Martin Walker
Explaining black boxes with a SMILE: Statistical Model-agnostic Interpretability with Local Explanations
Nov 13, 2023Abstract:Machine learning is currently undergoing an explosion in capability, popularity, and sophistication. However, one of the major barriers to widespread acceptance of machine learning (ML) is trustworthiness: most ML models operate as black boxes, their inner workings opaque and mysterious, and it can be difficult to trust their conclusions without understanding how those conclusions are reached. Explainability is therefore a key aspect of improving trustworthiness: the ability to better understand, interpret, and anticipate the behaviour of ML models. To this end, we propose SMILE, a new method that builds on previous approaches by making use of statistical distance measures to improve explainability while remaining applicable to a wide range of input data domains.
SafeDrones: Real-Time Reliability Evaluation of UAVs using Executable Digital Dependable Identities
Jul 12, 2022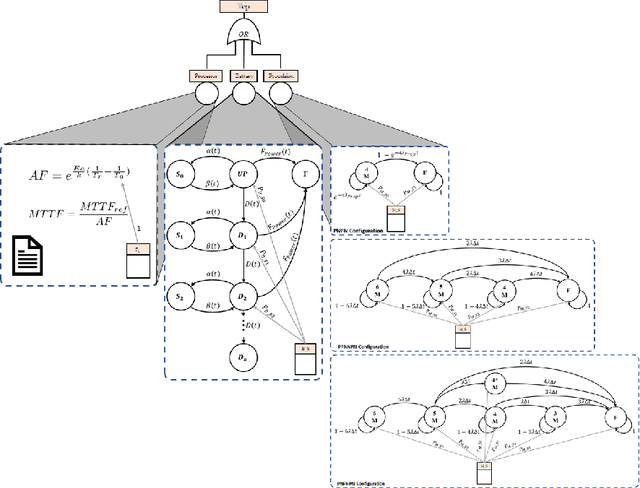
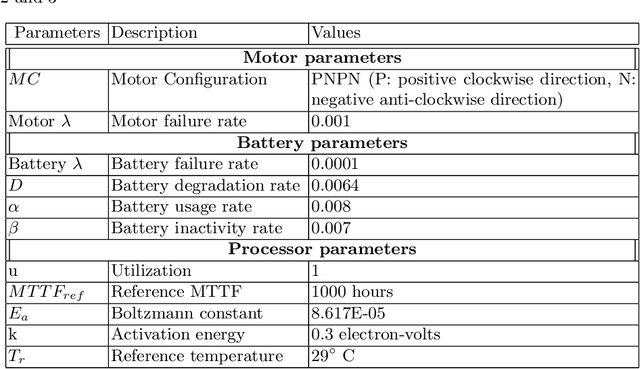
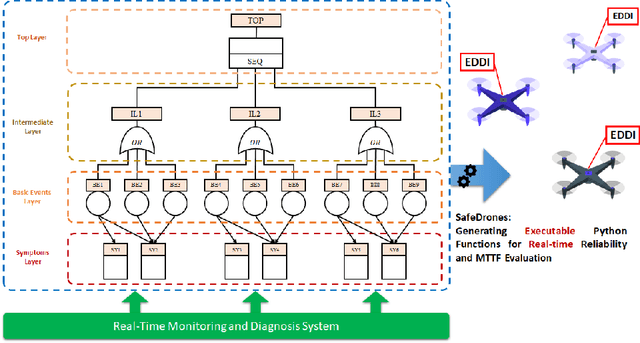

Abstract:The use of Unmanned Arial Vehicles (UAVs) offers many advantages across a variety of applications. However, safety assurance is a key barrier to widespread usage, especially given the unpredictable operational and environmental factors experienced by UAVs, which are hard to capture solely at design-time. This paper proposes a new reliability modeling approach called SafeDrones to help address this issue by enabling runtime reliability and risk assessment of UAVs. It is a prototype instantiation of the Executable Digital Dependable Identity (EDDI) concept, which aims to create a model-based solution for real-time, data-driven dependability assurance for multi-robot systems. By providing real-time reliability estimates, SafeDrones allows UAVs to update their missions accordingly in an adaptive manner.
In Search of Meaning: Lessons, Resources and Next Steps for Computational Analysis of Financial Discourse
Mar 28, 2019
Abstract:We critically assess mainstream accounting and finance research applying methods from computational linguistics (CL) to study financial discourse. We also review common themes and innovations in the literature and assess the incremental contributions of work applying CL methods over manual content analysis. Key conclusions emerging from our analysis are: (a) accounting and finance research is behind the curve in terms of CL methods generally and word sense disambiguation in particular; (b) implementation issues mean the proposed benefits of CL are often less pronounced than proponents suggest; (c) structural issues limit practical relevance; and (d) CL methods and high quality manual analysis represent complementary approaches to analyzing financial discourse. We describe four CL tools that have yet to gain traction in mainstream AF research but which we believe offer promising ways to enhance the study of meaning in financial discourse. The four tools are named entity recognition (NER), summarization, semantics and corpus linguistics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge