Marina Litvak
Improving Factual Error Correction for Abstractive Summarization via Data Distillation and Conditional-generation Cloze
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:Improving factual consistency in abstractive summarization has been a focus of current research. One promising approach is the post-editing method. However, previous works have yet to make sufficient use of factual factors in summaries and suffers from the negative effect of the training datasets. In this paper, we first propose a novel factual error correction model FactCloze based on a conditional-generation cloze task. FactCloze can construct the causality among factual factors while being able to determine whether the blank can be answered or not. Then, we propose a data distillation method to generate a more faithful summarization dataset SummDSC via multiple-dimensional evaluation. We experimentally validate the effectiveness of our approach, which leads to an improvement in multiple factual consistency metrics compared to baselines.
Just ClozE! A Fast and Simple Method for Evaluating the Factual Consistency in Abstractive Summarization
Oct 06, 2022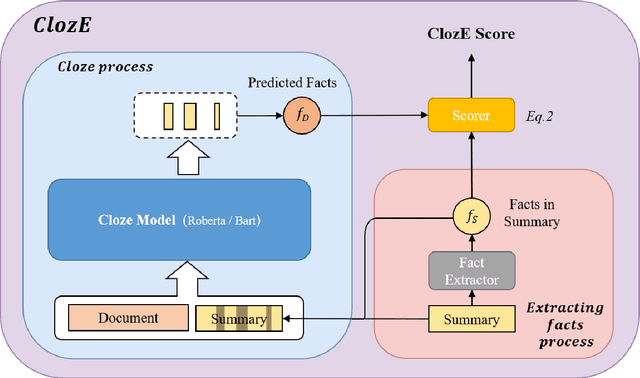
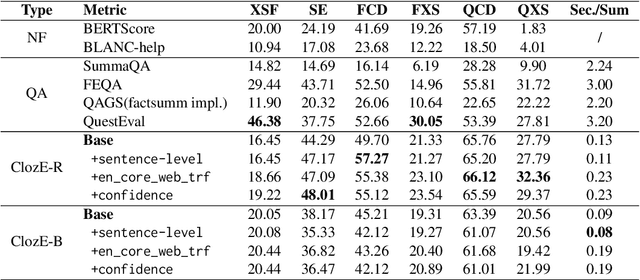
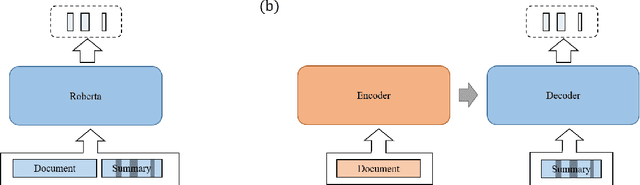
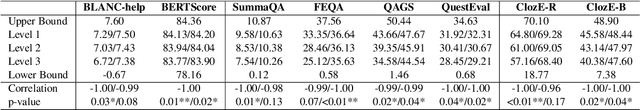
Abstract:The issue of factual consistency in abstractive summarization has attracted much attention in recent years, and the evaluation of factual consistency between summary and document has become an important and urgent task. Most of the current evaluation metrics are adopted from the question answering (QA). However, the application of QA-based metrics is extremely time-consuming in practice, causing the iteration cycle of abstractive summarization research to be severely prolonged. In this paper, we propose a new method called ClozE to evaluate factual consistency by cloze model, instantiated based on masked language model(MLM), with strong interpretability and substantially higher speed. We demonstrate that ClozE can reduce the evaluation time by nearly 96$\%$ relative to QA-based metrics while retaining their interpretability and performance through experiments on six human-annotated datasets and a meta-evaluation benchmark GO FIGURE \citep{gabriel2020go}. We also implement experiments to further demonstrate more characteristics of ClozE in terms of performance and speed. In addition, we conduct an experimental analysis of the limitations of ClozE, which suggests future research directions. The code and models for ClozE will be released upon the paper acceptance.
Subjective Bias in Abstractive Summarization
Jun 18, 2021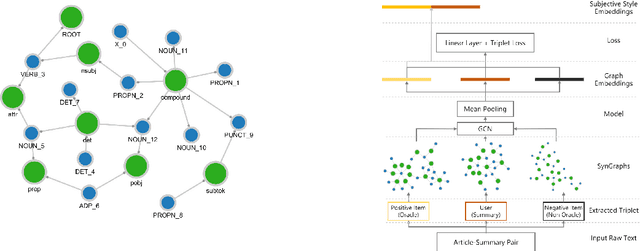

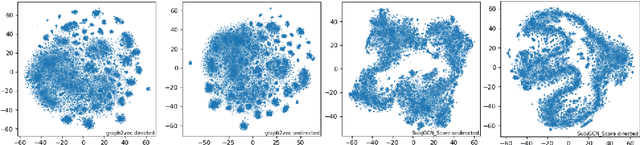
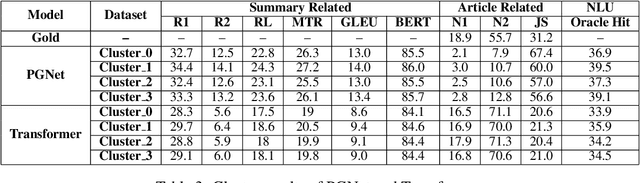
Abstract:Due to the subjectivity of the summarization, it is a good practice to have more than one gold summary for each training document. However, many modern large-scale abstractive summarization datasets have only one-to-one samples written by different human with different styles. The impact of this phenomenon is understudied. We formulate the differences among possible multiple expressions summarizing the same content as subjective bias and examine the role of this bias in the context of abstractive summarization. In this paper a lightweight and effective method to extract the feature embeddings of subjective styles is proposed. Results of summarization models trained on style-clustered datasets show that there are certain types of styles that lead to better convergence, abstraction and generalization. The reproducible code and generated summaries are available online.
Automated Discovery of Mathematical Definitions in Text with Deep Neural Networks
Nov 09, 2020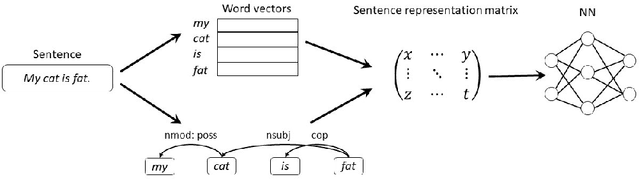
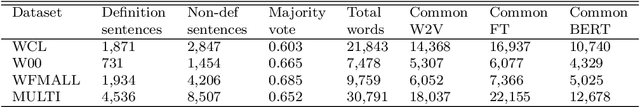

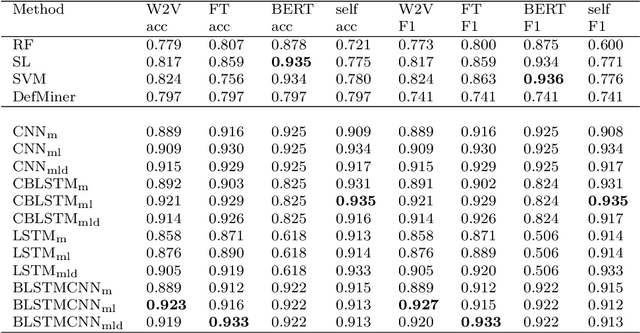
Abstract:Automatic definition extraction from texts is an important task that has numerous applications in several natural language processing fields such as summarization, analysis of scientific texts, automatic taxonomy generation, ontology generation, concept identification, and question answering. For definitions that are contained within a single sentence, this problem can be viewed as a binary classification of sentences into definitions and non-definitions. In this paper, we focus on automatic detection of one-sentence definitions in mathematical texts, which are difficult to separate from surrounding text. We experiment with several data representations, which include sentence syntactic structure and word embeddings, and apply deep learning methods such as the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and the Long Short-Term Memory network (LSTM), in order to identify mathematical definitions. Our experiments demonstrate the superiority of CNN and its combination with LSTM, when applied on the syntactically-enriched input representation. We also present a new dataset for definition extraction from mathematical texts. We demonstrate that this dataset is beneficial for training supervised models aimed at extraction of mathematical definitions. Our experiments with different domains demonstrate that mathematical definitions require special treatment, and that using cross-domain learning is inefficient for that task.
In Conclusion Not Repetition: Comprehensive Abstractive Summarization With Diversified Attention Based On Determinantal Point Processes
Sep 24, 2019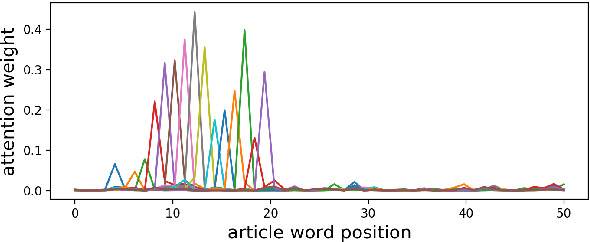
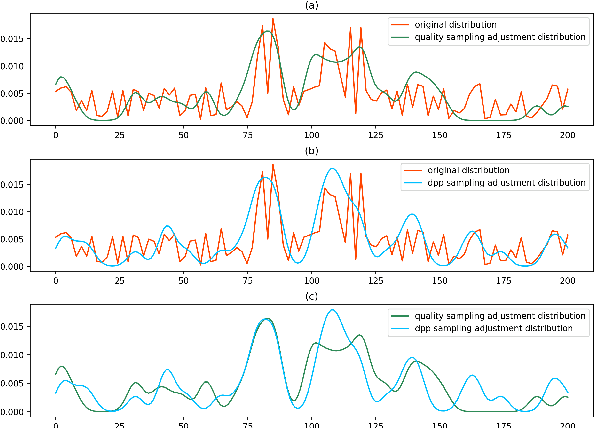

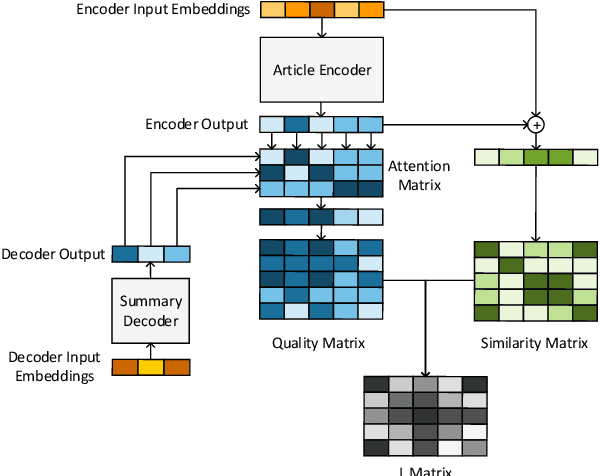
Abstract:Various Seq2Seq learning models designed for machine translation were applied for abstractive summarization task recently. Despite these models provide high ROUGE scores, they are limited to generate comprehensive summaries with a high level of abstraction due to its degenerated attention distribution. We introduce Diverse Convolutional Seq2Seq Model(DivCNN Seq2Seq) using Determinantal Point Processes methods(Micro DPPs and Macro DPPs) to produce attention distribution considering both quality and diversity. Without breaking the end to end architecture, DivCNN Seq2Seq achieves a higher level of comprehensiveness compared to vanilla models and strong baselines. All the reproducible codes and datasets are available online.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge