Mashrur Chowdhury
Professor, Glenn Department of Civil Engineering, Clemson University
FairAgent: Democratizing Fairness-Aware Machine Learning with LLM-Powered Agents
Oct 05, 2025Abstract:Training fair and unbiased machine learning models is crucial for high-stakes applications, yet it presents significant challenges. Effective bias mitigation requires deep expertise in fairness definitions, metrics, data preprocessing, and machine learning techniques. In addition, the complex process of balancing model performance with fairness requirements while properly handling sensitive attributes makes fairness-aware model development inaccessible to many practitioners. To address these challenges, we introduce FairAgent, an LLM-powered automated system that significantly simplifies fairness-aware model development. FairAgent eliminates the need for deep technical expertise by automatically analyzing datasets for potential biases, handling data preprocessing and feature engineering, and implementing appropriate bias mitigation strategies based on user requirements. Our experiments demonstrate that FairAgent achieves significant performance improvements while significantly reducing development time and expertise requirements, making fairness-aware machine learning more accessible to practitioners.
DisPatch: Disarming Adversarial Patches in Object Detection with Diffusion Models
Sep 04, 2025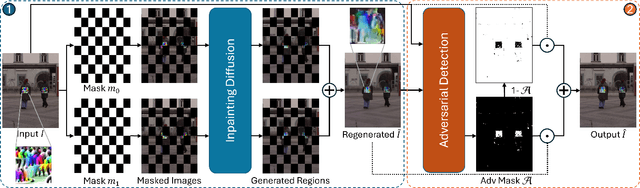
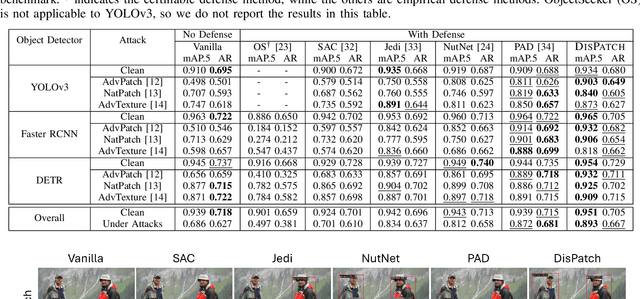
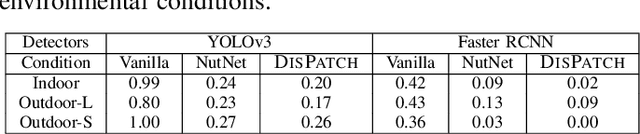
Abstract:Object detection is fundamental to various real-world applications, such as security monitoring and surveillance video analysis. Despite their advancements, state-of-theart object detectors are still vulnerable to adversarial patch attacks, which can be easily applied to real-world objects to either conceal actual items or create non-existent ones, leading to severe consequences. Given the current diversity of adversarial patch attacks and potential unknown threats, an ideal defense method should be effective, generalizable, and robust against adaptive attacks. In this work, we introduce DISPATCH, the first diffusion-based defense framework for object detection. Unlike previous works that aim to "detect and remove" adversarial patches, DISPATCH adopts a "regenerate and rectify" strategy, leveraging generative models to disarm attack effects while preserving the integrity of the input image. Specifically, we utilize the in-distribution generative power of diffusion models to regenerate the entire image, aligning it with benign data. A rectification process is then employed to identify and replace adversarial regions with their regenerated benign counterparts. DISPATCH is attack-agnostic and requires no prior knowledge of the existing patches. Extensive experiments across multiple detectors and attacks demonstrate that DISPATCH consistently outperforms state-of-the-art defenses on both hiding attacks and creating attacks, achieving the best overall mAP.5 score of 89.3% on hiding attacks, and lowering the attack success rate to 24.8% on untargeted creating attacks. Moreover, it maintains strong robustness against adaptive attacks, making it a practical and reliable defense for object detection systems.
Quantum-Classical Hybrid Framework for Zero-Day Time-Push GNSS Spoofing Detection
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) are critical for Positioning, Navigation, and Timing (PNT) applications. However, GNSS are highly vulnerable to spoofing attacks, where adversaries transmit counterfeit signals to mislead receivers. Such attacks can lead to severe consequences, including misdirected navigation, compromised data integrity, and operational disruptions. Most existing spoofing detection methods depend on supervised learning techniques and struggle to detect novel, evolved, and unseen attacks. To overcome this limitation, we develop a zero-day spoofing detection method using a Hybrid Quantum-Classical Autoencoder (HQC-AE), trained solely on authentic GNSS signals without exposure to spoofed data. By leveraging features extracted during the tracking stage, our method enables proactive detection before PNT solutions are computed. We focus on spoofing detection in static GNSS receivers, which are particularly susceptible to time-push spoofing attacks, where attackers manipulate timing information to induce incorrect time computations at the receiver. We evaluate our model against different unseen time-push spoofing attack scenarios: simplistic, intermediate, and sophisticated. Our analysis demonstrates that the HQC-AE consistently outperforms its classical counterpart, traditional supervised learning-based models, and existing unsupervised learning-based methods in detecting zero-day, unseen GNSS time-push spoofing attacks, achieving an average detection accuracy of 97.71% with an average false negative rate of 0.62% (when an attack occurs but is not detected). For sophisticated spoofing attacks, the HQC-AE attains an accuracy of 98.23% with a false negative rate of 1.85%. These findings highlight the effectiveness of our method in proactively detecting zero-day GNSS time-push spoofing attacks across various stationary GNSS receiver platforms.
Retrieval Augmented Generation-based Large Language Models for Bridging Transportation Cybersecurity Legal Knowledge Gaps
May 23, 2025Abstract:As connected and automated transportation systems evolve, there is a growing need for federal and state authorities to revise existing laws and develop new statutes to address emerging cybersecurity and data privacy challenges. This study introduces a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) based Large Language Model (LLM) framework designed to support policymakers by extracting relevant legal content and generating accurate, inquiry-specific responses. The framework focuses on reducing hallucinations in LLMs by using a curated set of domain-specific questions to guide response generation. By incorporating retrieval mechanisms, the system enhances the factual grounding and specificity of its outputs. Our analysis shows that the proposed RAG-based LLM outperforms leading commercial LLMs across four evaluation metrics: AlignScore, ParaScore, BERTScore, and ROUGE, demonstrating its effectiveness in producing reliable and context-aware legal insights. This approach offers a scalable, AI-driven method for legislative analysis, supporting efforts to update legal frameworks in line with advancements in transportation technologies.
Quantum Computing Supported Adversarial Attack-Resilient Autonomous Vehicle Perception Module for Traffic Sign Classification
Apr 17, 2025
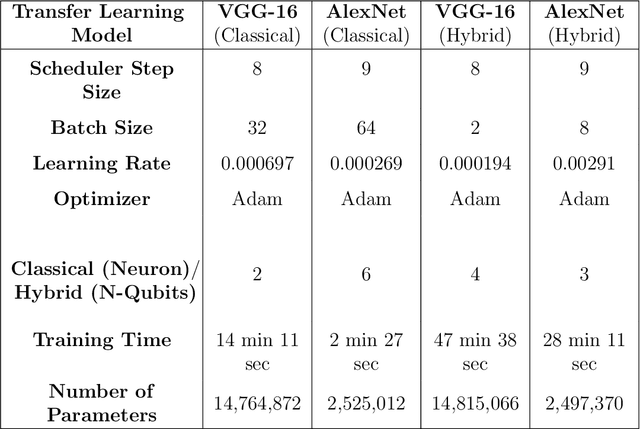
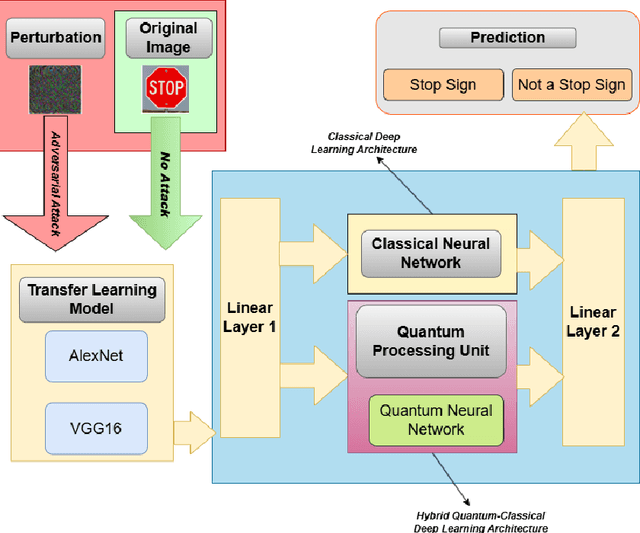
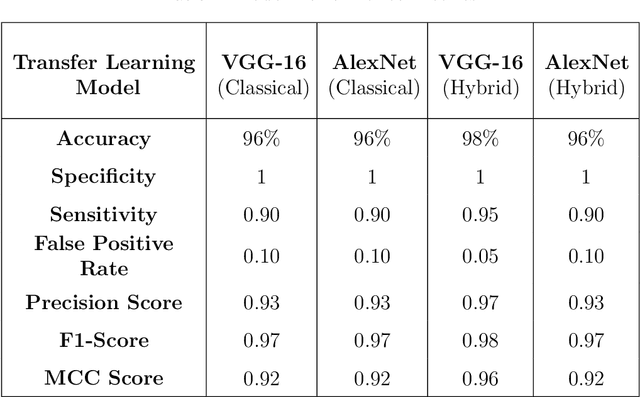
Abstract:Deep learning (DL)-based image classification models are essential for autonomous vehicle (AV) perception modules since incorrect categorization might have severe repercussions. Adversarial attacks are widely studied cyberattacks that can lead DL models to predict inaccurate output, such as incorrectly classified traffic signs by the perception module of an autonomous vehicle. In this study, we create and compare hybrid classical-quantum deep learning (HCQ-DL) models with classical deep learning (C-DL) models to demonstrate robustness against adversarial attacks for perception modules. Before feeding them into the quantum system, we used transfer learning models, alexnet and vgg-16, as feature extractors. We tested over 1000 quantum circuits in our HCQ-DL models for projected gradient descent (PGD), fast gradient sign attack (FGSA), and gradient attack (GA), which are three well-known untargeted adversarial approaches. We evaluated the performance of all models during adversarial attacks and no-attack scenarios. Our HCQ-DL models maintain accuracy above 95\% during a no-attack scenario and above 91\% for GA and FGSA attacks, which is higher than C-DL models. During the PGD attack, our alexnet-based HCQ-DL model maintained an accuracy of 85\% compared to C-DL models that achieved accuracies below 21\%. Our results highlight that the HCQ-DL models provide improved accuracy for traffic sign classification under adversarial settings compared to their classical counterparts.
GAN-Based Single-Stage Defense for Traffic Sign Classification Under Adversarial Patch Attack
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Computer Vision plays a critical role in ensuring the safe navigation of autonomous vehicles (AVs). An AV perception module is responsible for capturing and interpreting the surrounding environment to facilitate safe navigation. This module enables AVs to recognize traffic signs, traffic lights, and various road users. However, the perception module is vulnerable to adversarial attacks, which can compromise their accuracy and reliability. One such attack is the adversarial patch attack (APA), a physical attack in which an adversary strategically places a specially crafted sticker on an object to deceive object classifiers. In APA, an adversarial patch is positioned on a target object, leading the classifier to misidentify it. Such an APA can cause AVs to misclassify traffic signs, leading to catastrophic incidents. To enhance the security of an AV perception system against APAs, this study develops a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based single-stage defense strategy for traffic sign classification. This approach is tailored to defend against APAs on different classes of traffic signs without prior knowledge of a patch's design. This study found this approach to be effective against patches of varying sizes. Our experimental analysis demonstrates that the defense strategy presented in this paper improves the classifier's accuracy under APA conditions by up to 80.8% and enhances overall classification accuracy for all the traffic signs considered in this study by 58%, compared to a classifier without any defense mechanism. Our defense strategy is model-agnostic, making it applicable to any traffic sign classifier, regardless of the underlying classification model.
Graph-Powered Defense: Controller Area Network Intrusion Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:The network of services, including delivery, farming, and environmental monitoring, has experienced exponential expansion in the past decade with Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Yet, UAVs are not robust enough against cyberattacks, especially on the Controller Area Network (CAN) bus. The CAN bus is a general-purpose vehicle-bus standard to enable microcontrollers and in-vehicle computers to interact, primarily connecting different Electronic Control Units (ECUs). In this study, we focus on solving some of the most critical security weaknesses in UAVs by developing a novel graph-based intrusion detection system (IDS) leveraging the Uncomplicated Application-level Vehicular Communication and Networking (UAVCAN) protocol. First, we decode CAN messages based on UAVCAN protocol specification; second, we present a comprehensive method of transforming tabular UAVCAN messages into graph structures. Lastly, we apply various graph-based machine learning models for detecting cyber-attacks on the CAN bus, including graph convolutional neural networks (GCNNs), graph attention networks (GATs), Graph Sample and Aggregate Networks (GraphSAGE), and graph structure-based transformers. Our findings show that inductive models such as GATs, GraphSAGE, and graph-based transformers can achieve competitive and even better accuracy than transductive models like GCNNs in detecting various types of intrusions, with minimum information on protocol specification, thus providing a generic robust solution for CAN bus security for the UAVs. We also compared our results with baseline single-layer Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and found that all our graph-based models perform better without using any decoded features based on the UAVCAN protocol, highlighting higher detection performance with protocol-independent capability.
Crash Severity Risk Modeling Strategies under Data Imbalance
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates crash severity risk modeling strategies for work zones involving large vehicles (i.e., trucks, buses, and vans) when there are crash data imbalance between low-severity (LS) and high-severity (HS) crashes. We utilized crash data, involving large vehicles in South Carolina work zones for the period between 2014 and 2018, which included 4 times more LS crashes compared to HS crashes. The objective of this study is to explore crash severity prediction performance of various models under different feature selection and data balancing techniques. The findings of this study highlight a disparity between LS and HS predictions, with less-accurate prediction of HS crashes compared to LS crashes due to class imbalance and feature overlaps between LS and HS crashes. Combining features from multiple feature selection techniques: statistical correlation, feature importance, recursive elimination, statistical tests, and mutual information, slightly improves HS crash prediction performance. Data balancing techniques such as NearMiss-1 and RandomUnderSampler, maximize HS recall when paired with certain prediction models, such as Bayesian Mixed Logit (BML), NeuralNet, and RandomForest, making them suitable for HS crash prediction. Conversely, RandomOverSampler, HS Class Weighting, and Kernel-based Synthetic Minority Oversampling (K-SMOTE), used with certain prediction models such as BML, CatBoost, and LightGBM, achieve a balanced performance, defined as achieving an equitable trade-off between LS and HS prediction performance metrics. These insights provide safety analysts with guidance to select models, feature selection techniques, and data balancing techniques that align with their specific safety objectives, offering a robust foundation for enhancing work-zone crash severity prediction.
A Hybrid Quantum-Classical AI-Based Detection Strategy for Generative Adversarial Network-Based Deepfake Attacks on an Autonomous Vehicle Traffic Sign Classification System
Sep 25, 2024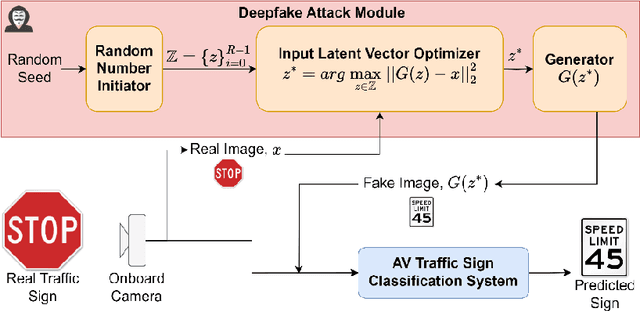

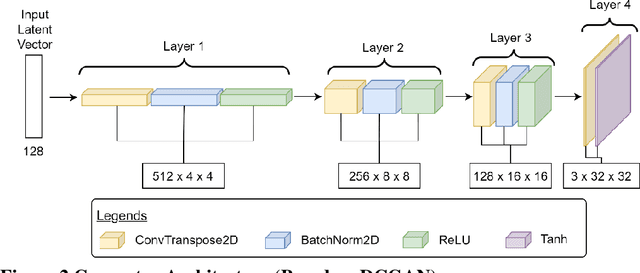

Abstract:The perception module in autonomous vehicles (AVs) relies heavily on deep learning-based models to detect and identify various objects in their surrounding environment. An AV traffic sign classification system is integral to this module, which helps AVs recognize roadway traffic signs. However, adversarial attacks, in which an attacker modifies or alters the image captured for traffic sign recognition, could lead an AV to misrecognize the traffic signs and cause hazardous consequences. Deepfake presents itself as a promising technology to be used for such adversarial attacks, in which a deepfake traffic sign would replace a real-world traffic sign image before the image is fed to the AV traffic sign classification system. In this study, the authors present how a generative adversarial network-based deepfake attack can be crafted to fool the AV traffic sign classification systems. The authors developed a deepfake traffic sign image detection strategy leveraging hybrid quantum-classical neural networks (NNs). This hybrid approach utilizes amplitude encoding to represent the features of an input traffic sign image using quantum states, which substantially reduces the memory requirement compared to its classical counterparts. The authors evaluated this hybrid deepfake detection approach along with several baseline classical convolutional NNs on real-world and deepfake traffic sign images. The results indicate that the hybrid quantum-classical NNs for deepfake detection could achieve similar or higher performance than the baseline classical convolutional NNs in most cases while requiring less than one-third of the memory required by the shallowest classical convolutional NN considered in this study.
Development and Evaluation of Ensemble Learning-based Environmental Methane Detection and Intensity Prediction Models
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:The environmental impacts of global warming driven by methane (CH4) emissions have catalyzed significant research initiatives in developing novel technologies that enable proactive and rapid detection of CH4. Several data-driven machine learning (ML) models were tested to determine how well they identified fugitive CH4 and its related intensity in the affected areas. Various meteorological characteristics, including wind speed, temperature, pressure, relative humidity, water vapor, and heat flux, were included in the simulation. We used the ensemble learning method to determine the best-performing weighted ensemble ML models built upon several weaker lower-layer ML models to (i) detect the presence of CH4 as a classification problem and (ii) predict the intensity of CH4 as a regression problem.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge