Masayuki Asahara
Step-by-step Instructions and a Simple Tabular Output Format Improve the Dependency Parsing Accuracy of LLMs
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have enabled impressive performance in various tasks. However, standard prompting often struggles to produce structurally valid and accurate outputs, especially in dependency parsing. We propose a novel step-by-step instruction strategy, where universal part-of-speech tagging precedes the prediction of syntactic heads and dependency labels, and a simplified CoNLL-U like output format, our method achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on Universal Dependencies datasets across 17 languages without hallucination or contamination. We further show that multilingual fine-tuning simultaneously improves cross-language generalization performance. Our results highlight the effectiveness of explicit reasoning steps in LLM-based parsing and offer a scalable, format-consistent alternative to bracket-based approaches.
AcTED: Automatic Acquisition of Typical Event Duration for Semi-supervised Temporal Commonsense QA
Mar 27, 2024



Abstract:We propose a voting-driven semi-supervised approach to automatically acquire the typical duration of an event and use it as pseudo-labeled data. The human evaluation demonstrates that our pseudo labels exhibit surprisingly high accuracy and balanced coverage. In the temporal commonsense QA task, experimental results show that using only pseudo examples of 400 events, we achieve performance comparable to the existing BERT-based weakly supervised approaches that require a significant amount of training examples. When compared to the RoBERTa baselines, our best approach establishes state-of-the-art performance with a 7% improvement in Exact Match.
Dynamically Updating Event Representations for Temporal Relation Classification with Multi-category Learning
Oct 31, 2023Abstract:Temporal relation classification is a pair-wise task for identifying the relation of a temporal link (TLINK) between two mentions, i.e. event, time, and document creation time (DCT). It leads to two crucial limits: 1) Two TLINKs involving a common mention do not share information. 2) Existing models with independent classifiers for each TLINK category (E2E, E2T, and E2D) hinder from using the whole data. This paper presents an event centric model that allows to manage dynamic event representations across multiple TLINKs. Our model deals with three TLINK categories with multi-task learning to leverage the full size of data. The experimental results show that our proposal outperforms state-of-the-art models and two transfer learning baselines on both the English and Japanese data.
Lower Perplexity is Not Always Human-Like
Jun 02, 2021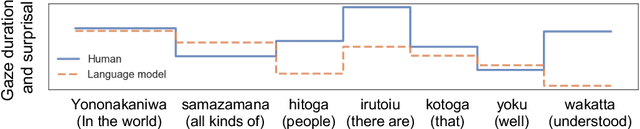
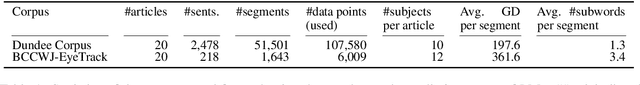
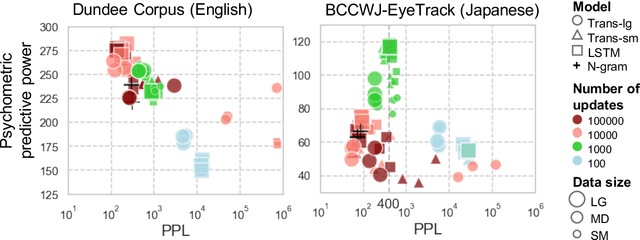
Abstract:In computational psycholinguistics, various language models have been evaluated against human reading behavior (e.g., eye movement) to build human-like computational models. However, most previous efforts have focused almost exclusively on English, despite the recent trend towards linguistic universal within the general community. In order to fill the gap, this paper investigates whether the established results in computational psycholinguistics can be generalized across languages. Specifically, we re-examine an established generalization -- the lower perplexity a language model has, the more human-like the language model is -- in Japanese with typologically different structures from English. Our experiments demonstrate that this established generalization exhibits a surprising lack of universality; namely, lower perplexity is not always human-like. Moreover, this discrepancy between English and Japanese is further explored from the perspective of (non-)uniform information density. Overall, our results suggest that a cross-lingual evaluation will be necessary to construct human-like computational models.
A Gamification of Japanese Dependency Parsing
Jan 09, 2021



Abstract:Gamification approaches have been used as a way for creating language resources for NLP. It is also used for presenting and teaching the algorithms in NLP and linguistic phenomena. This paper argues about a design of gamification for Japanese syntactic dependendency parsing for the latter objective. The user interface design is based on a transition-based shift reduce dependency parsing which needs only two actions of SHIFT (not attach) and REDUCE (attach) in Japanese dependency structure. We assign the two actions for two-way directional control on a gamepad or other devices. We also design the target sentences from psycholinguistics researches.
Adversarial Training for Commonsense Inference
May 17, 2020


Abstract:We propose an AdversariaL training algorithm for commonsense InferenCE (ALICE). We apply small perturbations to word embeddings and minimize the resultant adversarial risk to regularize the model. We exploit a novel combination of two different approaches to estimate these perturbations: 1) using the true label and 2) using the model prediction. Without relying on any human-crafted features, knowledge bases, or additional datasets other than the target datasets, our model boosts the fine-tuning performance of RoBERTa, achieving competitive results on multiple reading comprehension datasets that require commonsense inference.
* 6 pages, Accepted to ACL2020 RepL4NLP workshop
Japanese-Spanish Thesaurus Construction Using English as a Pivot
Mar 06, 2013



Abstract:We present the results of research with the goal of automatically creating a multilingual thesaurus based on the freely available resources of Wikipedia and WordNet. Our goal is to increase resources for natural language processing tasks such as machine translation targeting the Japanese-Spanish language pair. Given the scarcity of resources, we use existing English resources as a pivot for creating a trilingual Japanese-Spanish-English thesaurus. Our approach consists of extracting the translation tuples from Wikipedia, disambiguating them by mapping them to WordNet word senses. We present results comparing two methods of disambiguation, the first using VSM on Wikipedia article texts and WordNet definitions, and the second using categorical information extracted from Wikipedia, We find that mixing the two methods produces favorable results. Using the proposed method, we have constructed a multilingual Spanish-Japanese-English thesaurus consisting of 25,375 entries. The same method can be applied to any pair of languages that are linked to English in Wikipedia.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge