Mary Ellen Foster
University of Glasgow
A Socially Assistive Robot using Automated Planning in a Paediatric Clinical Setting
Oct 18, 2022



Abstract:We present an ongoing project that aims to develop a social robot to help children cope with painful and distressing medical procedures in a clinical setting. Our approach uses automated planning as a core component for action selection in order to generate plans that include physical, sensory, and social actions for the robot to use when interacting with humans. A key capability of our system is that the robot's behaviour adapts based on the affective state of the child patient. The robot must operate in a challenging physical and social environment where appropriate and safe interaction with children, parents/caregivers, and healthcare professionals is crucial. In this paper, we present our system, examine some of the key challenges of the scenario, and describe how they are addressed by our system.
GISE-51: A scalable isolated sound events dataset
Mar 23, 2021
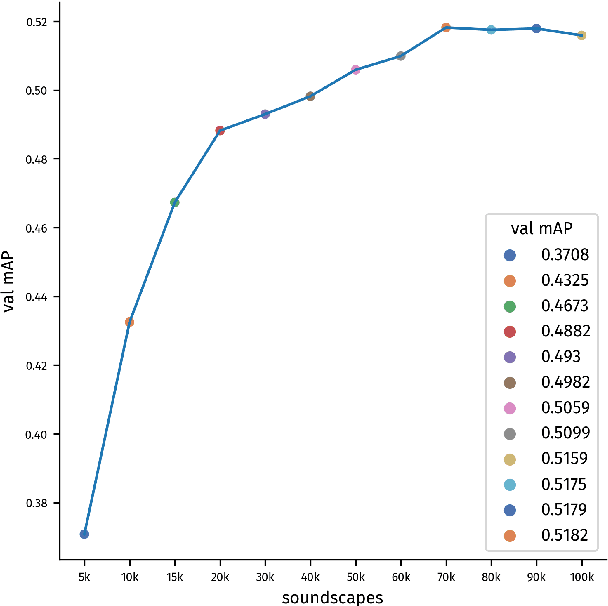


Abstract:Most of the existing isolated sound event datasets comprise a small number of sound event classes, usually 10 to 15, restricted to a small domain, such as domestic and urban sound events. In this work, we introduce GISE-51, a dataset spanning 51 isolated sound events belonging to a broad domain of event types. We also release GISE-51-Mixtures, a dataset of 5-second soundscapes with hard-labelled event boundaries synthesized from GISE-51 isolated sound events. We conduct baseline sound event recognition (SER) experiments on the GISE-51-Mixtures dataset, benchmarking prominent convolutional neural networks, and models trained with the dataset demonstrate strong transfer learning performance on existing audio recognition benchmarks. Together, GISE-51 and GISE-51-Mixtures attempt to address some of the shortcomings of recent sound event datasets, providing an open, reproducible benchmark for future research along with the freedom to adapt the included isolated sound events for domain-specific applications.
Towards Social HRI for Improving Children's Healthcare Experiences
Oct 09, 2020

Abstract:This paper describes a new research project that aims to develop a social robot designed to help children cope with painful and distressing medical procedures in a clinical setting. While robots have previously been trialled for this task, with promising initial results, the systems have tended to be teleoperated, limiting their flexibility and robustness. This project will use epistemic planning techniques as a core component for action selection in the robot system, in order to generate plans that include physical, sensory, and social actions for interacting with humans. The robot will operate in a task environment where appropriate and safe interaction with children, parents/caregivers, and healthcare professionals is required. In addition to addressing the core technical challenge of building an autonomous social robot, the project will incorporate co-design techniques involving all participant groups, and the final robot system will be evaluated in a two-site clinical trial.
MuMMER: Socially Intelligent Human-Robot Interaction in Public Spaces
Sep 15, 2019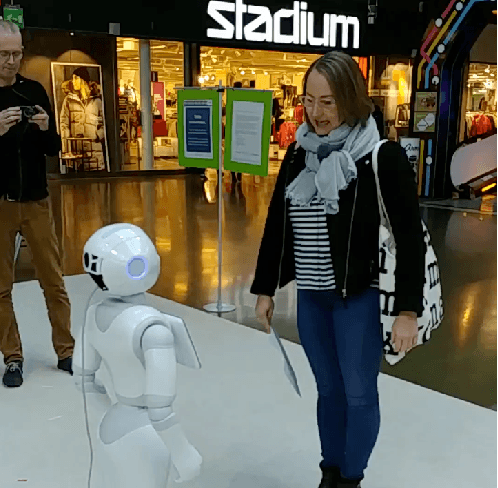
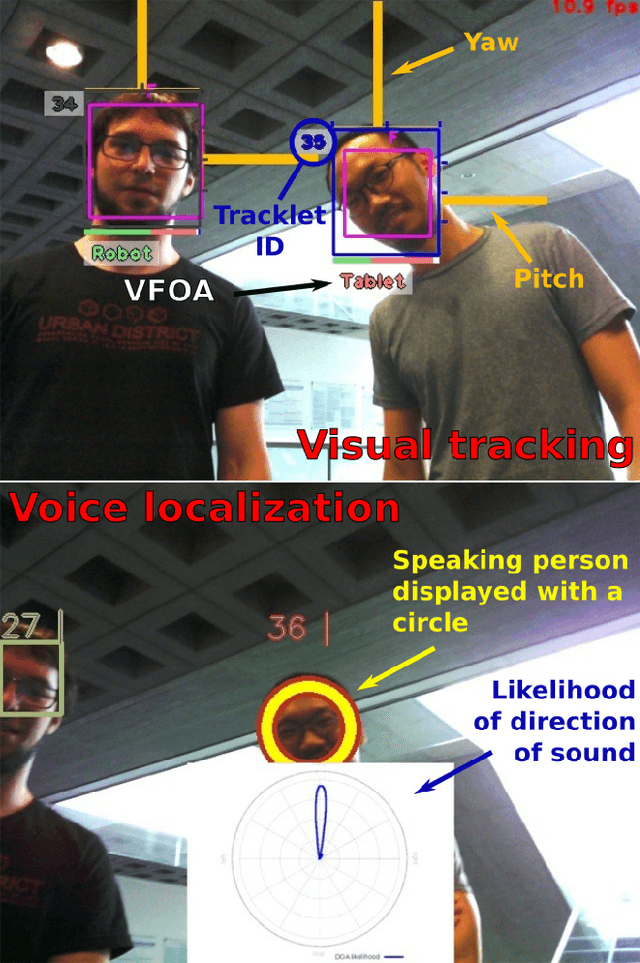
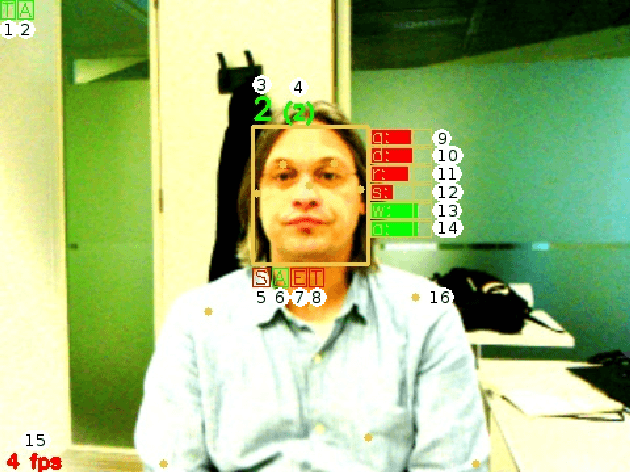
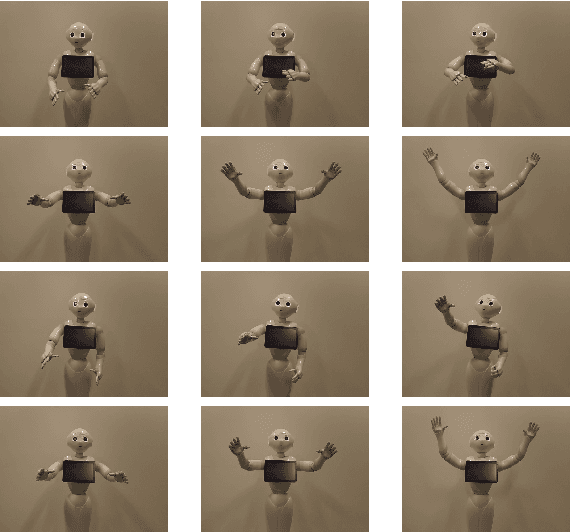
Abstract:In the EU-funded MuMMER project, we have developed a social robot designed to interact naturally and flexibly with users in public spaces such as a shopping mall. We present the latest version of the robot system developed during the project. This system encompasses audio-visual sensing, social signal processing, conversational interaction, perspective taking, geometric reasoning, and motion planning. It successfully combines all these components in an overarching framework using the Robot Operating System (ROS) and has been deployed to a shopping mall in Finland interacting with customers. In this paper, we describe the system components, their interplay, and the resulting robot behaviours and scenarios provided at the shopping mall.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge