Marianne Arriola
Learn from Your Mistakes: Self-Correcting Masked Diffusion Models
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:Masked diffusion models (MDMs) have emerged as a promising alternative to autoregressive models, enabling parallel token generation while achieving competitive performance. Despite these advantages, MDMs face a fundamental limitation: once tokens are unmasked, they remain fixed, leading to error accumulation and ultimately degrading sample quality. We address this by proposing a framework that trains a model to perform both unmasking and correction. By reusing outputs from the MDM denoising network as inputs for corrector training, we train a model to recover from potential mistakes. During generation we apply additional corrective refinement steps between unmasking ones in order to change decoded tokens and improve outputs. We name our training and sampling method Progressive Self-Correction (ProSeCo) for its unique ability to iteratively refine an entire sequence, including already generated tokens. We conduct extensive experimental validation across multiple conditional and unconditional tasks, demonstrating that ProSeCo yields better quality-efficiency trade-offs (up to ~2-3x faster sampling) and enables inference-time compute scaling to further increase sample quality beyond standard MDMs (up to ~1.3x improvement on benchmarks).
Encoder-Decoder Diffusion Language Models for Efficient Training and Inference
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Discrete diffusion models enable parallel token sampling for faster inference than autoregressive approaches. However, prior diffusion models use a decoder-only architecture, which requires sampling algorithms that invoke the full network at every denoising step and incur high computational cost. Our key insight is that discrete diffusion models perform two types of computation: 1) representing clean tokens and 2) denoising corrupted tokens, which enables us to use separate modules for each task. We propose an encoder-decoder architecture to accelerate discrete diffusion inference, which relies on an encoder to represent clean tokens and a lightweight decoder to iteratively refine a noised sequence. We also show that this architecture enables faster training of block diffusion models, which partition sequences into blocks for better quality and are commonly used in diffusion language model inference. We introduce a framework for Efficient Encoder-Decoder Diffusion (E2D2), consisting of an architecture with specialized training and sampling algorithms, and we show that E2D2 achieves superior trade-offs between generation quality and inference throughput on summarization, translation, and mathematical reasoning tasks. We provide the code, model weights, and blog post on the project page: https://m-arriola.com/e2d2
Block Diffusion: Interpolating Between Autoregressive and Diffusion Language Models
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:Diffusion language models offer unique benefits over autoregressive models due to their potential for parallelized generation and controllability, yet they lag in likelihood modeling and are limited to fixed-length generation. In this work, we introduce a class of block diffusion language models that interpolate between discrete denoising diffusion and autoregressive models. Block diffusion overcomes key limitations of both approaches by supporting flexible-length generation and improving inference efficiency with KV caching and parallel token sampling. We propose a recipe for building effective block diffusion models that includes an efficient training algorithm, estimators of gradient variance, and data-driven noise schedules to minimize the variance. Block diffusion sets a new state-of-the-art performance among diffusion models on language modeling benchmarks and enables generation of arbitrary-length sequences. We provide the code, along with the model weights and blog post on the project page: https://m-arriola.com/bd3lms/
Simple and Effective Masked Diffusion Language Models
Jun 11, 2024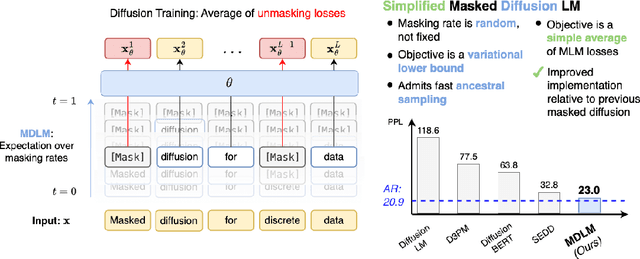
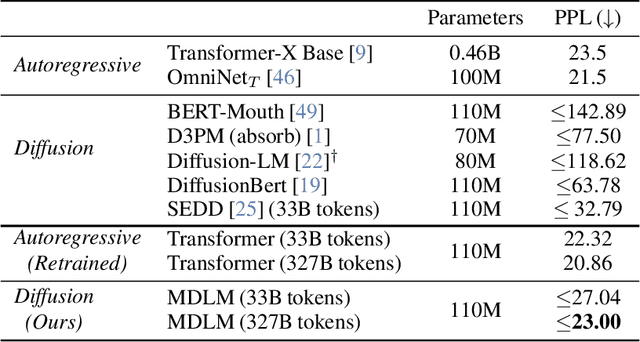
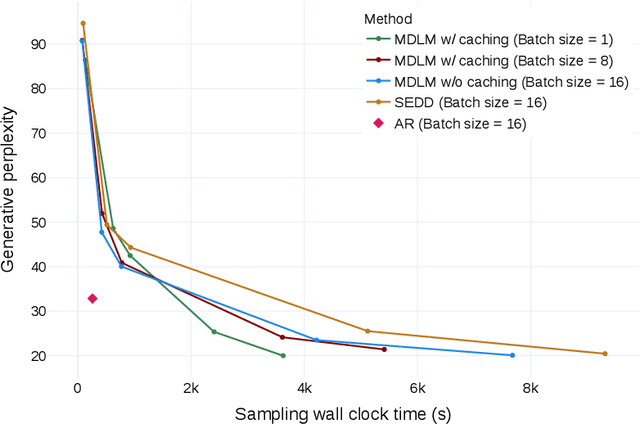
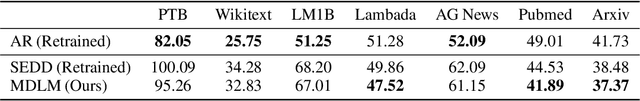
Abstract:While diffusion models excel at generating high-quality images, prior work reports a significant performance gap between diffusion and autoregressive (AR) methods in language modeling. In this work, we show that simple masked discrete diffusion is more performant than previously thought. We apply an effective training recipe that improves the performance of masked diffusion models and derive a simplified, Rao-Blackwellized objective that results in additional improvements. Our objective has a simple form -- it is a mixture of classical masked language modeling losses -- and can be used to train encoder-only language models that admit efficient samplers, including ones that can generate arbitrary lengths of text semi-autoregressively like a traditional language model. On language modeling benchmarks, a range of masked diffusion models trained with modern engineering practices achieves a new state-of-the-art among diffusion models, and approaches AR perplexity. We release our code at: https://github.com/kuleshov-group/mdlm
Joint Analysis of Single-Cell Data across Cohorts with Missing Modalities
May 18, 2024



Abstract:Joint analysis of multi-omic single-cell data across cohorts has significantly enhanced the comprehensive analysis of cellular processes. However, most of the existing approaches for this purpose require access to samples with complete modality availability, which is impractical in many real-world scenarios. In this paper, we propose (Single-Cell Cross-Cohort Cross-Category) integration, a novel framework that learns unified cell representations under domain shift without requiring full-modality reference samples. Our generative approach learns rich cross-modal and cross-domain relationships that enable imputation of these missing modalities. Through experiments on real-world multi-omic datasets, we demonstrate that offers a robust solution to single-cell tasks such as cell type clustering, cell type classification, and feature imputation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge