micro-expressions. Furthermore, an improved integral projection is incorporated with local binary pattern operators across spatial and temporal domains. Specifically, we extract the novel spatiotemporal features incorporating shape attributes into spatiotemporal texture features. For increasing the discrimination of micro-expressions, we propose a new feature selection based on Laplacian method to extract the discriminative information for facial micro-expression recognition. Intensive experiments are conducted on three availably published micro-expression databases. We compare our method with the state-of-the-art algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method achieves promising performance for micro-expression recognition.
LOAD: Local Orientation Adaptive Descriptor for Texture and Material Classification
Apr 22, 2015



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel local feature, called Local Orientation Adaptive Descriptor (LOAD), to capture regional texture in an image. In LOAD, we proposed to define point description on an Adaptive Coordinate System (ACS), adopt a binary sequence descriptor to capture relationships between one point and its neighbors and use multi-scale strategy to enhance the discriminative power of the descriptor. The proposed LOAD enjoys not only discriminative power to capture the texture information, but also has strong robustness to illumination variation and image rotation. Extensive experiments on benchmark data sets of texture classification and real-world material recognition show that the proposed LOAD yields the state-of-the-art performance. It is worth to mention that we achieve a 65.4\% classification accuracy-- which is, to the best of our knowledge, the highest record by far --on Flickr Material Database by using a single feature. Moreover, by combining LOAD with the feature extracted by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN), we obtain significantly better performance than both the LOAD and CNN. This result confirms that the LOAD is complementary to the learning-based features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge