Steven Young
ICDARTS: Improving the Stability and Performance of Cyclic DARTS
Sep 01, 2023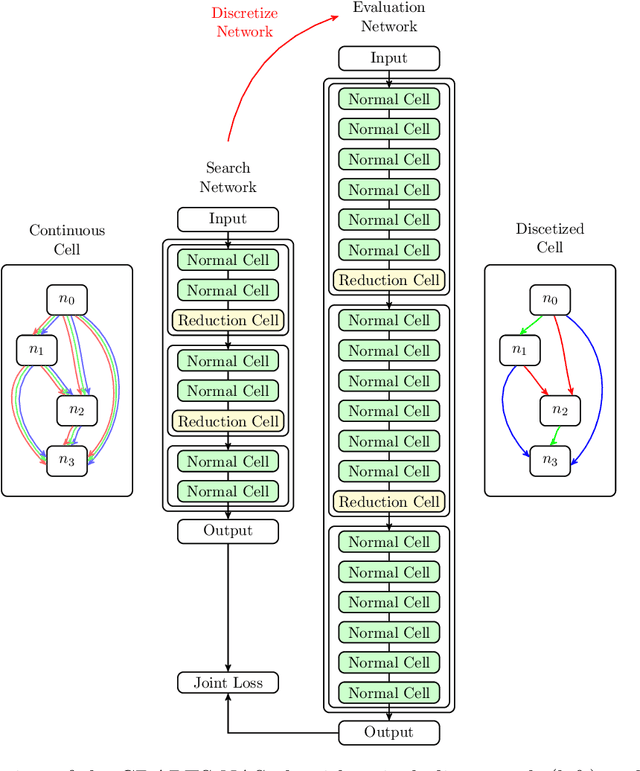
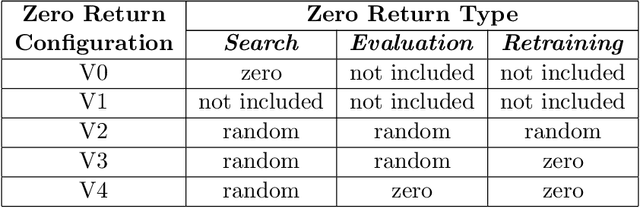
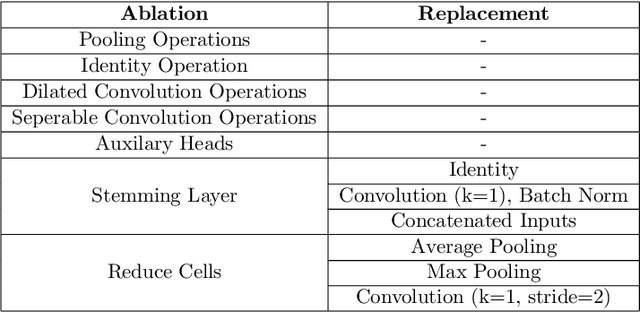
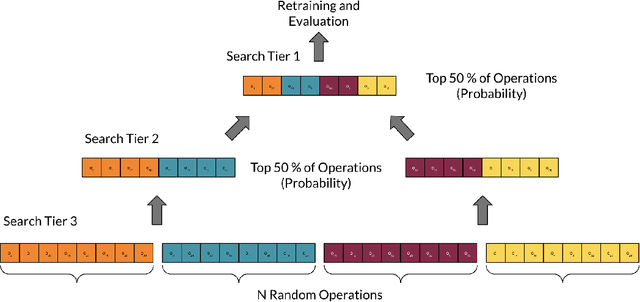
Abstract:This work introduces improvements to the stability and generalizability of Cyclic DARTS (CDARTS). CDARTS is a Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS)-based approach to neural architecture search (NAS) that uses a cyclic feedback mechanism to train search and evaluation networks concurrently. This training protocol aims to optimize the search process by enforcing that the search and evaluation networks produce similar outputs. However, CDARTS introduces a loss function for the evaluation network that is dependent on the search network. The dissimilarity between the loss functions used by the evaluation networks during the search and retraining phases results in a search-phase evaluation network that is a sub-optimal proxy for the final evaluation network that is utilized during retraining. We present ICDARTS, a revised approach that eliminates the dependency of the evaluation network weights upon those of the search network, along with a modified process for discretizing the search network's \textit{zero} operations that allows these operations to be retained in the final evaluation networks. We pair the results of these changes with ablation studies on ICDARTS' algorithm and network template. Finally, we explore methods for expanding the search space of ICDARTS by expanding its operation set and exploring alternate methods for discretizing its continuous search cells. These experiments resulted in networks with improved generalizability and the implementation of a novel method for incorporating a dynamic search space into ICDARTS.
In Search of Meaning: Lessons, Resources and Next Steps for Computational Analysis of Financial Discourse
Mar 28, 2019
Abstract:We critically assess mainstream accounting and finance research applying methods from computational linguistics (CL) to study financial discourse. We also review common themes and innovations in the literature and assess the incremental contributions of work applying CL methods over manual content analysis. Key conclusions emerging from our analysis are: (a) accounting and finance research is behind the curve in terms of CL methods generally and word sense disambiguation in particular; (b) implementation issues mean the proposed benefits of CL are often less pronounced than proponents suggest; (c) structural issues limit practical relevance; and (d) CL methods and high quality manual analysis represent complementary approaches to analyzing financial discourse. We describe four CL tools that have yet to gain traction in mainstream AF research but which we believe offer promising ways to enhance the study of meaning in financial discourse. The four tools are named entity recognition (NER), summarization, semantics and corpus linguistics.
Deep Super Learner: A Deep Ensemble for Classification Problems
Mar 06, 2018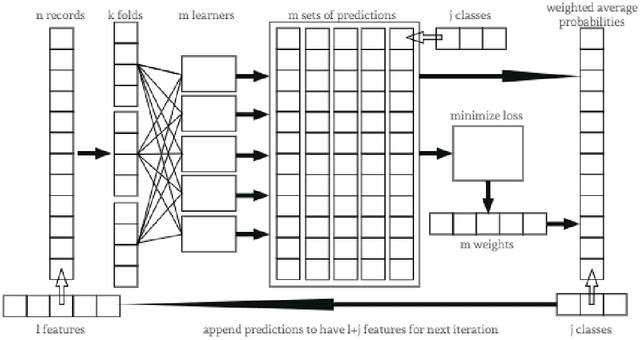
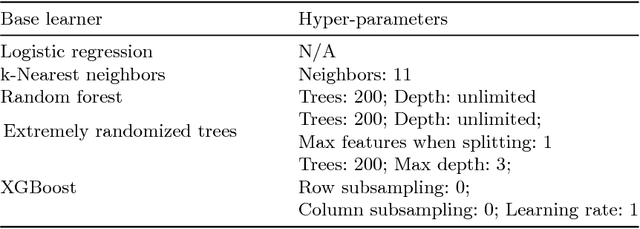
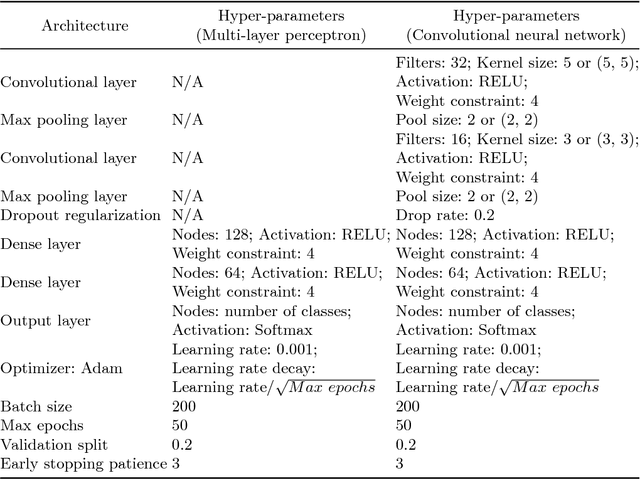

Abstract:Deep learning has become very popular for tasks such as predictive modeling and pattern recognition in handling big data. Deep learning is a powerful machine learning method that extracts lower level features and feeds them forward for the next layer to identify higher level features that improve performance. However, deep neural networks have drawbacks, which include many hyper-parameters and infinite architectures, opaqueness into results, and relatively slower convergence on smaller datasets. While traditional machine learning algorithms can address these drawbacks, they are not typically capable of the performance levels achieved by deep neural networks. To improve performance, ensemble methods are used to combine multiple base learners. Super learning is an ensemble that finds the optimal combination of diverse learning algorithms. This paper proposes deep super learning as an approach which achieves log loss and accuracy results competitive to deep neural networks while employing traditional machine learning algorithms in a hierarchical structure. The deep super learner is flexible, adaptable, and easy to train with good performance across different tasks using identical hyper-parameter values. Using traditional machine learning requires fewer hyper-parameters, allows transparency into results, and has relatively fast convergence on smaller datasets. Experimental results show that the deep super learner has superior performance compared to the individual base learners, single-layer ensembles, and in some cases deep neural networks. Performance of the deep super learner may further be improved with task-specific tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge