Alan Lindsay
A Socially Assistive Robot using Automated Planning in a Paediatric Clinical Setting
Oct 18, 2022



Abstract:We present an ongoing project that aims to develop a social robot to help children cope with painful and distressing medical procedures in a clinical setting. Our approach uses automated planning as a core component for action selection in order to generate plans that include physical, sensory, and social actions for the robot to use when interacting with humans. A key capability of our system is that the robot's behaviour adapts based on the affective state of the child patient. The robot must operate in a challenging physical and social environment where appropriate and safe interaction with children, parents/caregivers, and healthcare professionals is crucial. In this paper, we present our system, examine some of the key challenges of the scenario, and describe how they are addressed by our system.
Investigating Human Response, Behaviour, and Preference in Joint-Task Interaction
Nov 27, 2020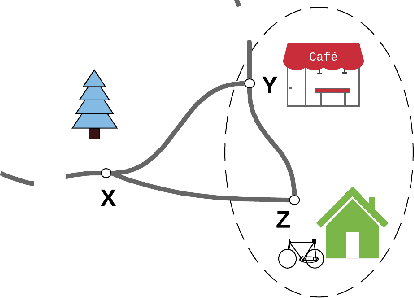
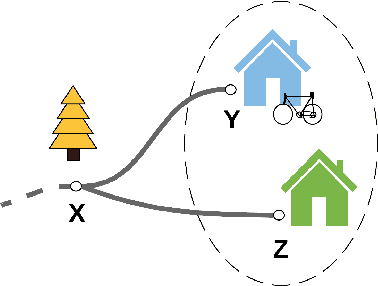
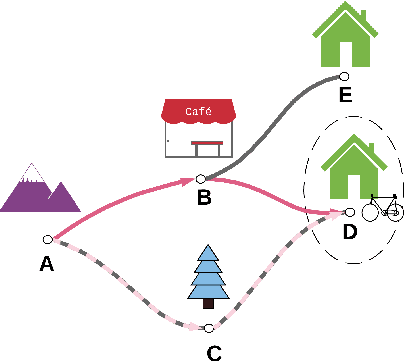
Abstract:Human interaction relies on a wide range of signals, including non-verbal cues. In order to develop effective Explainable Planning (XAIP) agents it is important that we understand the range and utility of these communication channels. Our starting point is existing results from joint task interaction and their study in cognitive science. Our intention is that these lessons can inform the design of interaction agents -- including those using planning techniques -- whose behaviour is conditioned on the user's response, including affective measures of the user (i.e., explicitly incorporating the user's affective state within the planning model). We have identified several concepts at the intersection of plan-based agent behaviour and joint task interaction and have used these to design two agents: one reactive and the other partially predictive. We have designed an experiment in order to examine human behaviour and response as they interact with these agents. In this paper we present the designed study and the key questions that are being investigated. We also present the results from an empirical analysis where we examined the behaviour of the two agents for simulated users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge